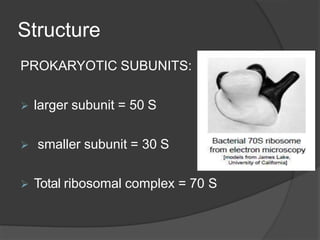
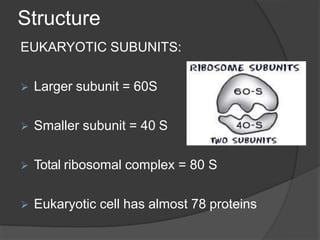
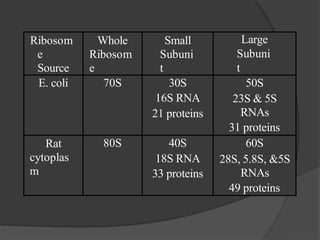
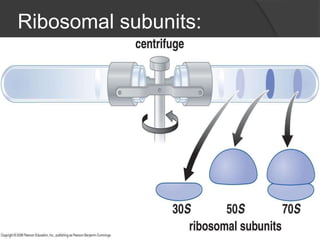
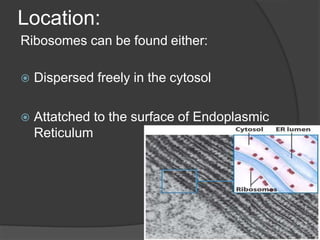
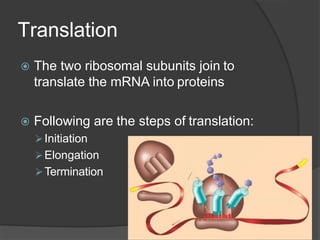
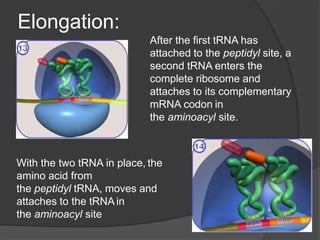
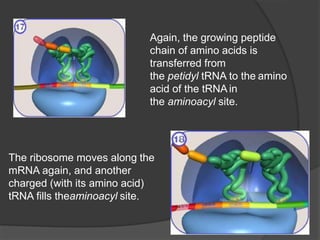
Ribosomes are organelles found in all cells that synthesize proteins. They consist of RNA and proteins and exist as two subunits - a smaller 30S subunit in prokaryotes and 40S in eukaryotes, and a larger 50S subunit in prokaryotes and 60S in eukaryotes. Ribosomes translate mRNA into proteins through initiation, elongation, and termination steps. Errors in ribosome functioning can lead to improper protein folding and diseases.