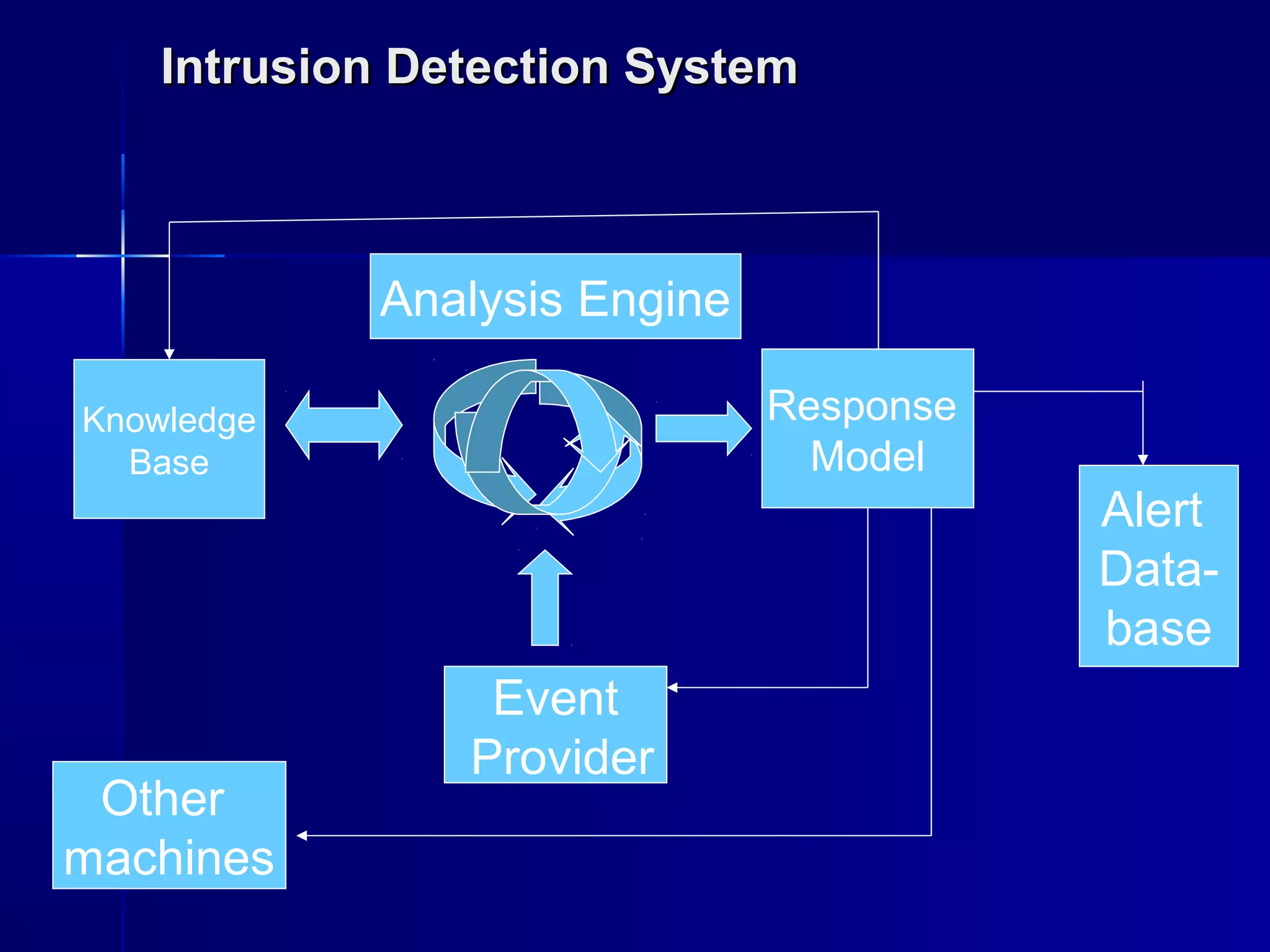
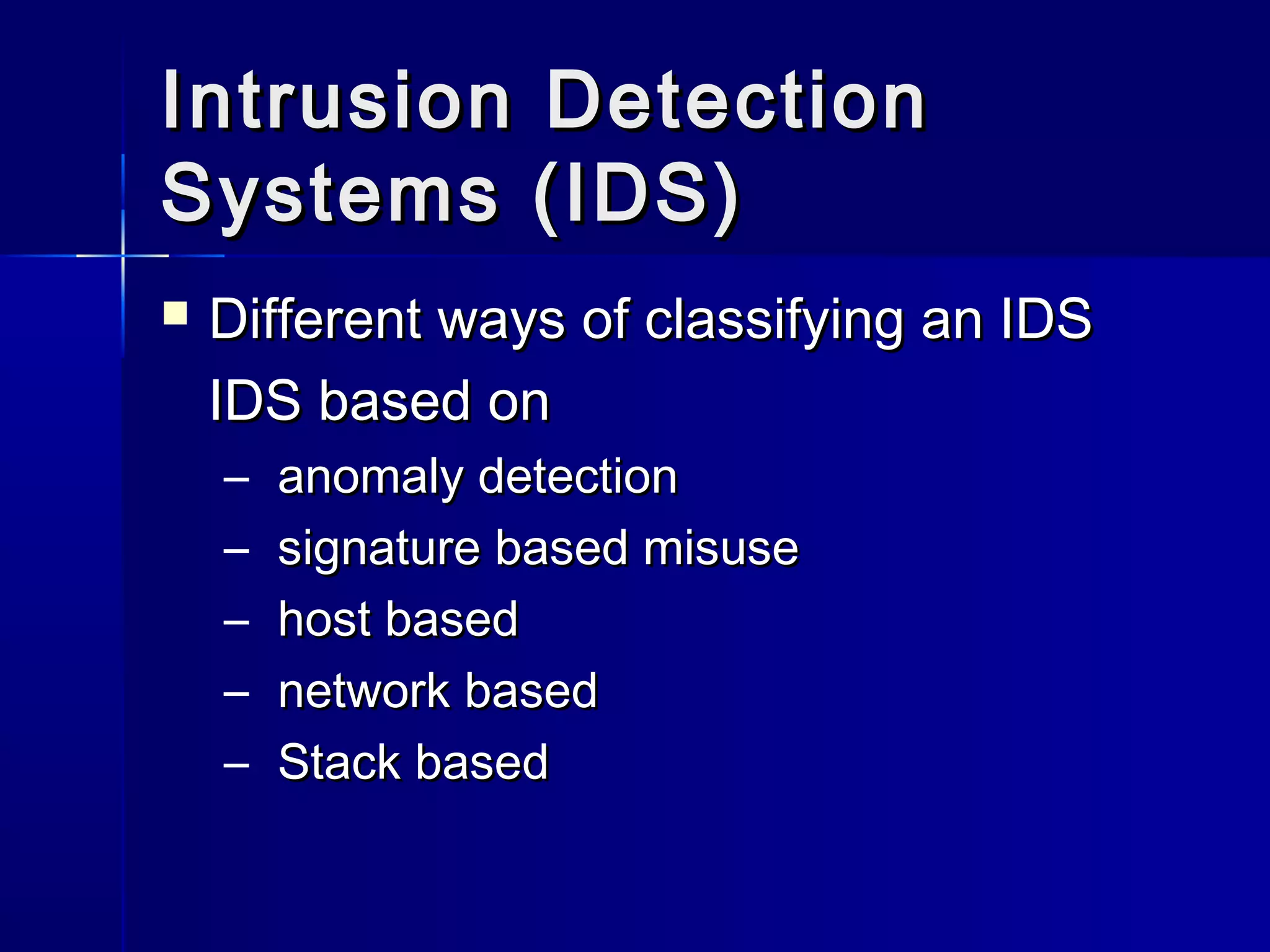
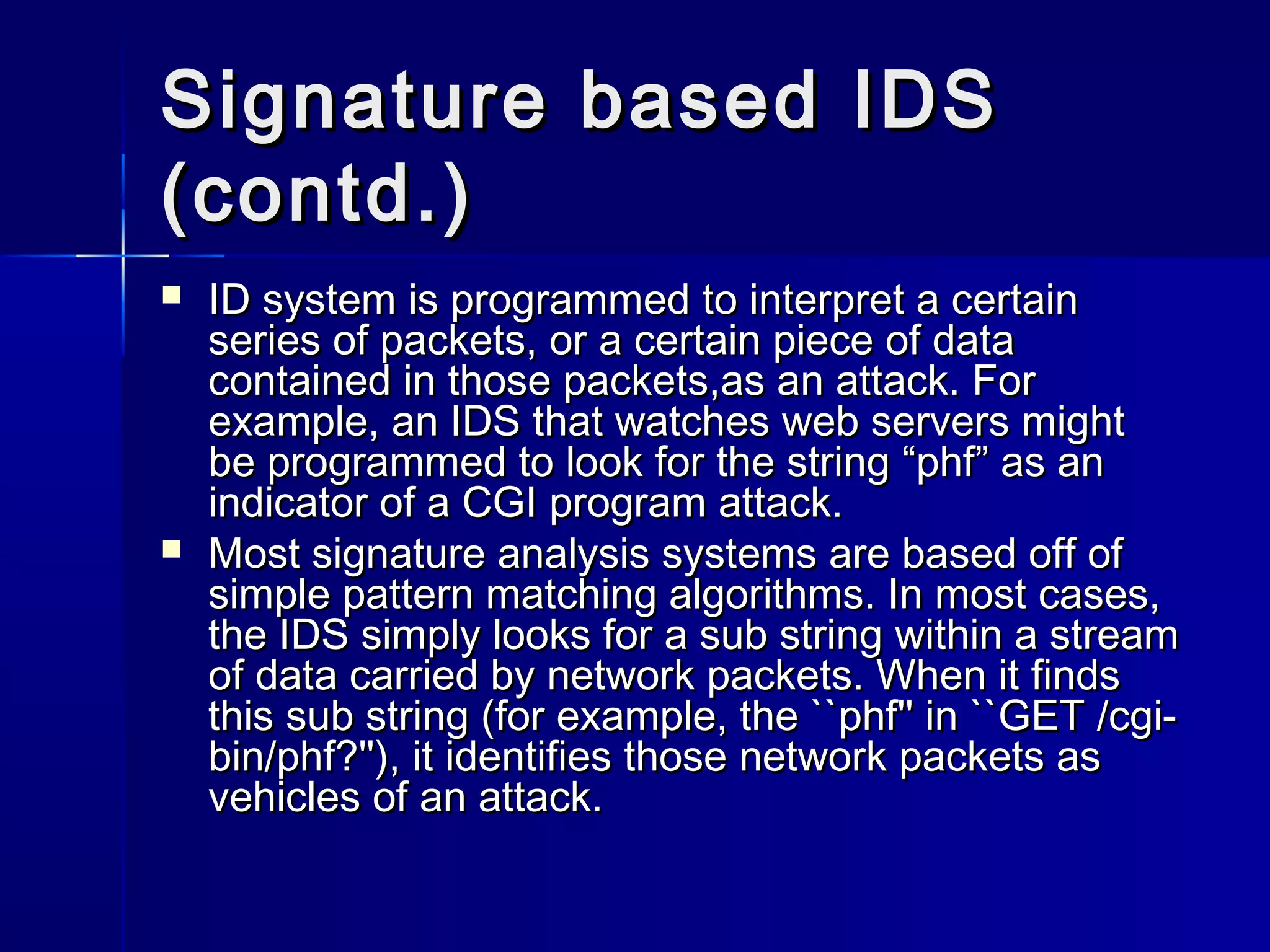
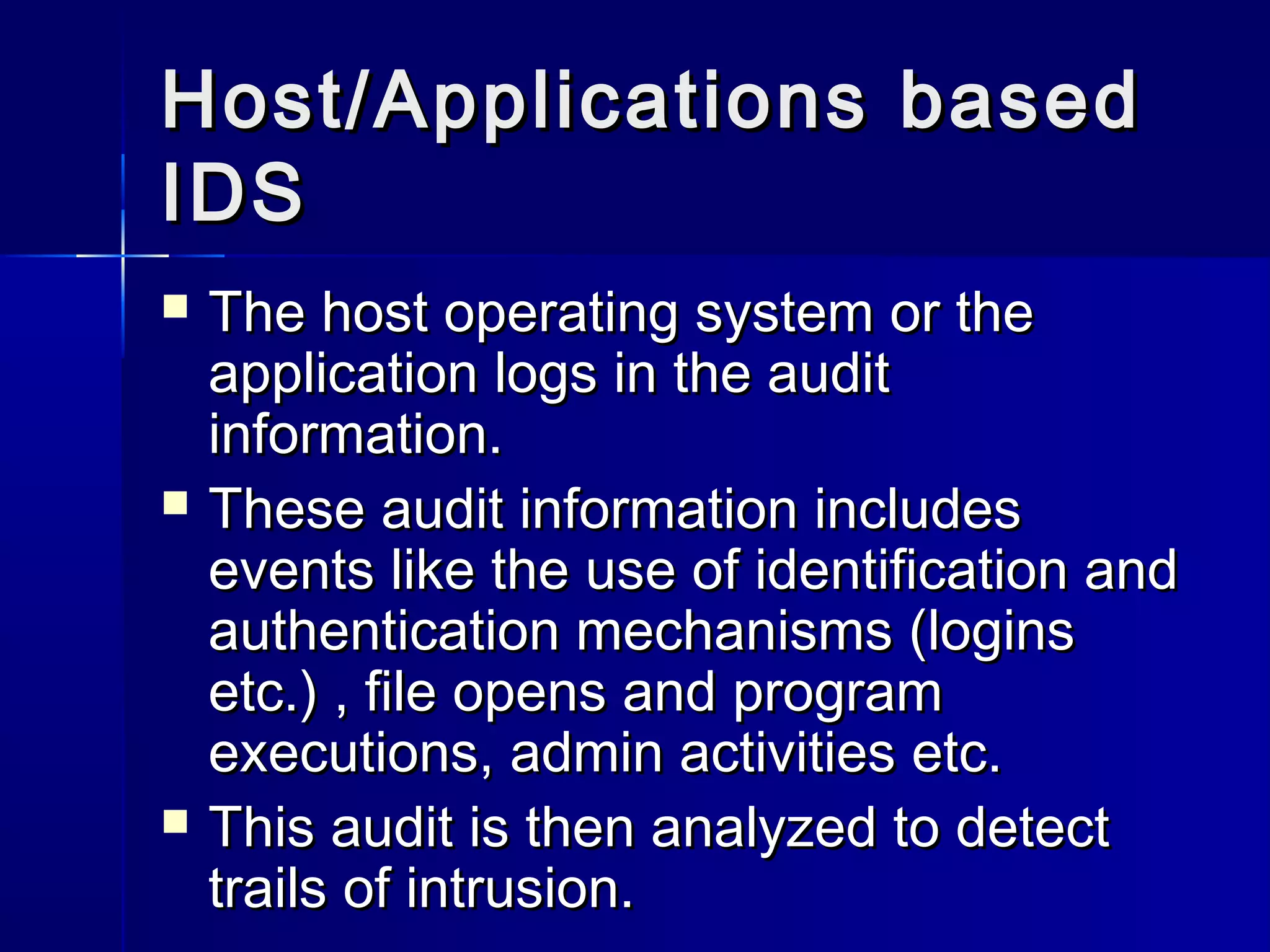
This document discusses intrusion detection systems (IDS). An IDS monitors network or system activities for malicious activities or policy violations. IDS can be classified based on detection method (anomaly-based detects deviations from normal usage, signature-based looks for known attack patterns) or location (host-based monitors individual systems, network-based monitors entire network traffic). The document outlines strengths and limitations of different IDS types and discusses the future of integrating detection methods.