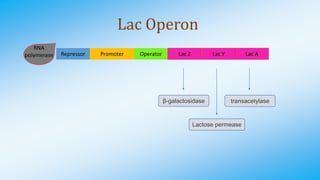
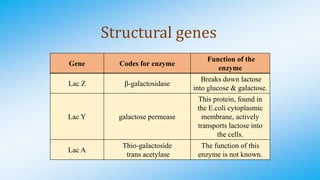
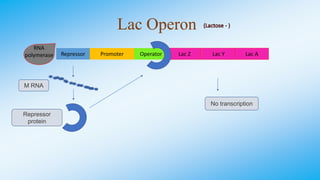
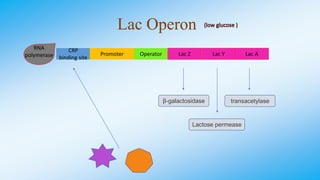
The document discusses the lac operon in bacteria. The lac operon is a cluster of genes involved in lactose metabolism. It includes three structural genes that encode enzymes for breaking down lactose. The operon is induced in the presence of lactose and repressed in its absence by a lac repressor protein. The lac operon demonstrates how bacteria efficiently regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions through an inducible operon system.