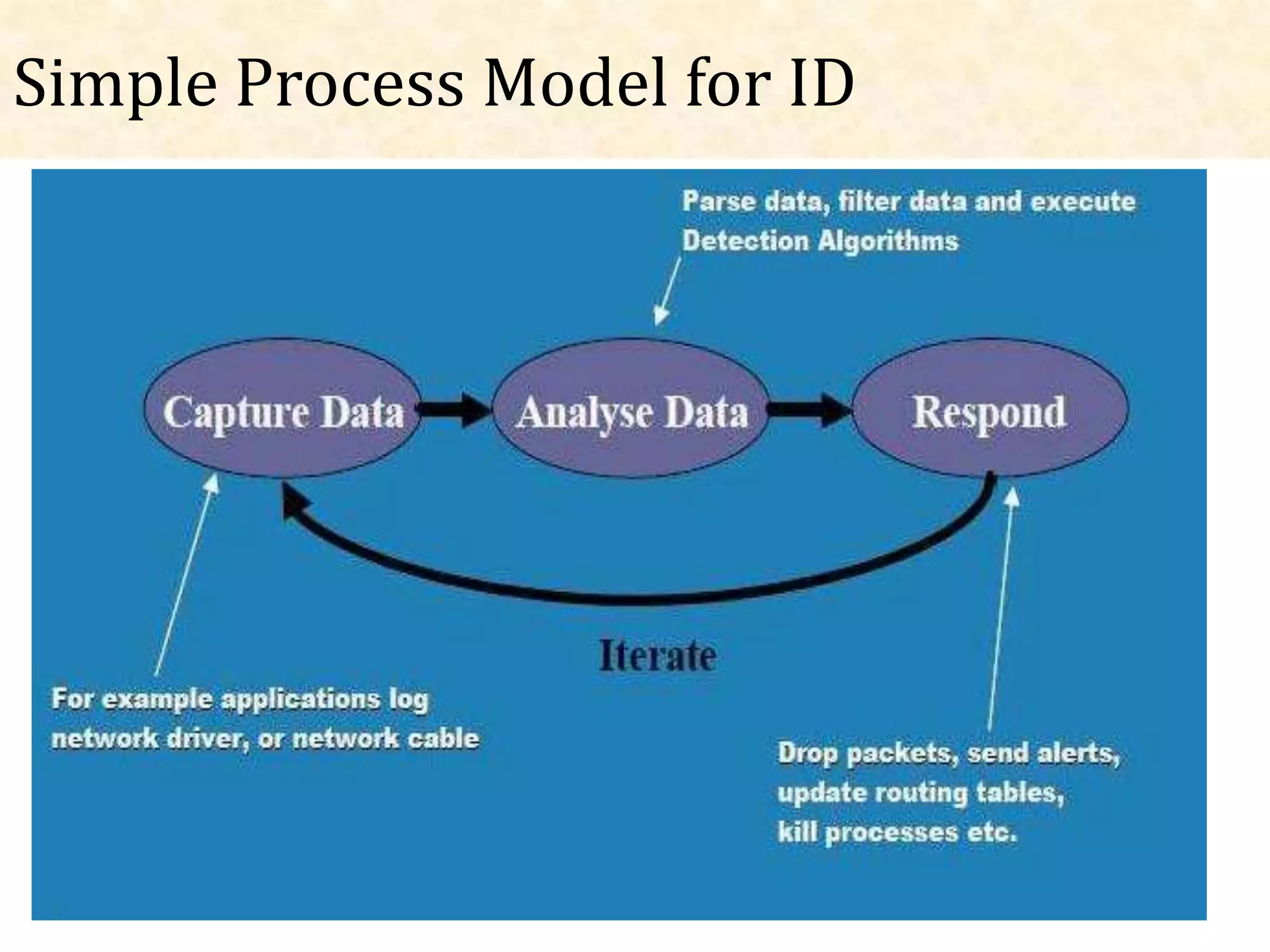
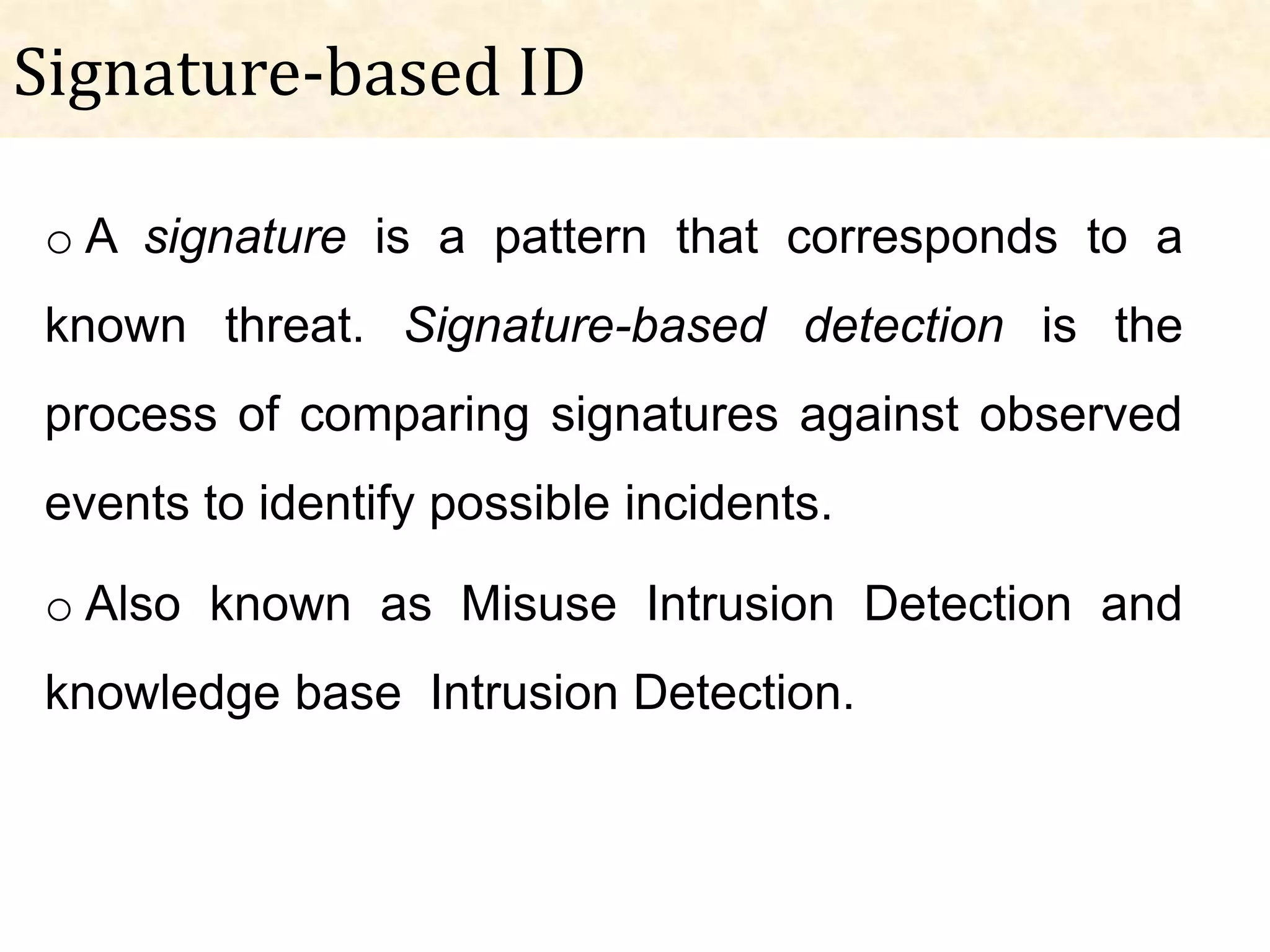
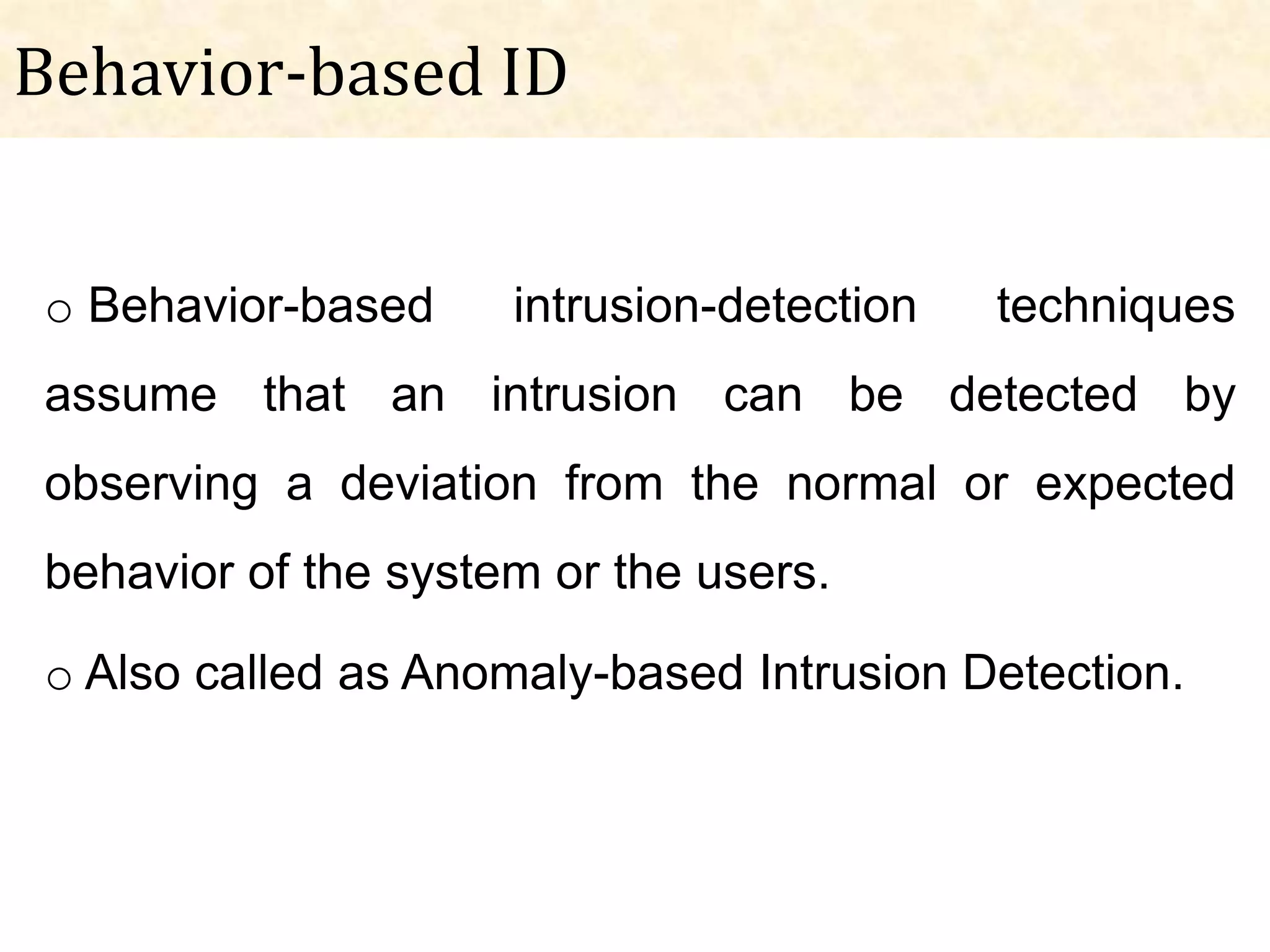
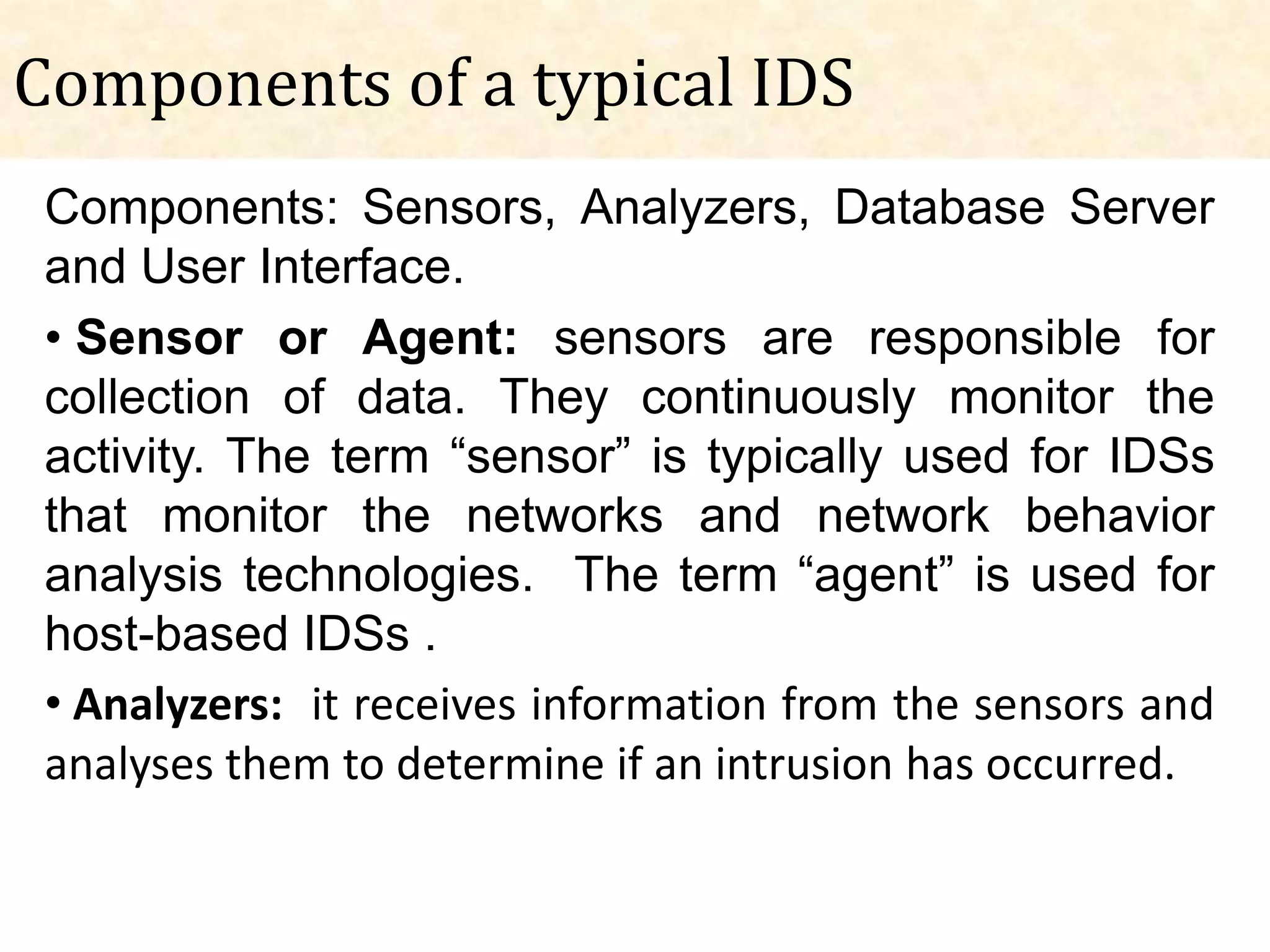
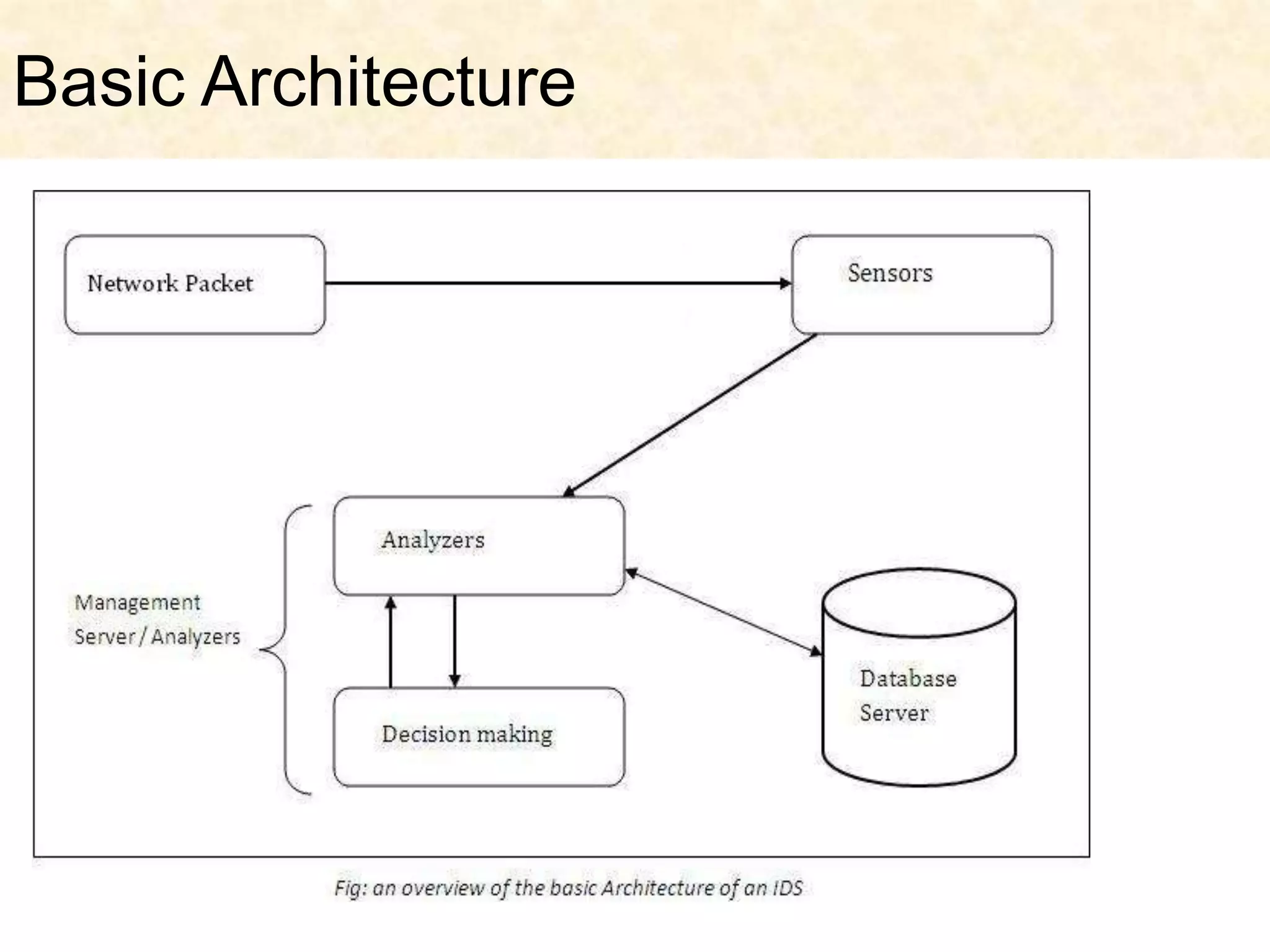
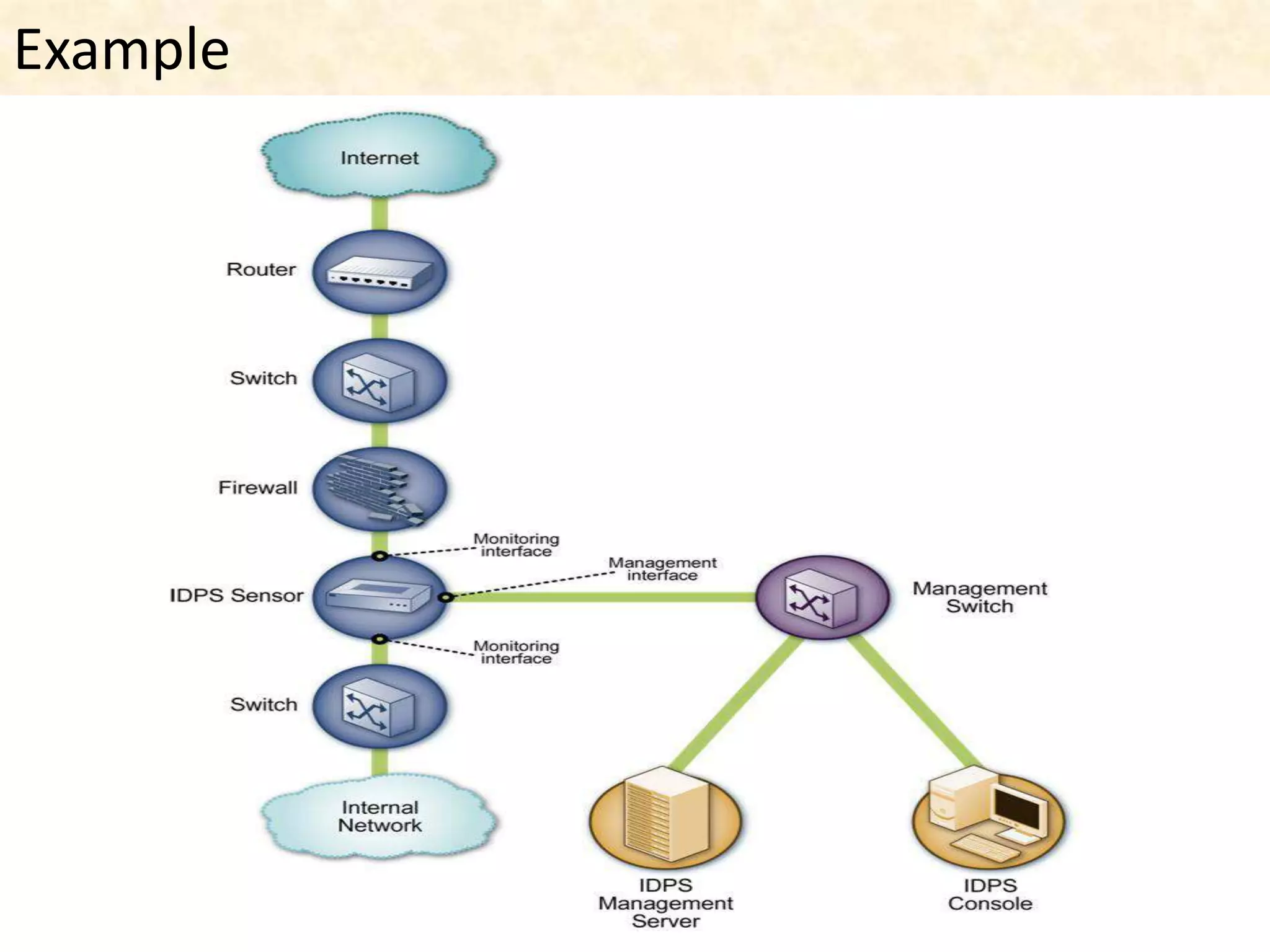
This document presents an overview of intrusion detection systems (IDS). It discusses the basic components and architecture of IDS, including sensors that monitor network activity and agents that monitor individual hosts. It also describes the two main types of methodologies IDS use - signature-based detection which compares observed events to known threats, and behavior-based detection which identifies deviations from normal behavior. Finally, it discusses the different types of IDS, including host-based IDS that monitor single systems and network-based IDS that monitor network traffic across multiple systems.