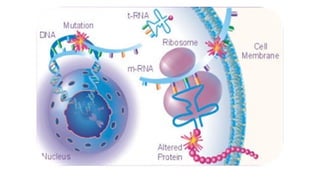
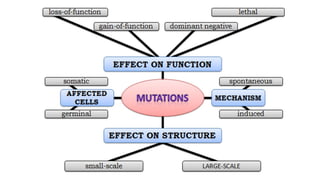
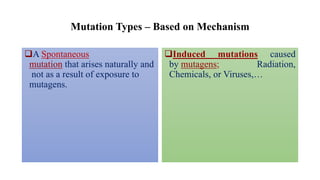
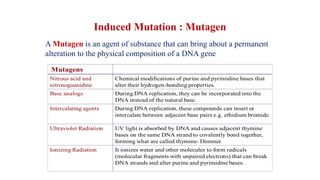
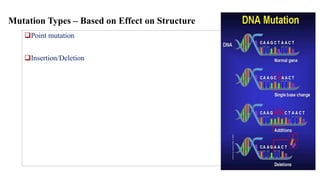
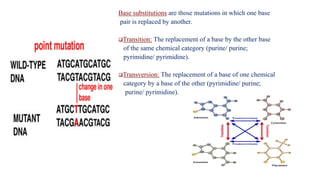
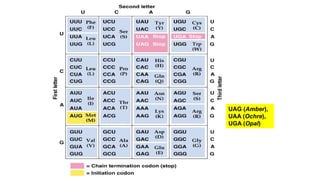
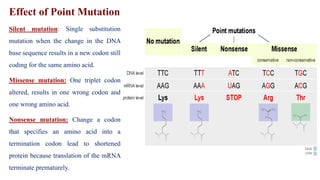
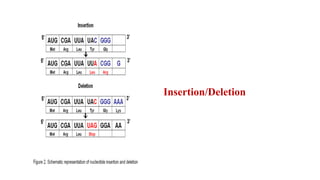
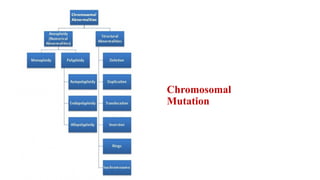
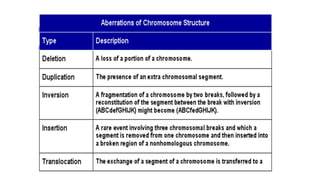
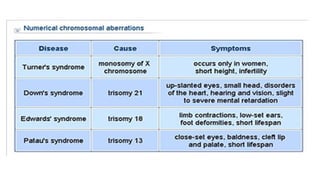
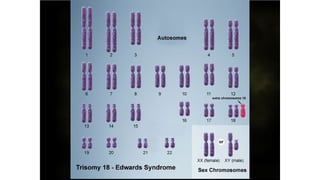
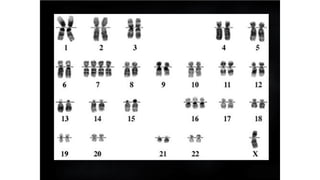
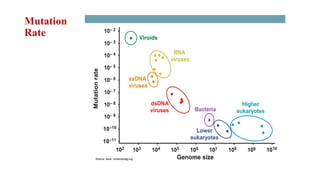
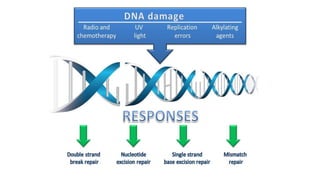
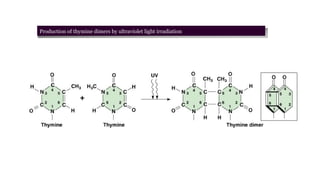
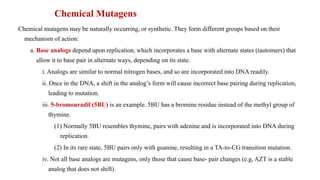
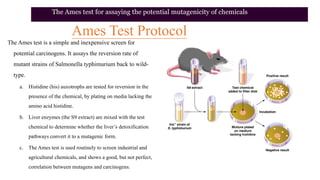
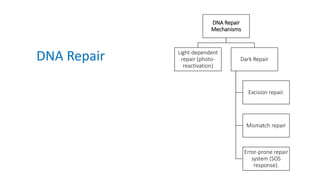
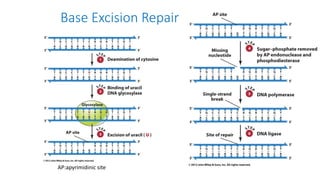
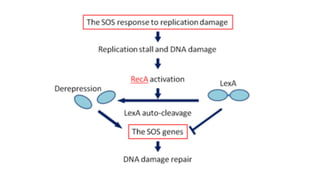
Mutation is a change in genetic material that can be caused by errors during DNA replication or DNA repair. There are several types of mutations including point mutations, insertions, deletions, and chromosomal mutations. Point mutations include transitions, transversions, missense mutations, and nonsense mutations. Insertions and deletions can disrupt the genetic code. Spontaneous mutations arise naturally while induced mutations are caused by mutagens like radiation, chemicals, or viruses. Mutations can be germline or somatic and can have different effects on protein function and the phenotype. The document provides examples of specific mutations and their effects.