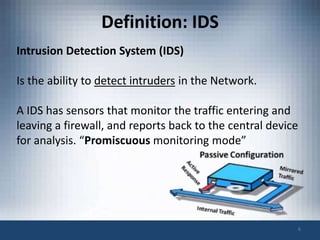
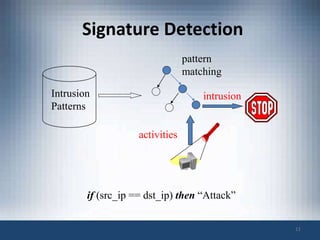
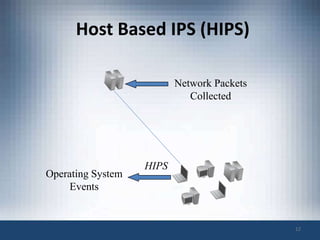
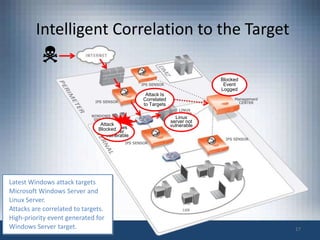
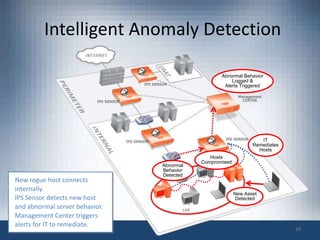
The document discusses intrusion prevention and intrusion detection systems. It defines intrusion as unauthorized access aimed at compromising network security assets. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network traffic to detect intrusions, while intrusion prevention systems (IPS) can also block attacks in real-time. An IPS provides increased visibility beyond a firewall by using techniques like signature detection, anomaly detection, and protocol analysis to identify intrusions and threats. The document outlines challenges faced by IPS like evasion techniques, and discusses next-generation IPS features like intelligent correlation, anomaly detection, and using global threat intelligence.