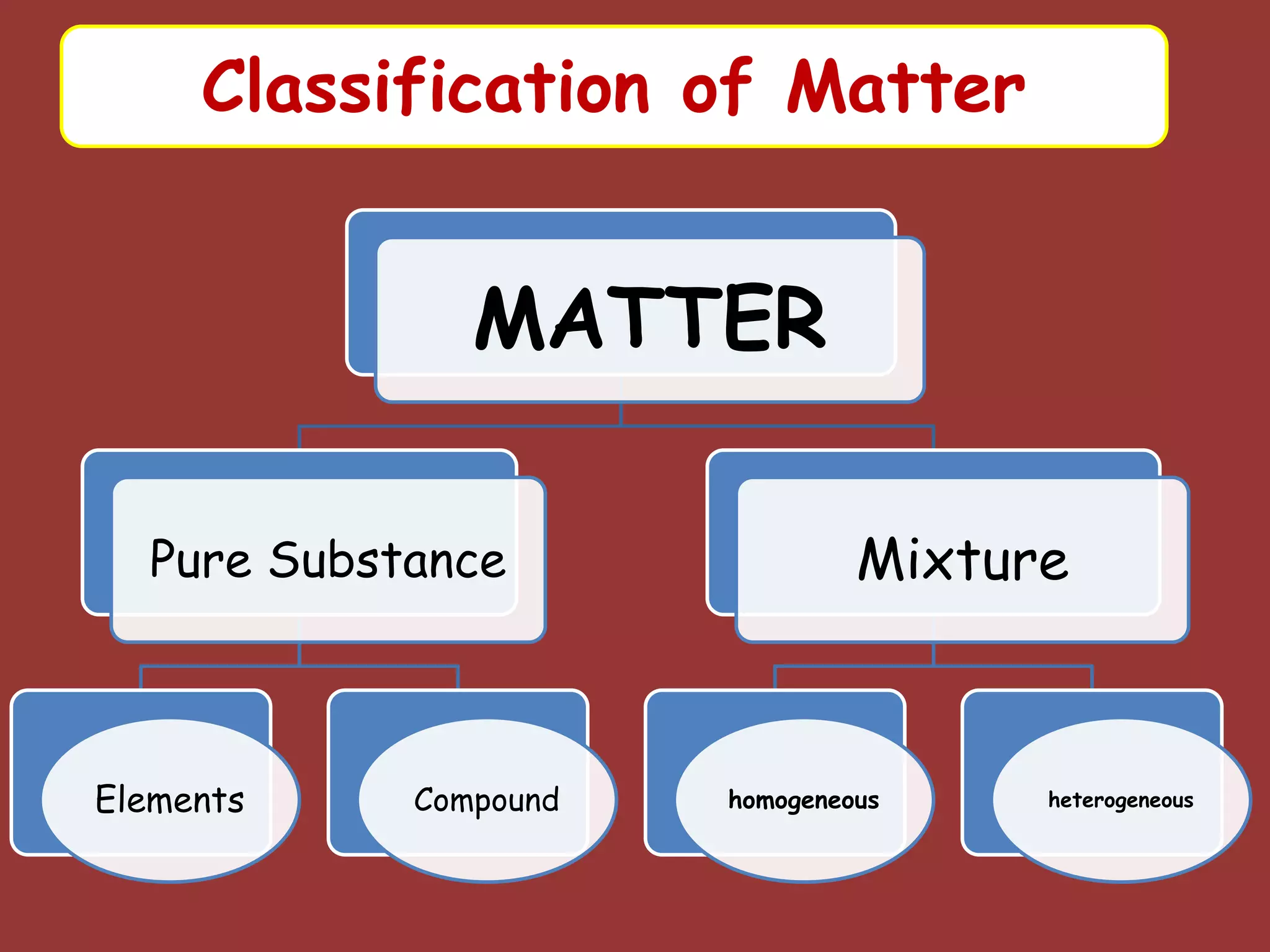
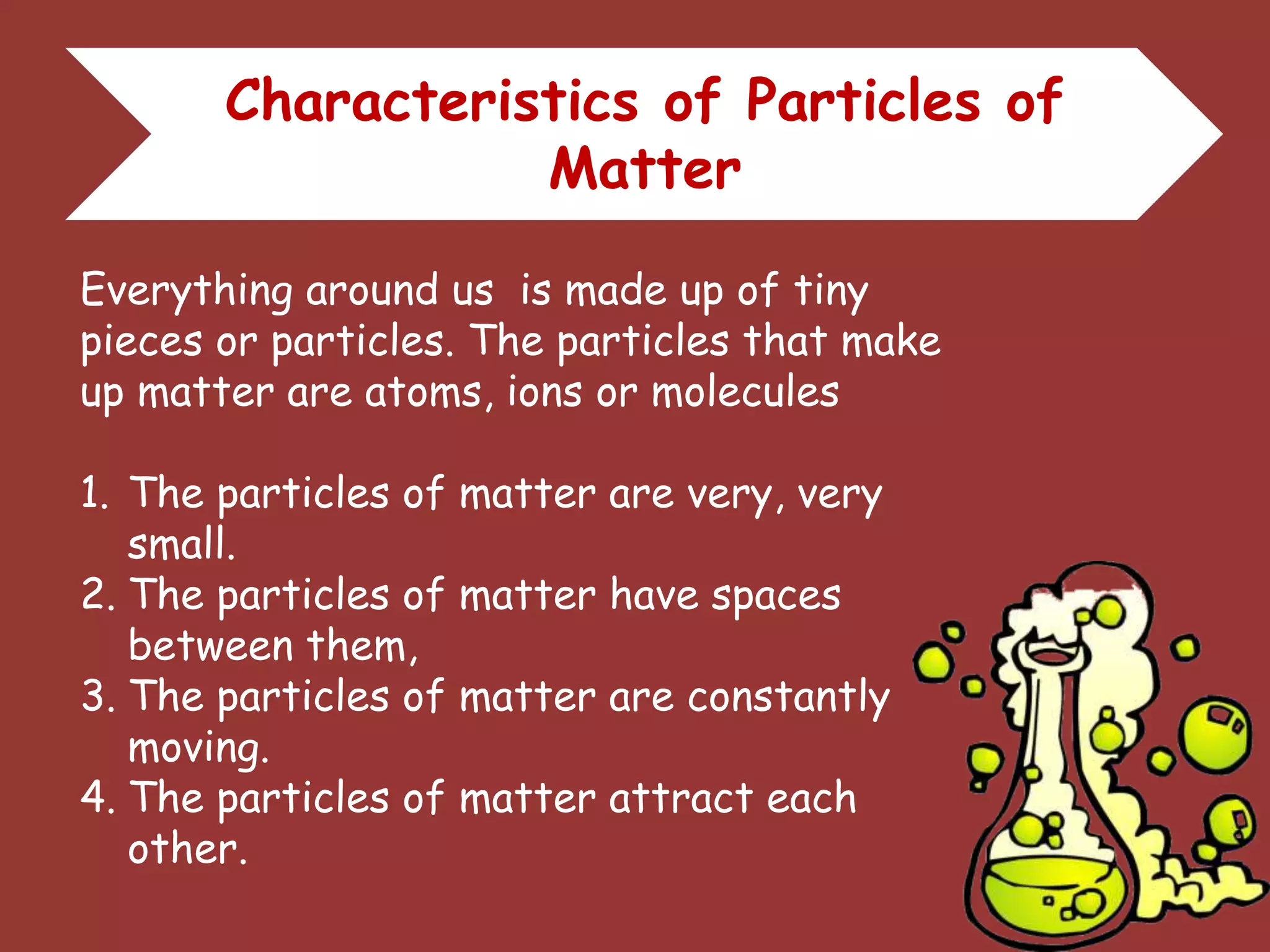
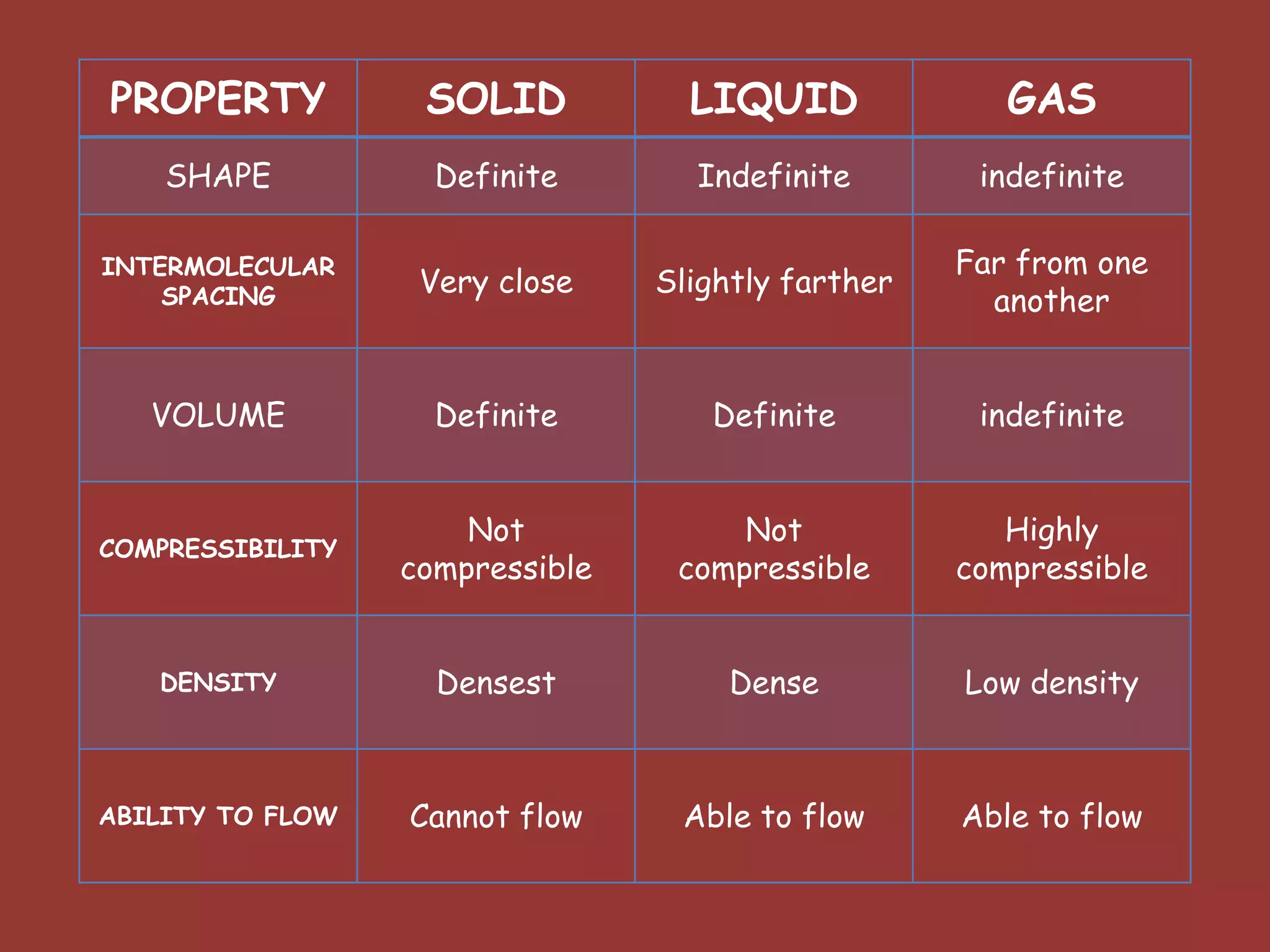
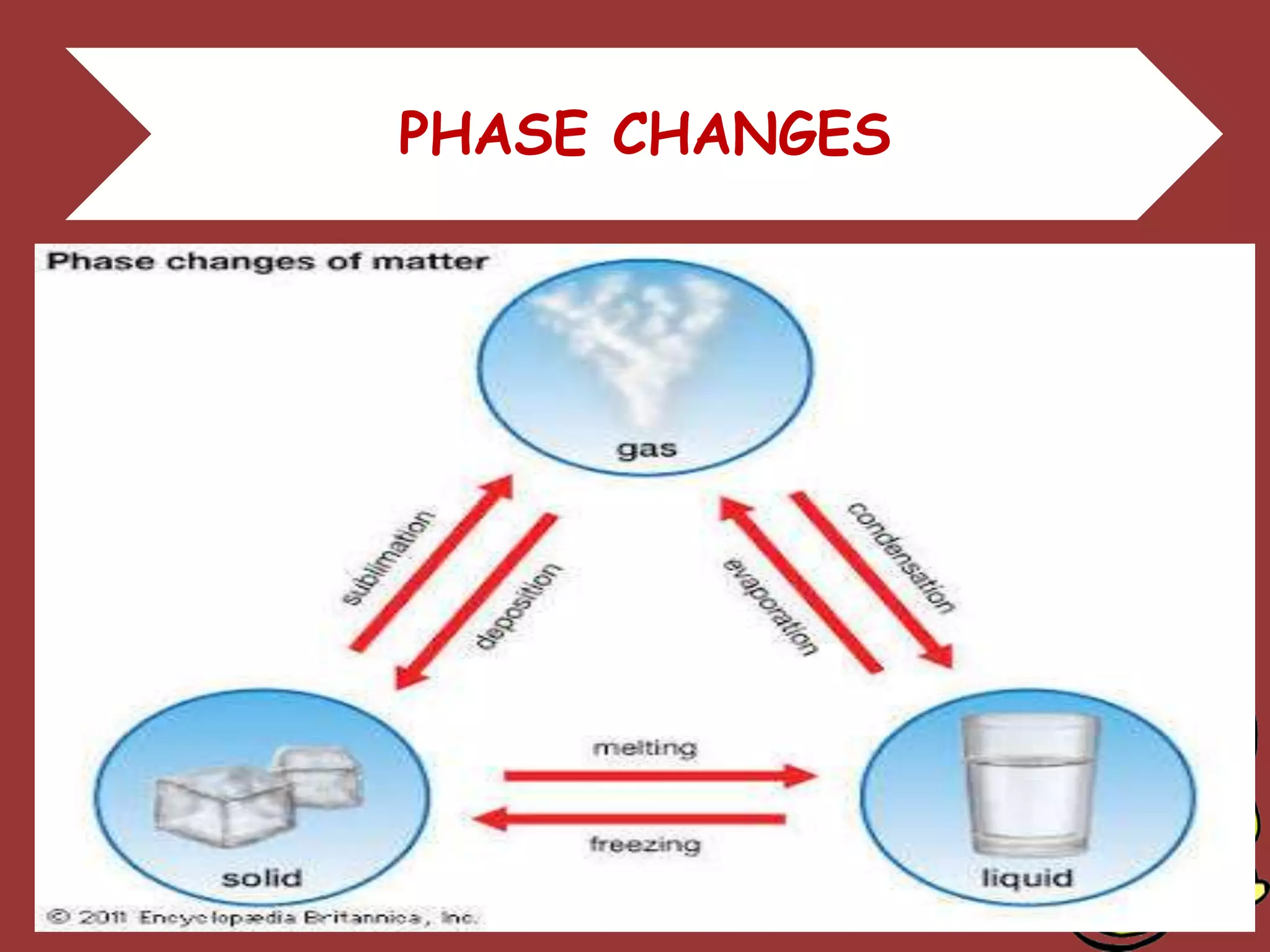
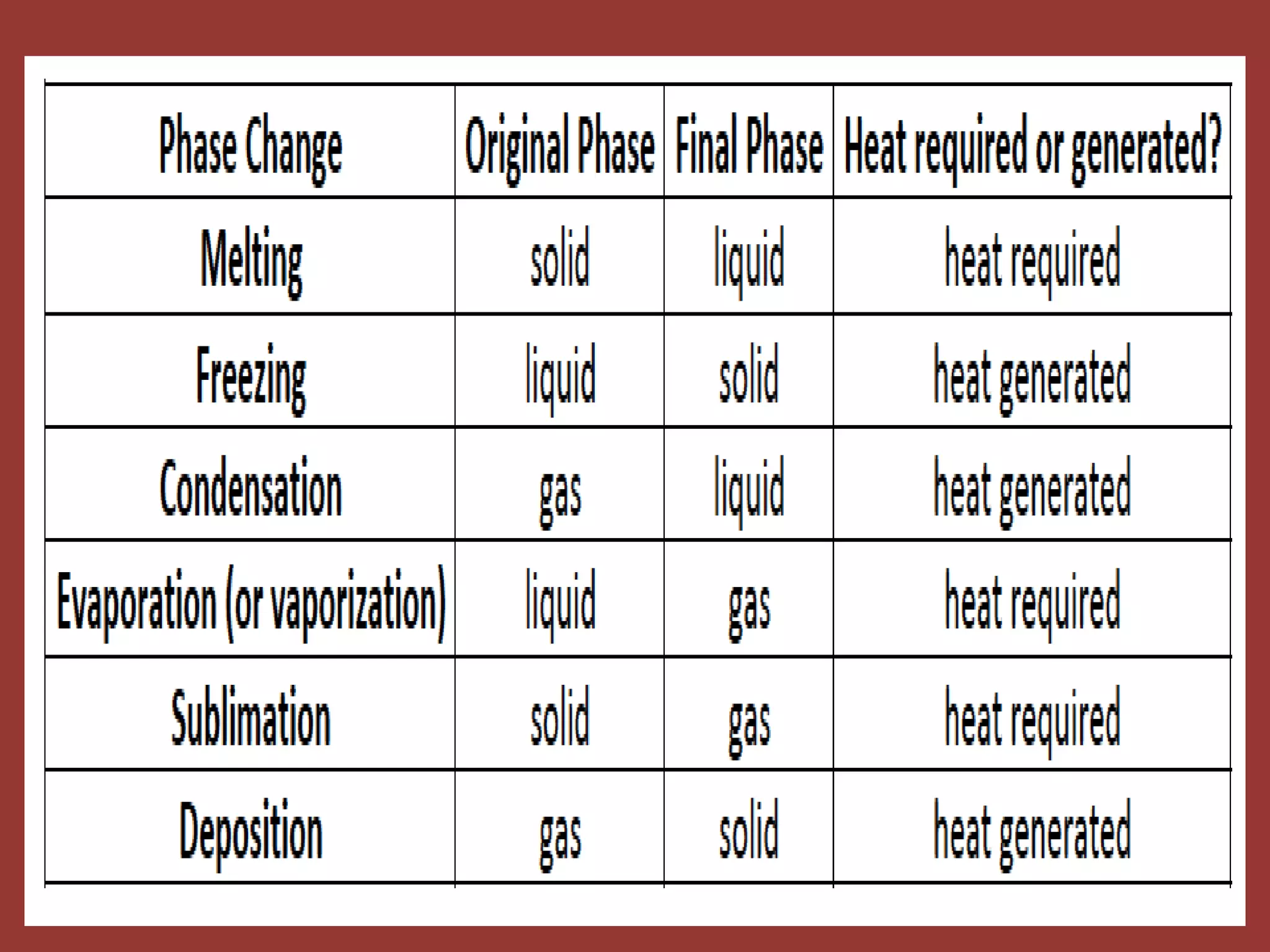
The document discusses the particle nature of matter, defining matter as anything that occupies space and has mass, classified into pure substances and mixtures. It outlines historical theories by Leucippus, Democritus, and Dalton on atoms and their properties, emphasizing that all matter is composed of atoms, molecules, or ions. Additionally, it describes the properties and characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases, explaining their differences in shape, volume, compressibility, and density.