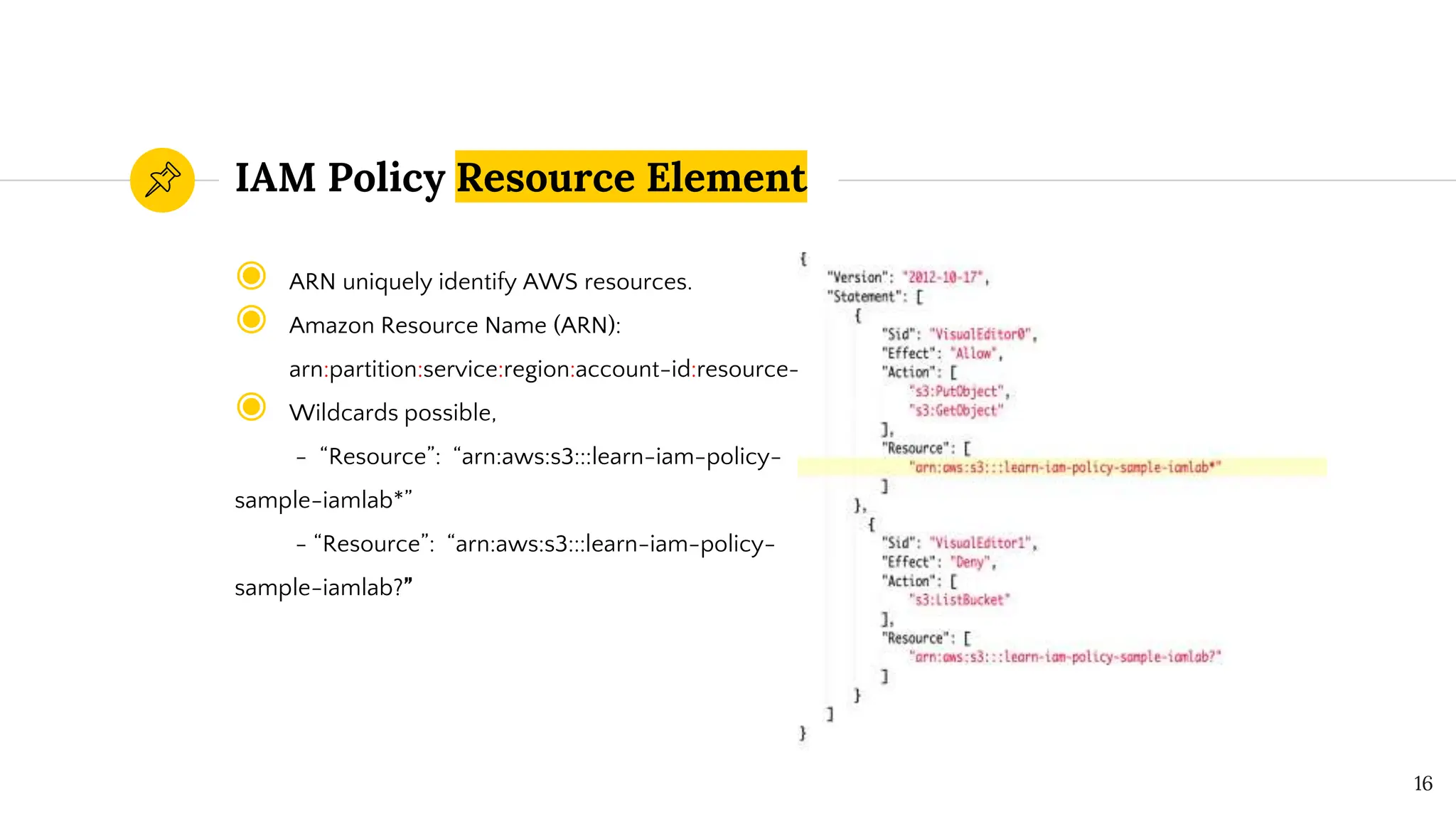
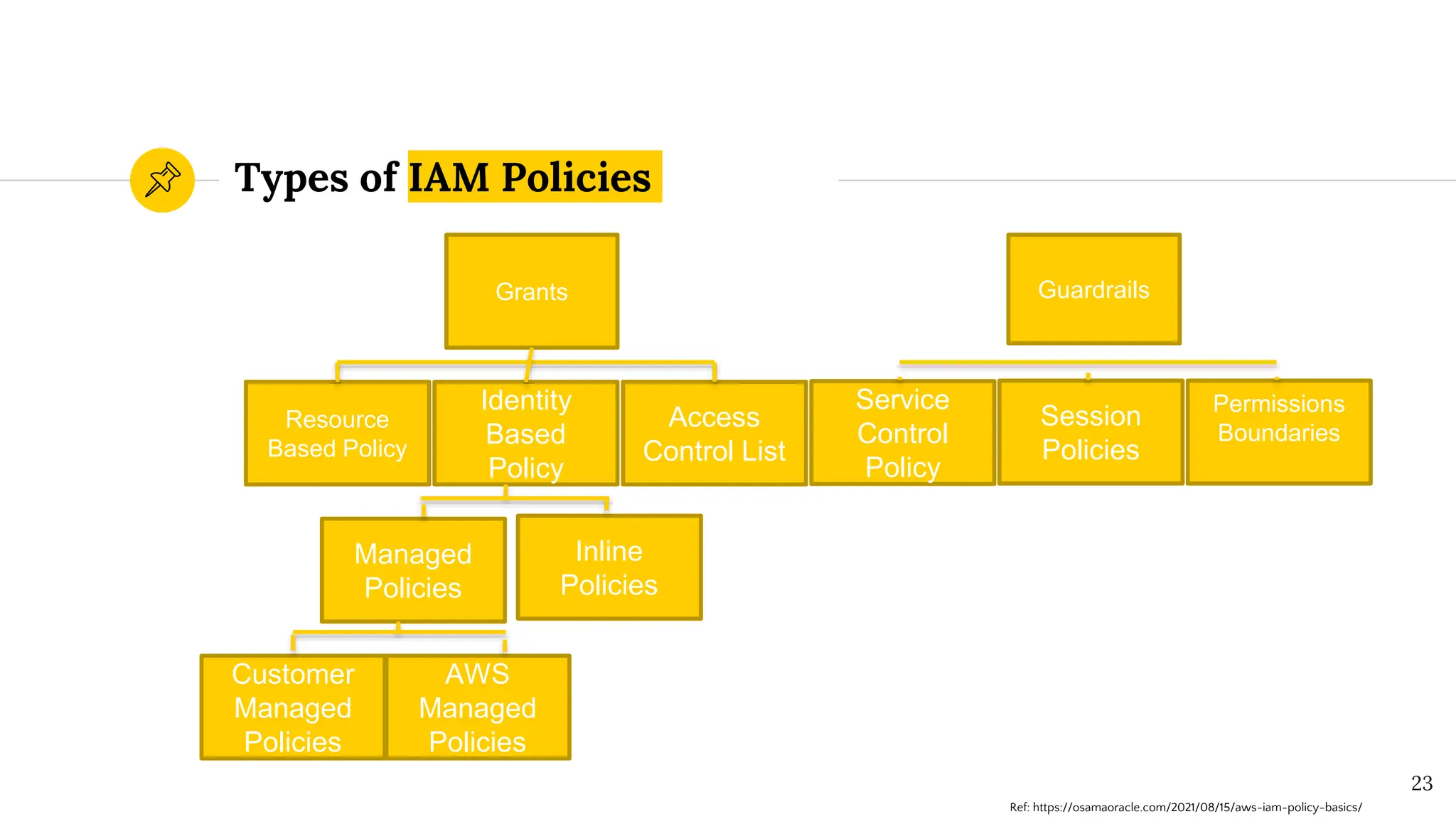
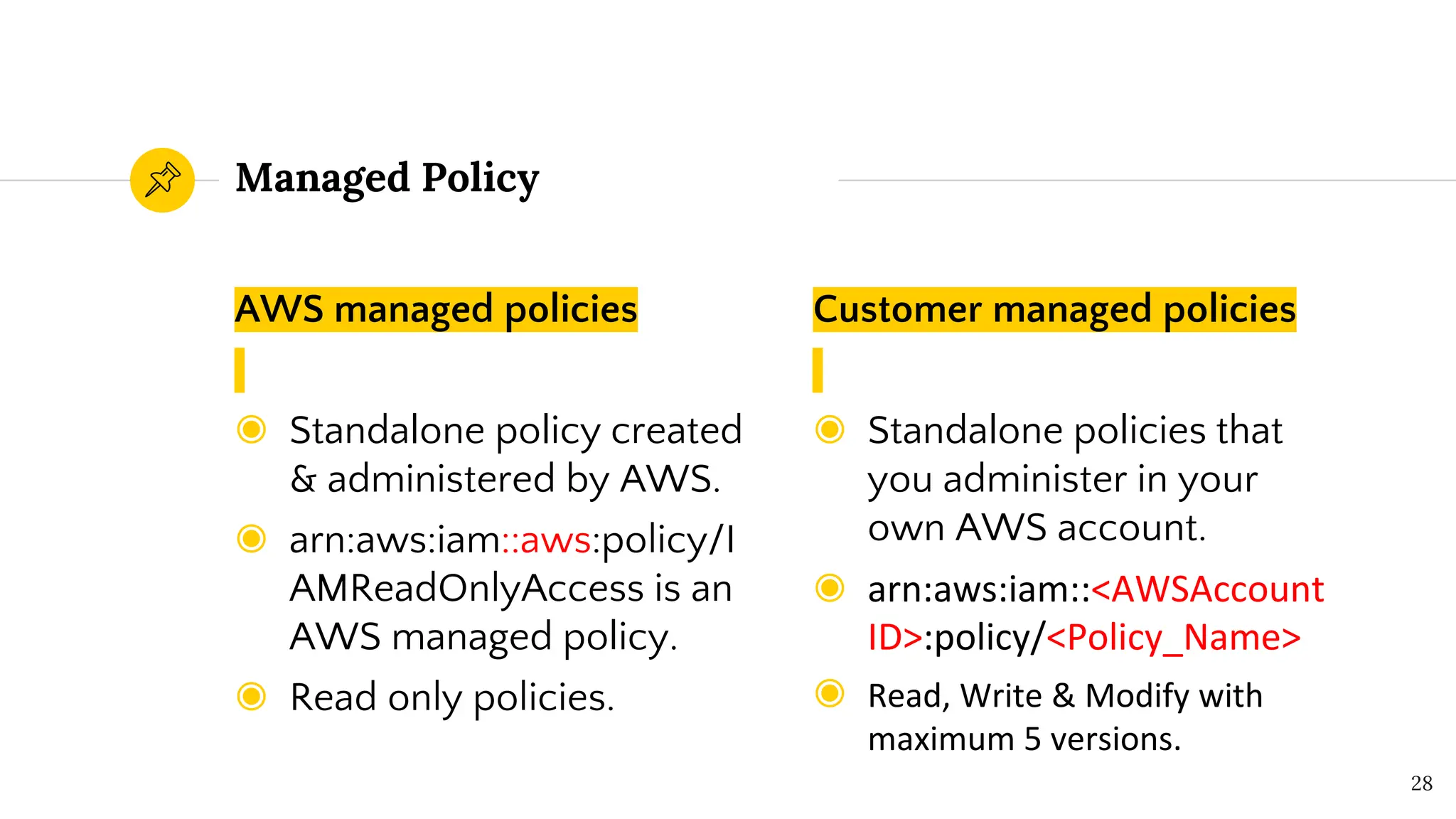
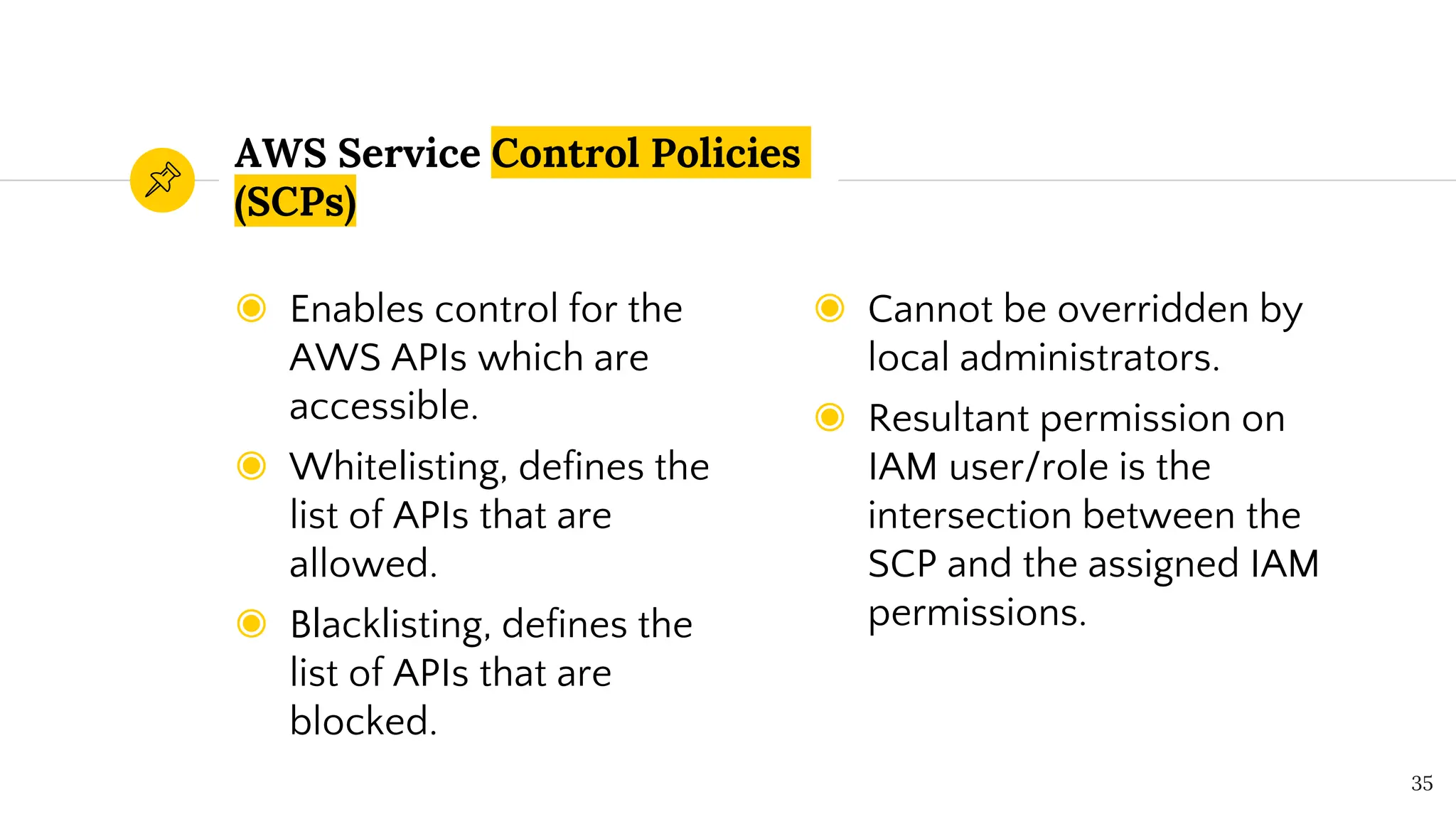
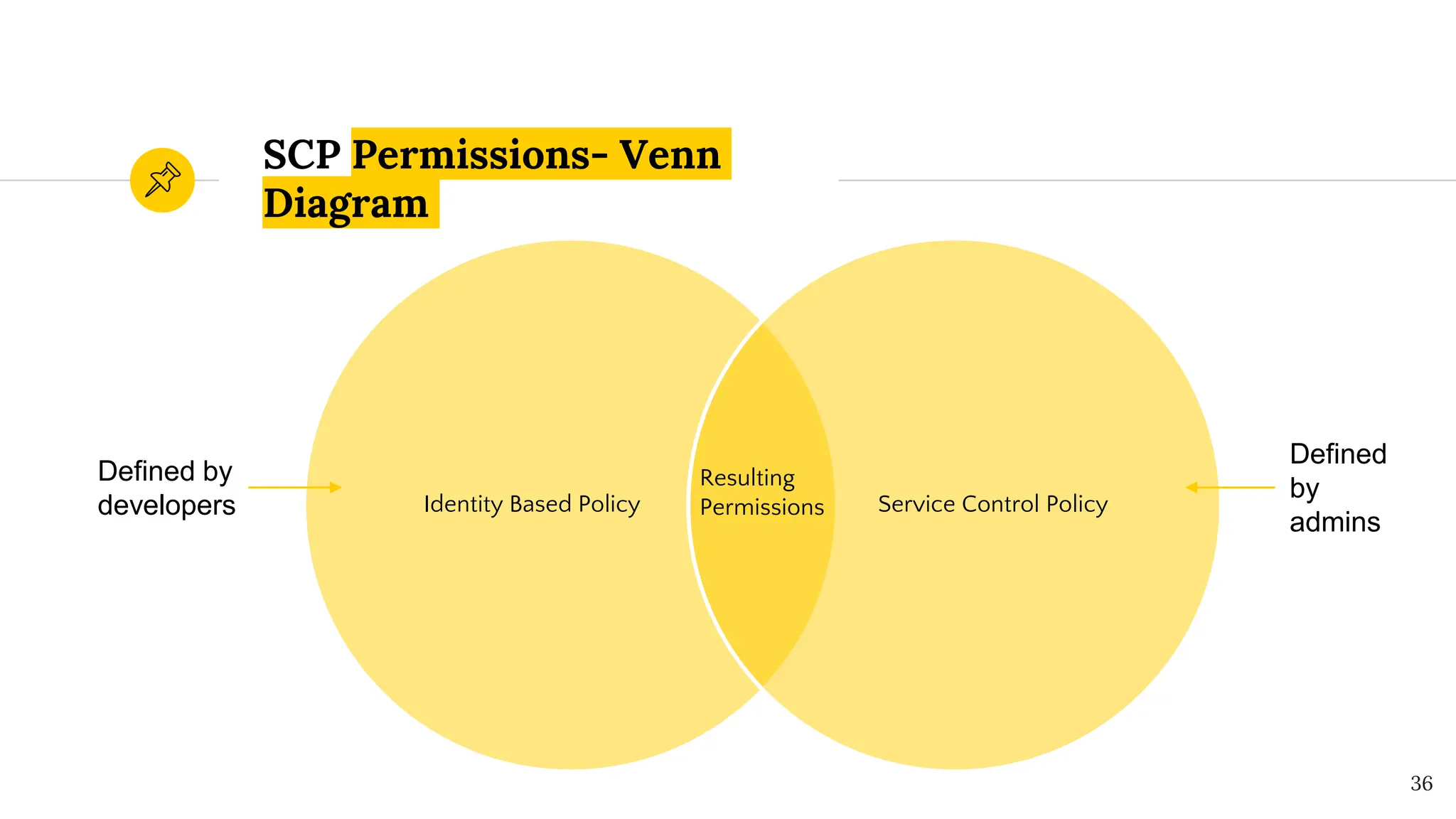
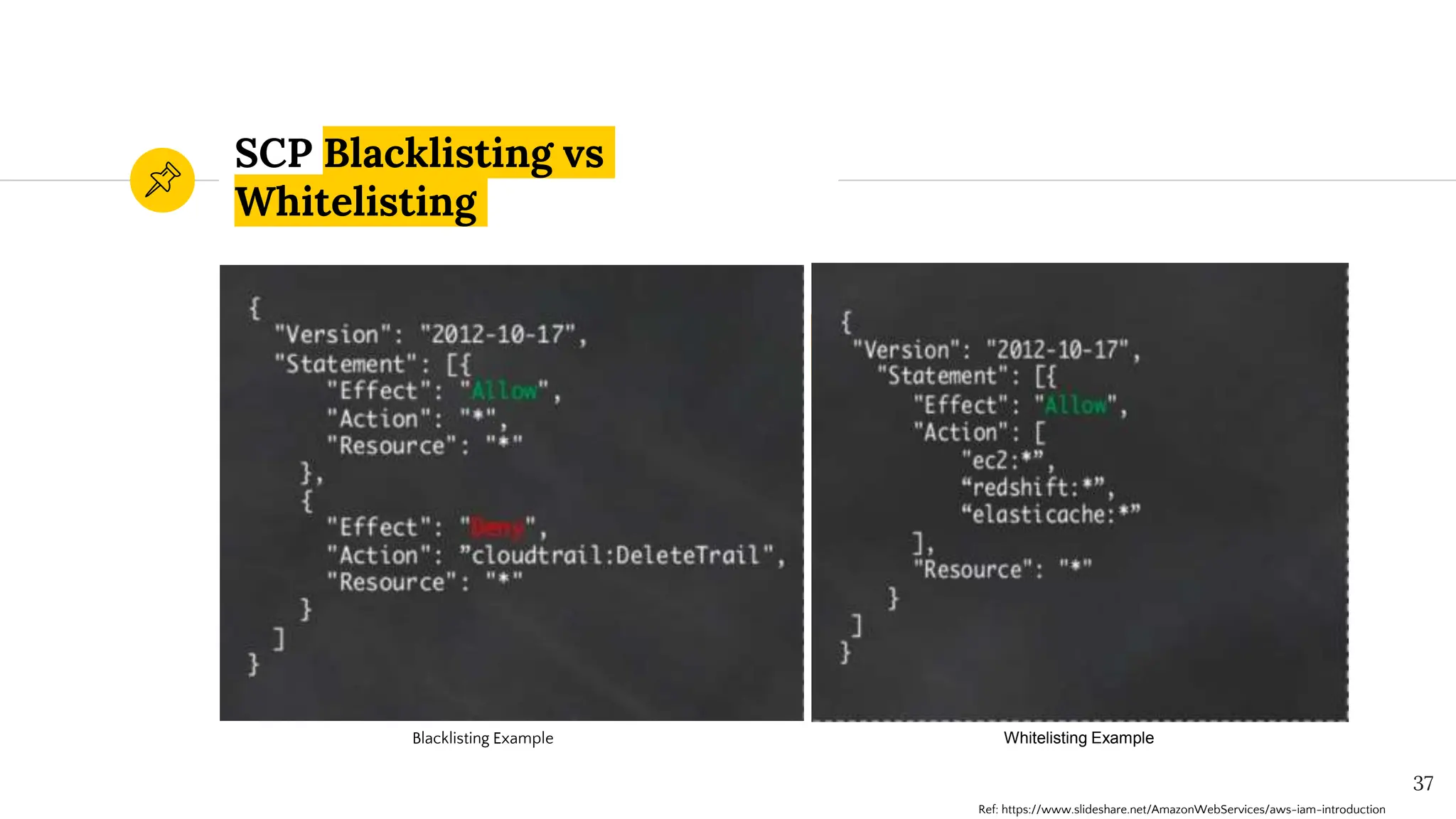
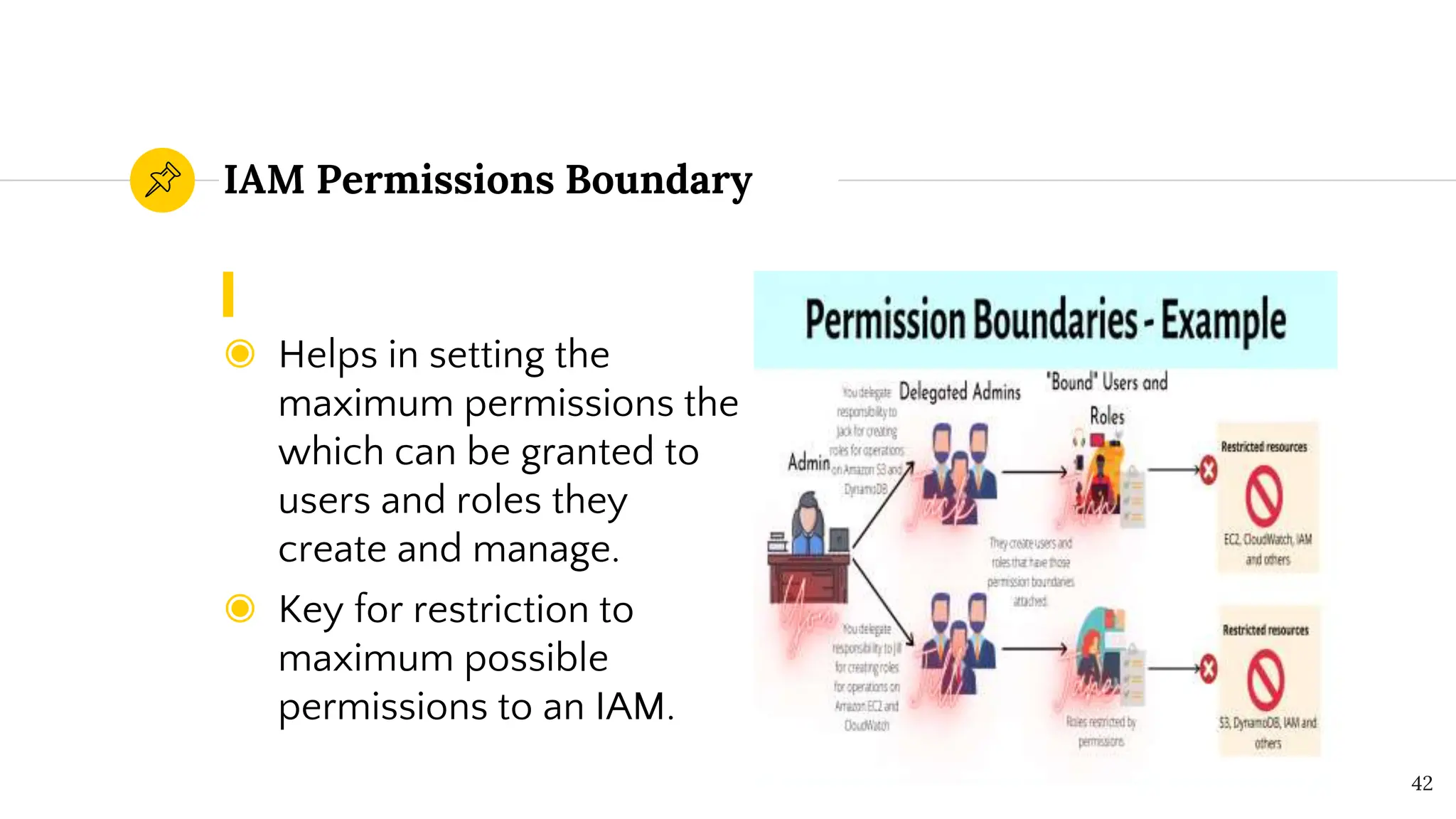
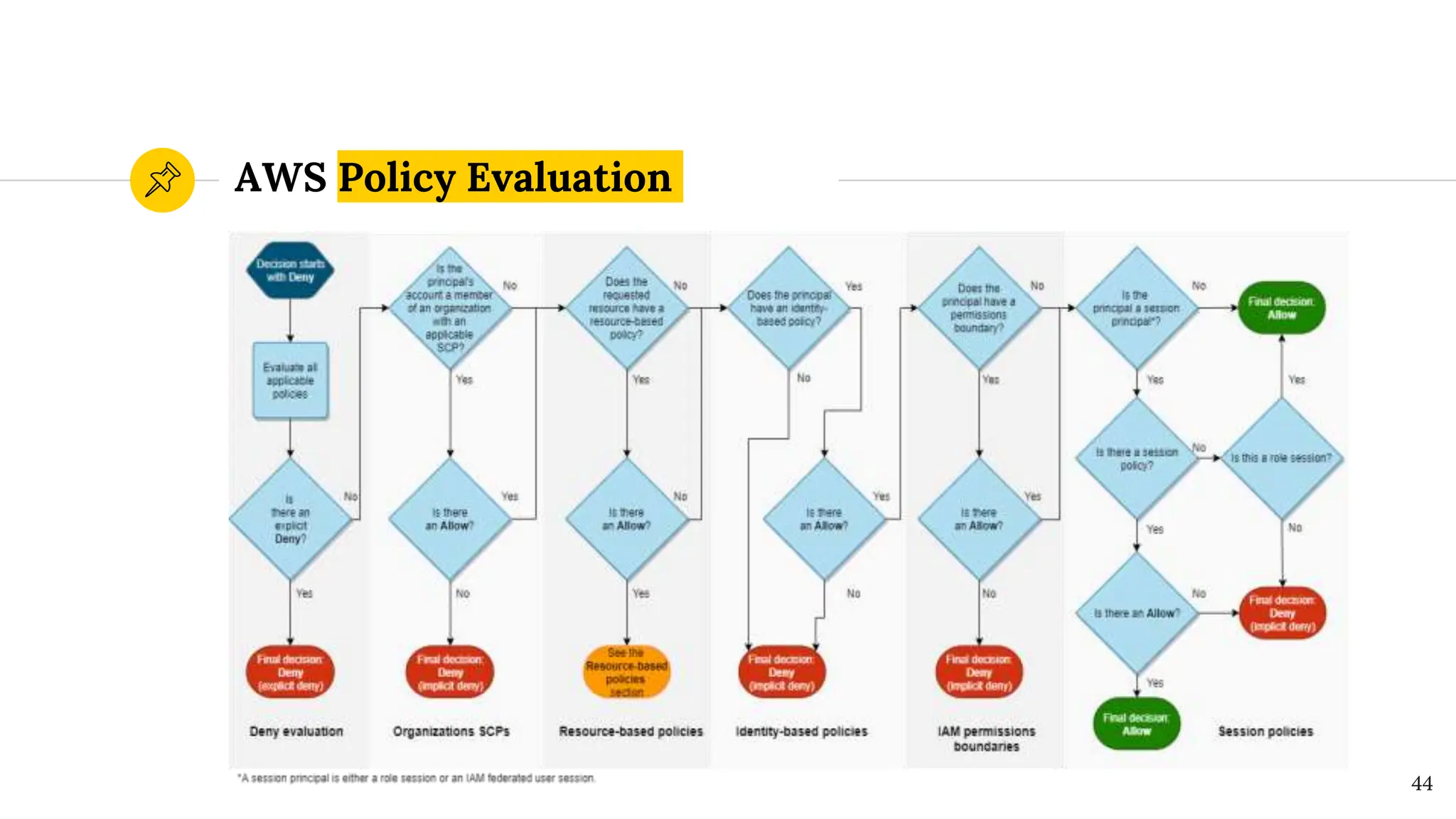
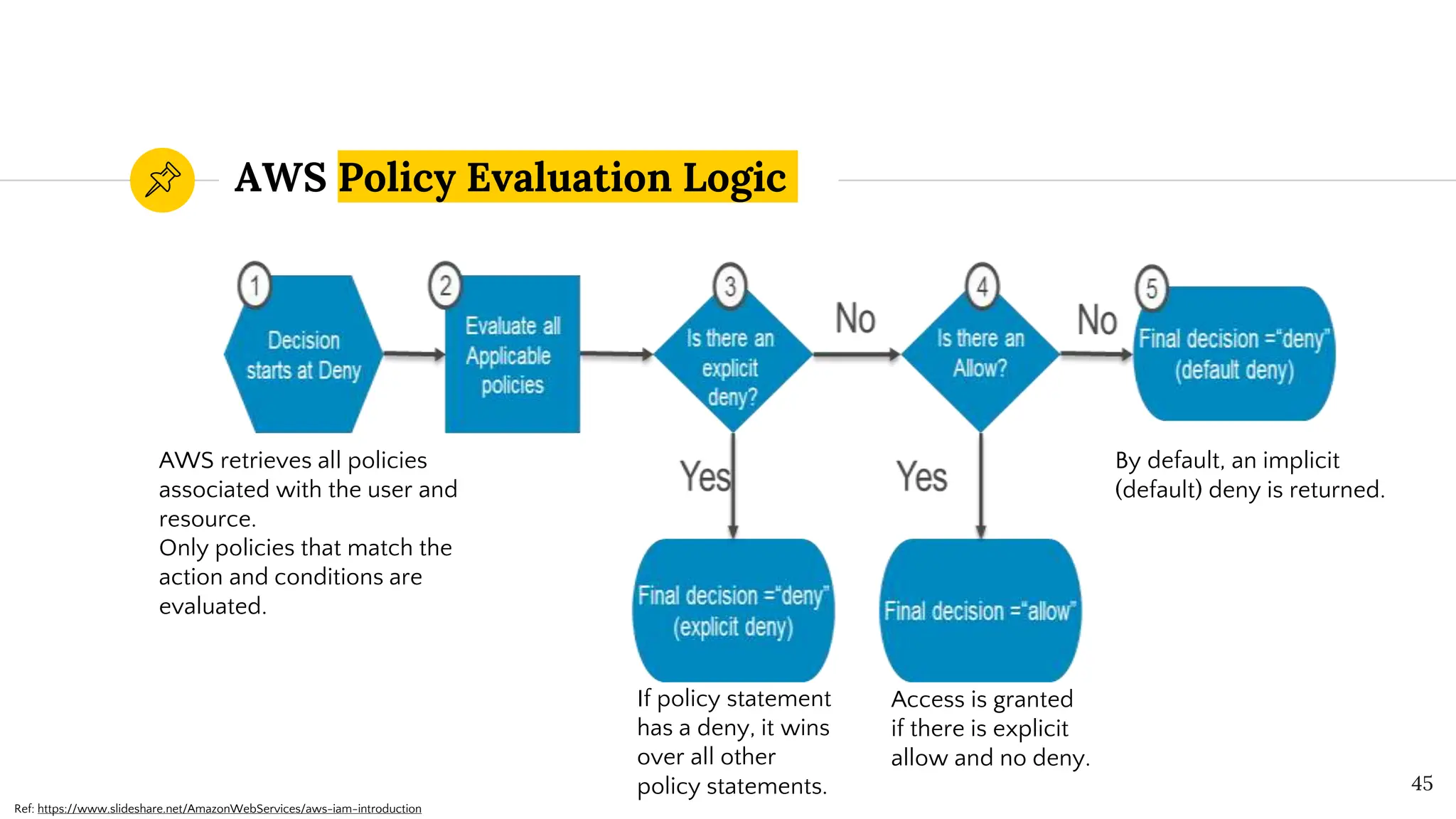
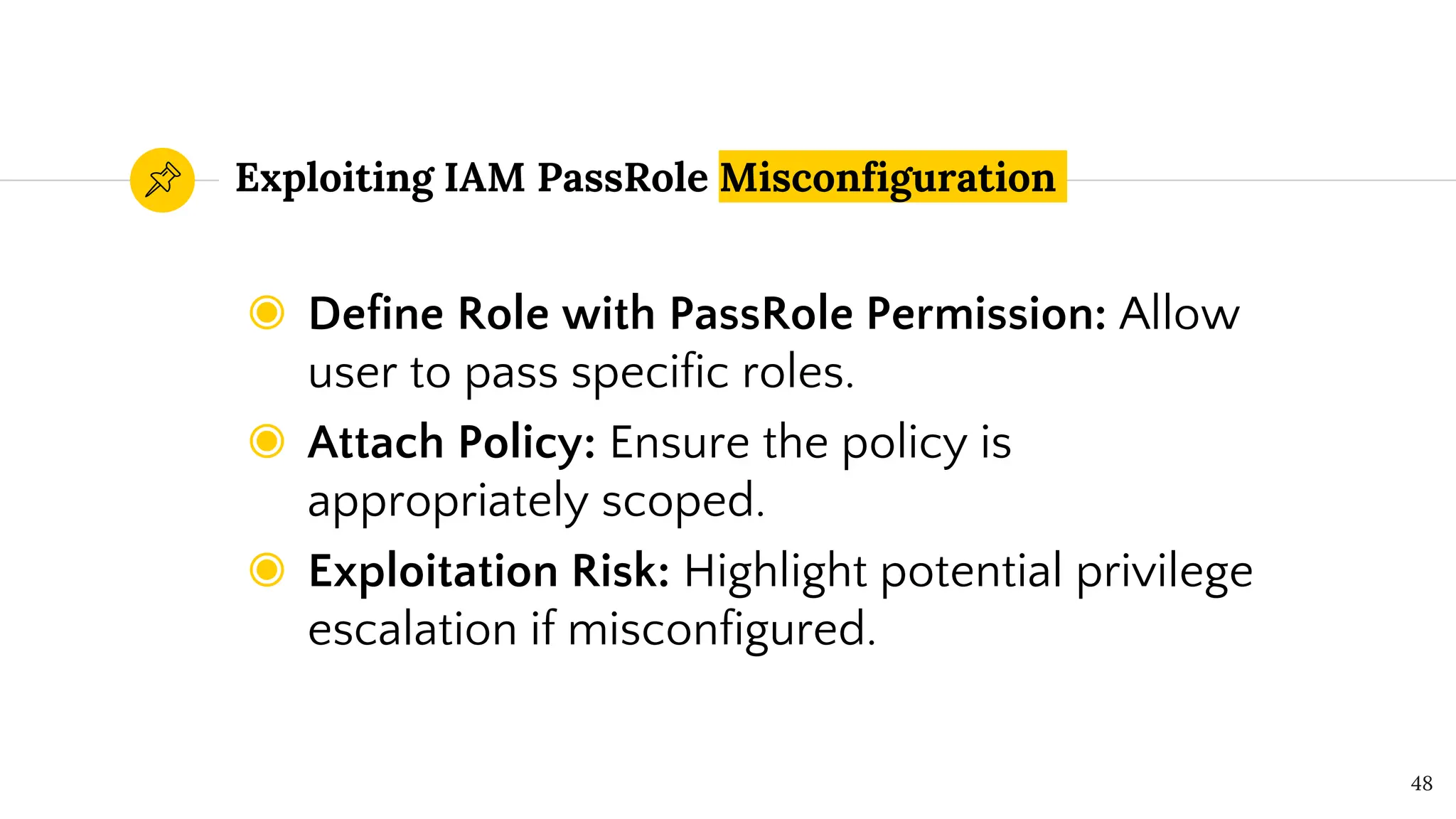
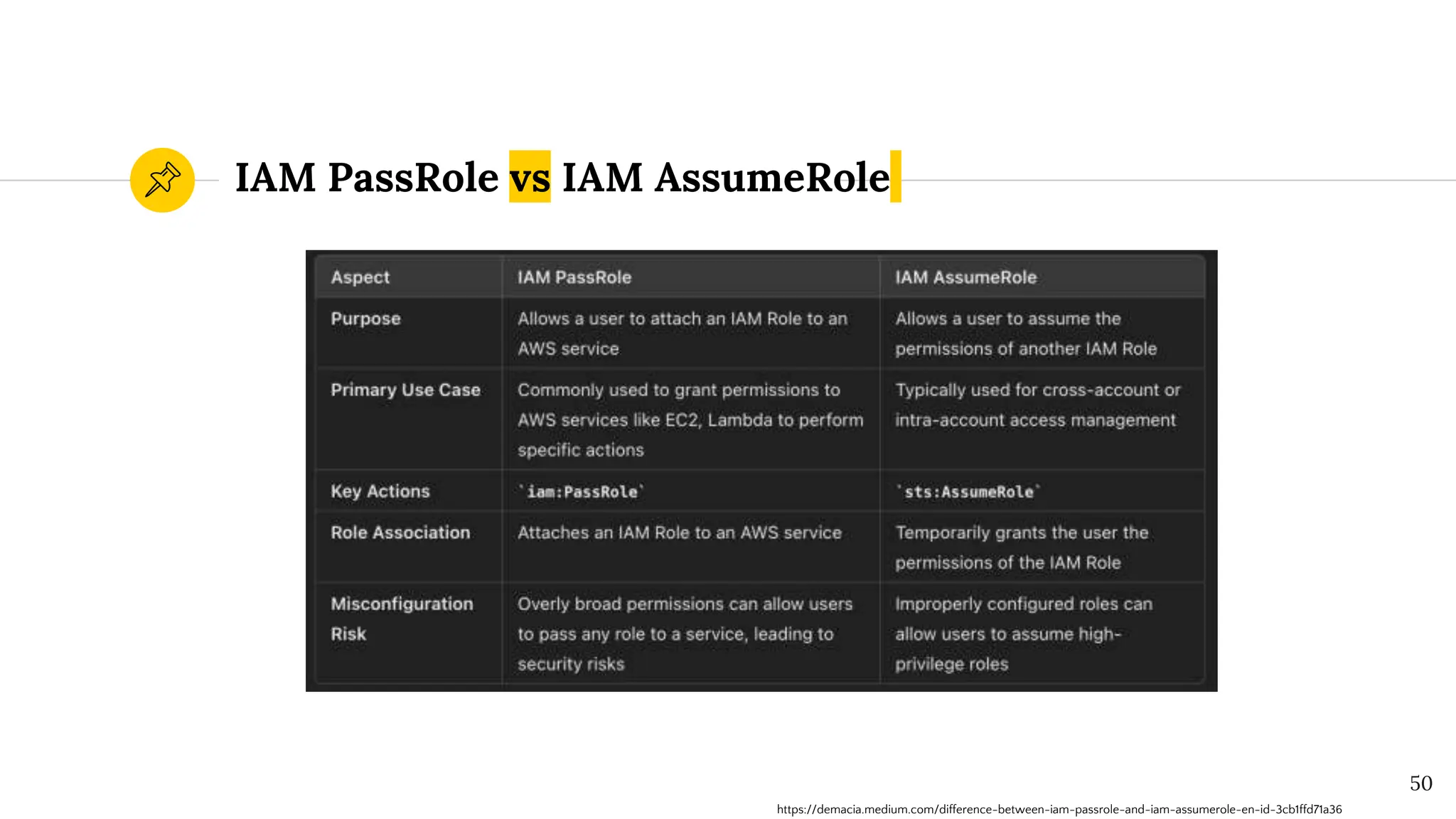
The document presents a comprehensive overview of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) focused on penetration testing by Divyanshu Shukla, a senior cloud security engineer. It explains IAM concepts, including user roles, policy types, evaluation logic, and potential attack vectors such as least privilege and misconfigurations. It emphasizes the importance of proper IAM policies to control access effectively and mitigate security risks.