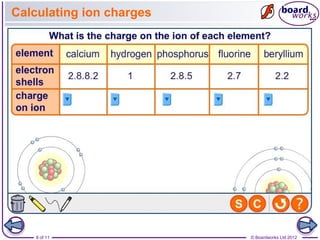
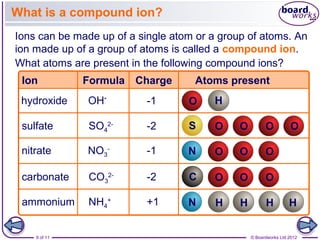
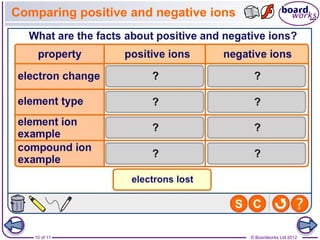
This document discusses ions and how they are formed. It explains that atoms become ions by gaining or losing electrons to obtain a full outer electron shell. Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged ions and atoms that lose electrons become positively charged ions. The document also discusses different types of ions including monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, and how to name compound ions that contain multiple atoms like sulfate, nitrate, and hydroxide ions.