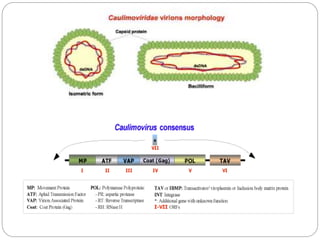
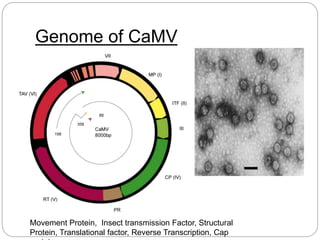
This document discusses the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV) and its potential use for gene transfer in plants. CaMV is a plant virus that infects brassica plants like cauliflower and turnips. It has a circular double-stranded DNA genome and is spherical in shape. The 35S promoter from CaMV is commonly used in plant transformation due to its strong constitutive expression in dicots. For gene transfer, foreign DNA can be inserted into the non-essential genes II or VII of CaMV. However, CaMV has limitations for gene transfer due to its limited insertion capacity and loss of infectivity if too many nucleotides are added.