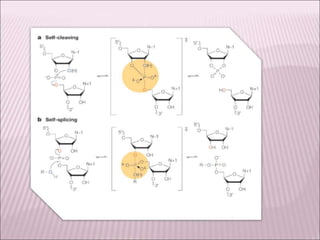
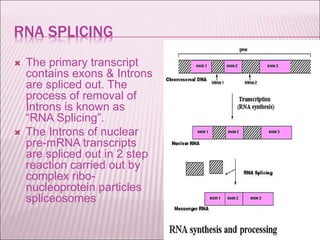
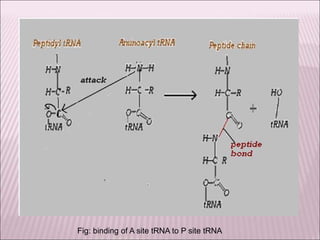
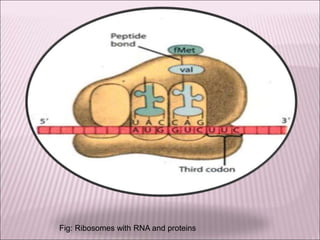
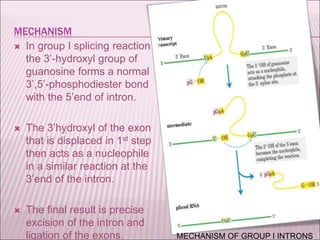
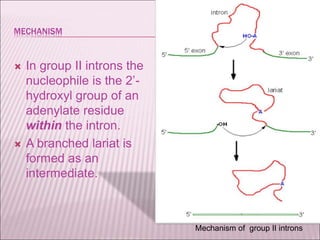
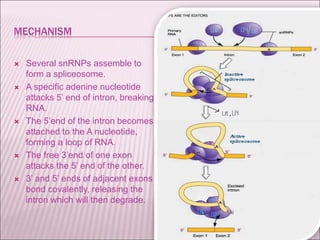
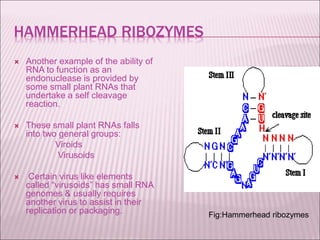
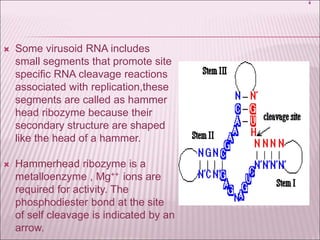
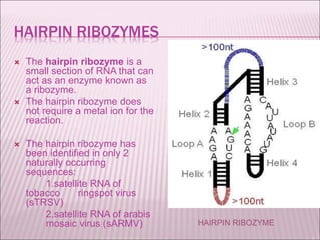
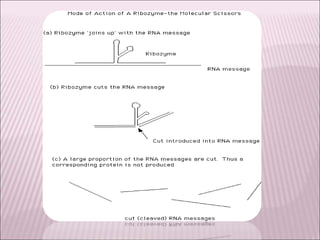
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that exhibit enzymatic activity by catalyzing chemical reactions, including RNA splicing and cleavage, without the assistance of proteins. There are several types of ribozymes that differ based on their structure and catalytic mechanism, including hammerhead ribozymes, hairpin ribozymes, hepatitis delta virus ribozymes, and the ribosome - a large and complex ribozyme responsible for protein synthesis. Ribozymes have potential clinical applications as they can be designed to selectively cleave target RNA sequences, offering possibilities for developing therapies for genetic diseases and viral infections like HIV.