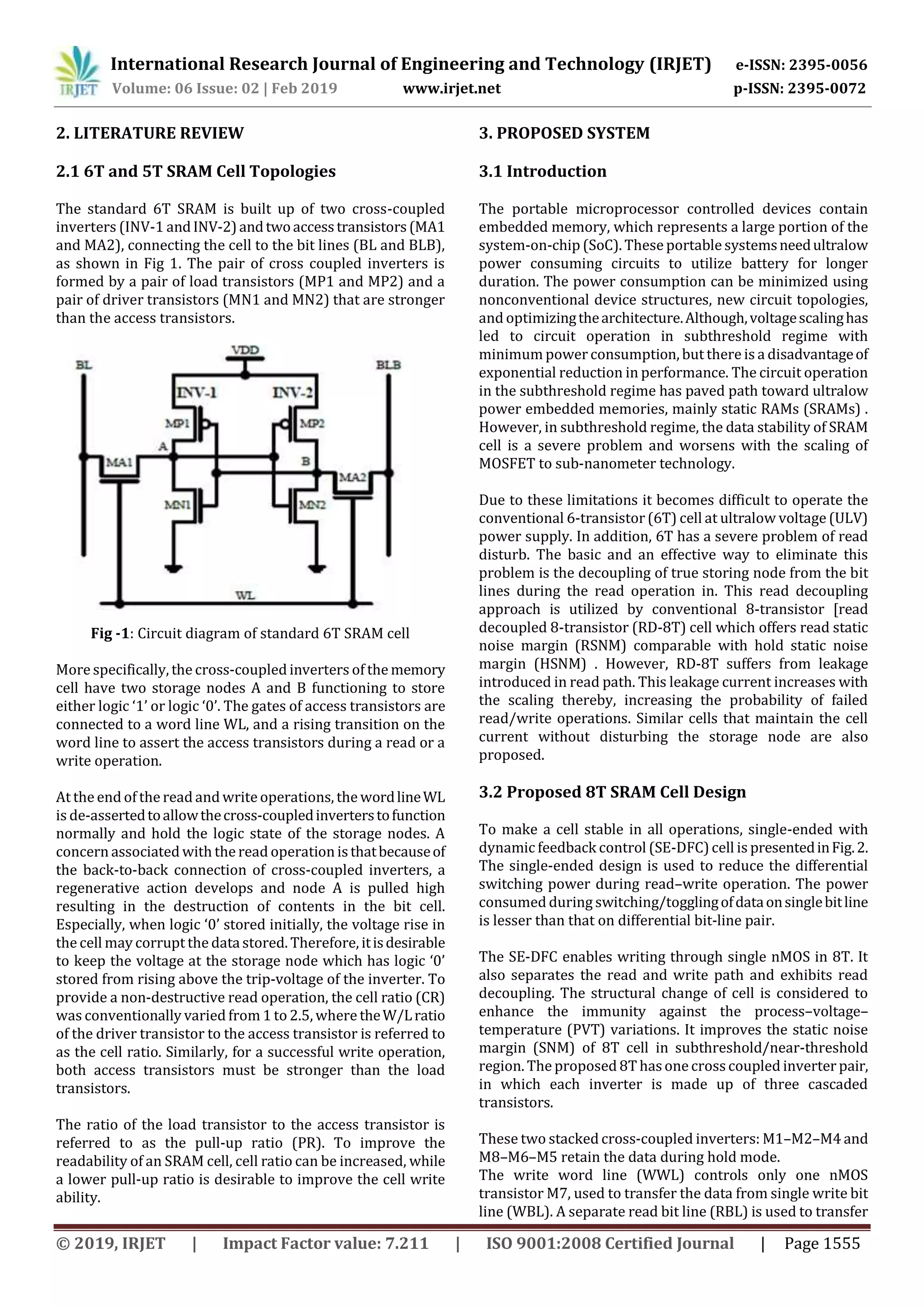
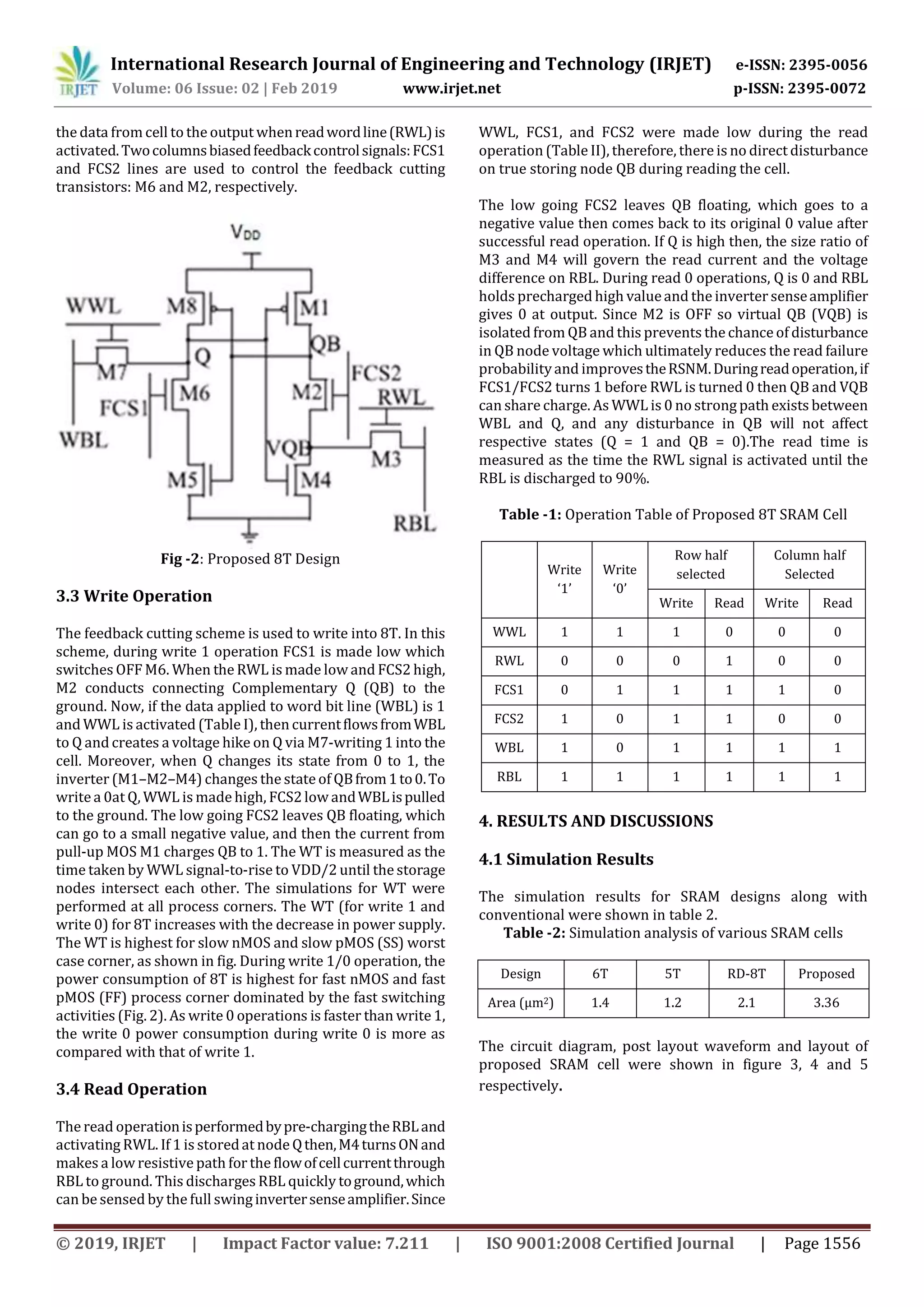
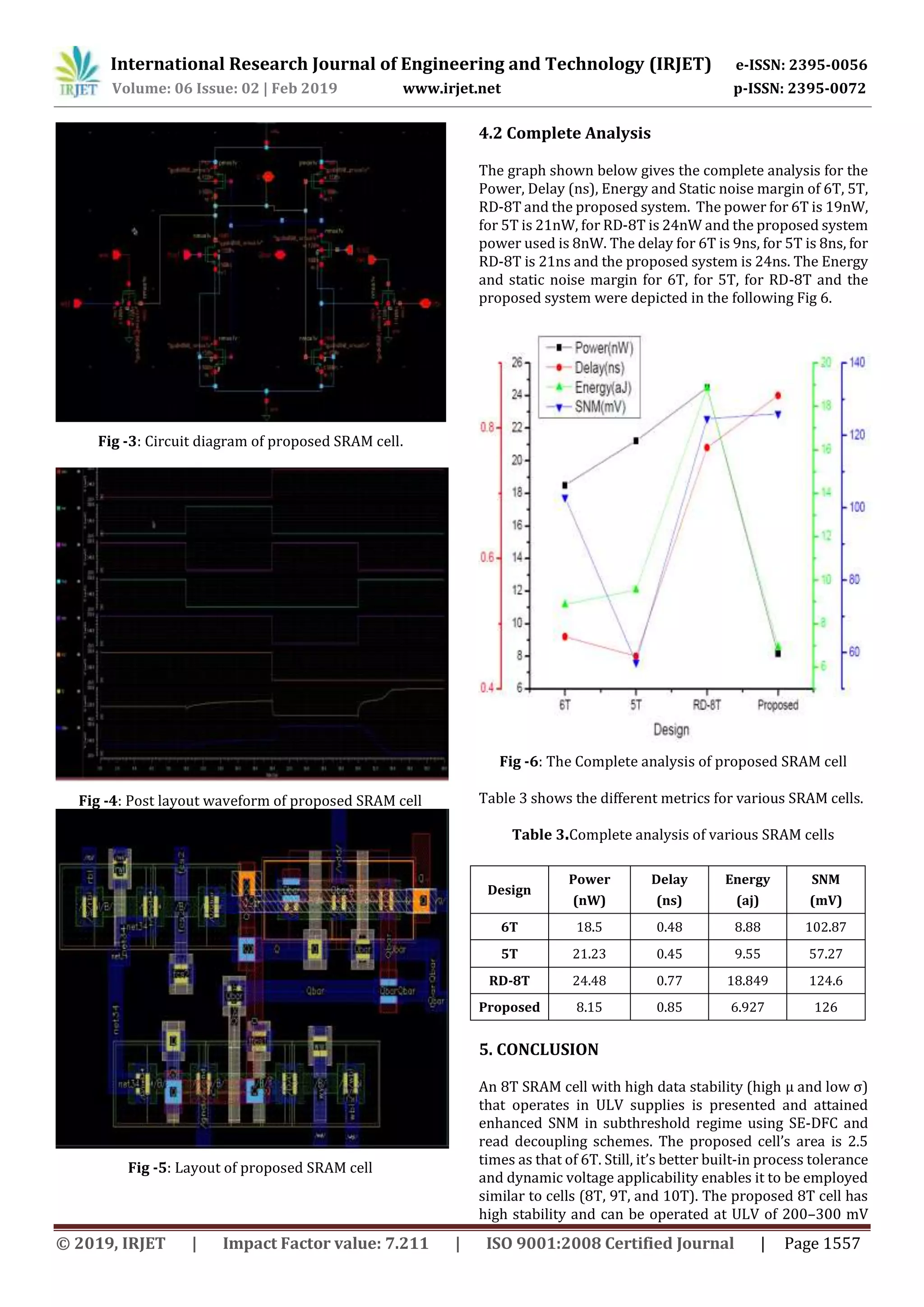
The document describes a study on designing an energy efficient 8-transistor (8T) static random access memory (SRAM) cell for use at 90nm technology. The proposed 8T SRAM cell enhances static noise margin for low power supply voltages, achieving higher write static noise margin than 6T and 8T SRAM cells at 300mV. It also has high read static noise margin similar to other cell designs while consuming less write power. Simulations of a 1-kb array of the 8T SRAM cells showed reduced read and write power/energy consumption compared to other cell designs. The 8T cell was designed and analyzed using CADENCE design tools at 90nm technology node to enable ultralow power applications.