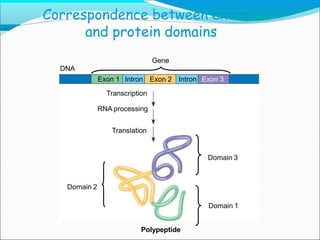
Eukaryotic pre-mRNA undergoes processing in the nucleus before being exported to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. This involves adding a 5' cap and poly-A tail to increase stability and facilitate export. Introns are also spliced out by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear RNAs and proteins that cuts out introns and joins exons to form mature mRNA. Capping occurs at the 5' end shortly after transcription, while polyadenylation adds around 200 adenine nucleotides to the 3' end. Splicing removes intervening intron sequences by cutting and religating exons. These processing steps produce translation-competent mRNA from initial pre-mRNA transcripts.