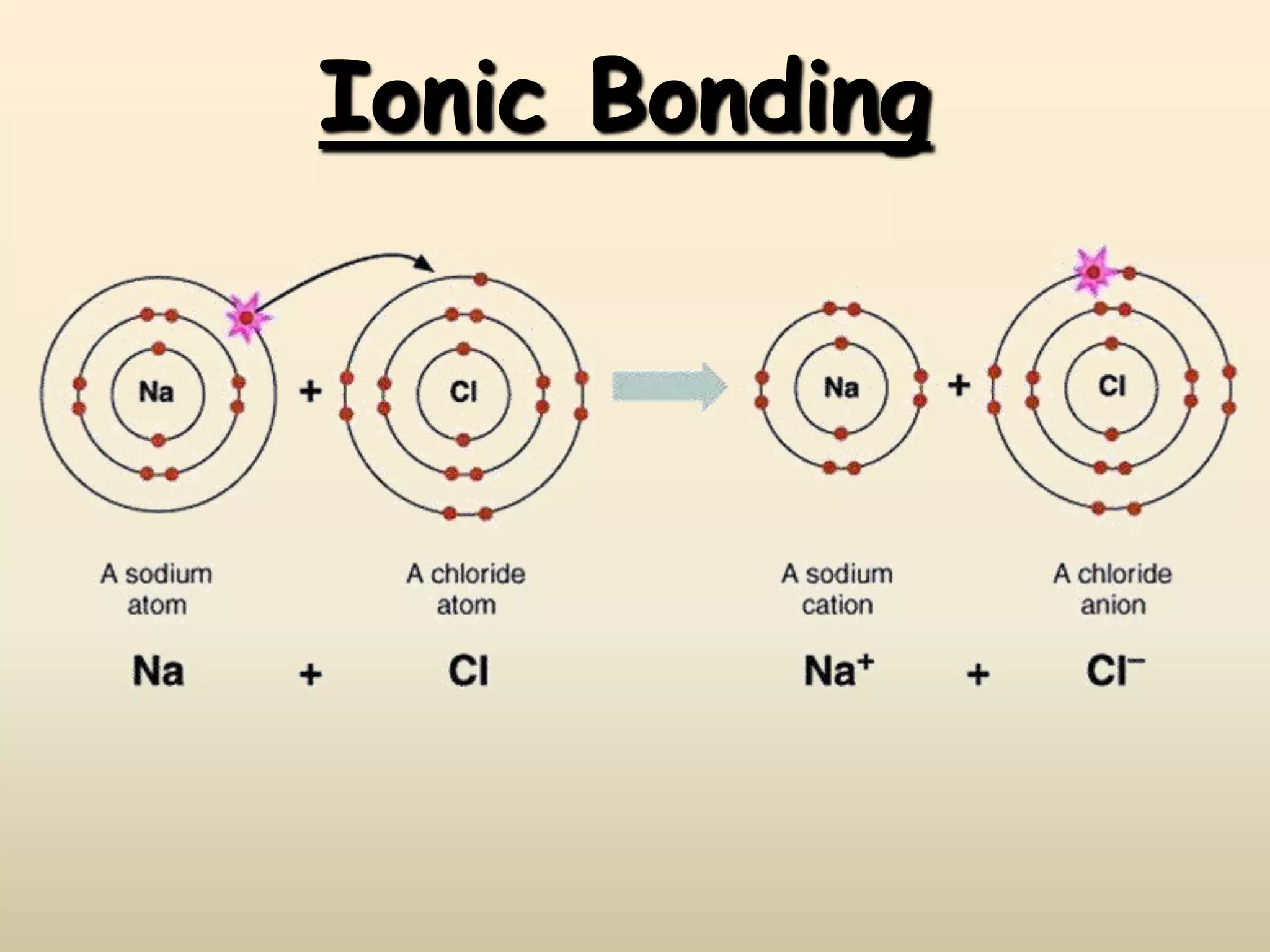
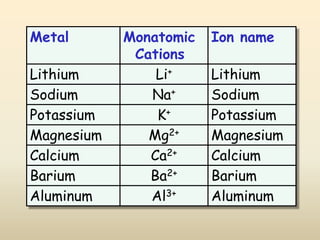
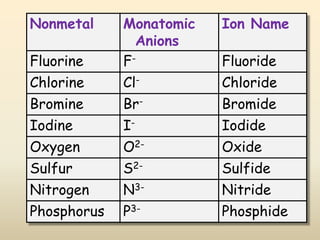
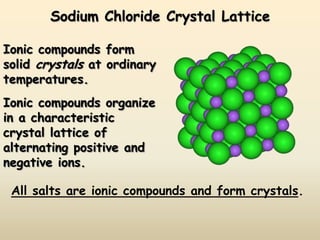
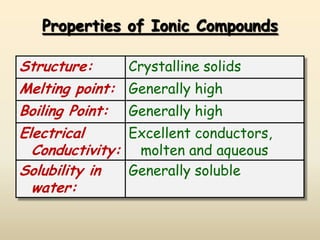
Ionic bonds form when a metal transfers an electron to a nonmetal, giving each atom an octet of electrons. For example, sodium loses an electron to form Na+ while chlorine gains that electron to form Cl-. The resulting ions are held together by electrostatic attraction to form an ionic compound, sodium chloride (NaCl). NaCl forms a crystalline lattice structure where the Na+ and Cl- ions are arranged in a repeating pattern. Ionic compounds have properties like high melting points, conductivity when molten or dissolved, and solubility in water.