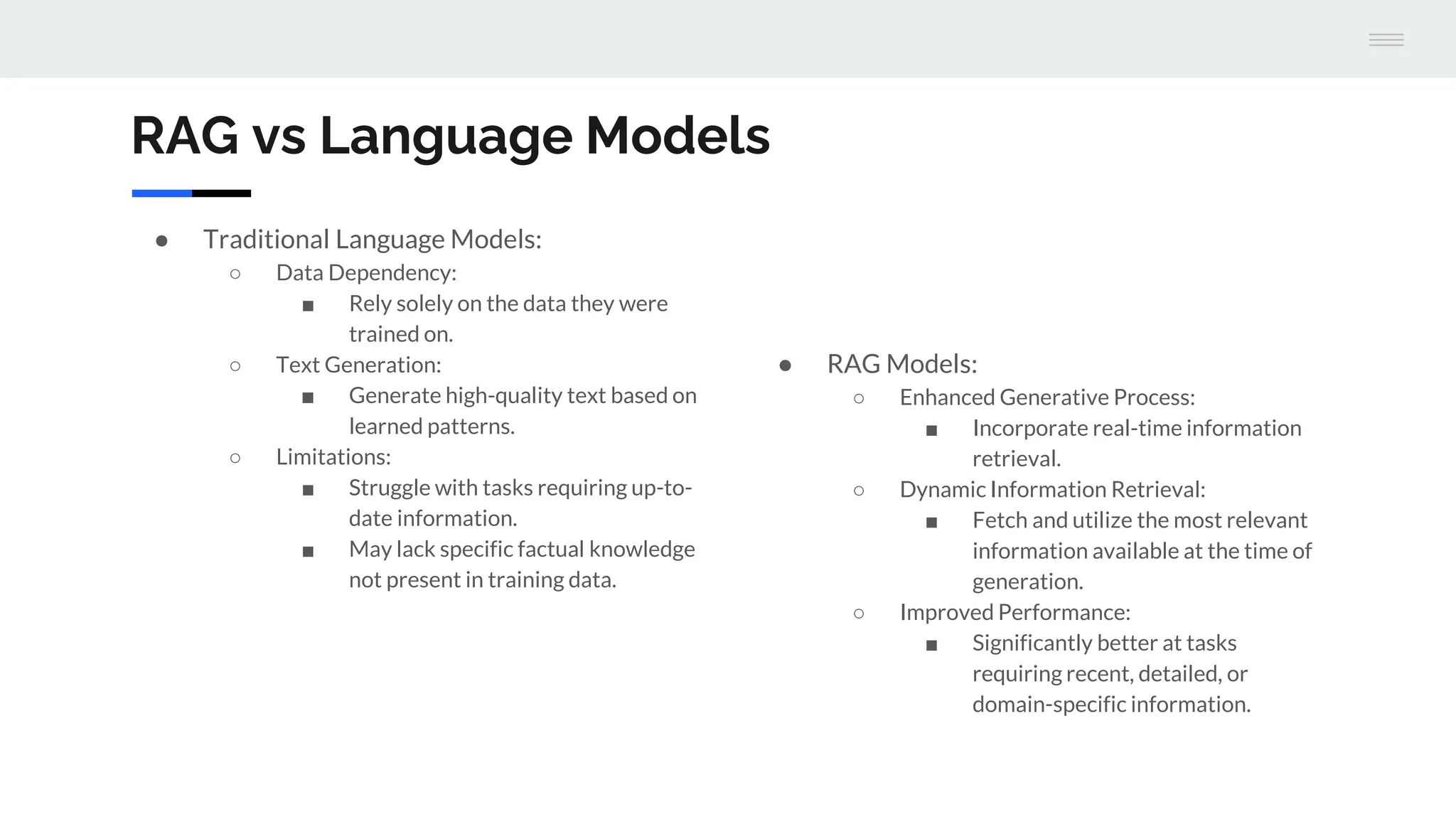
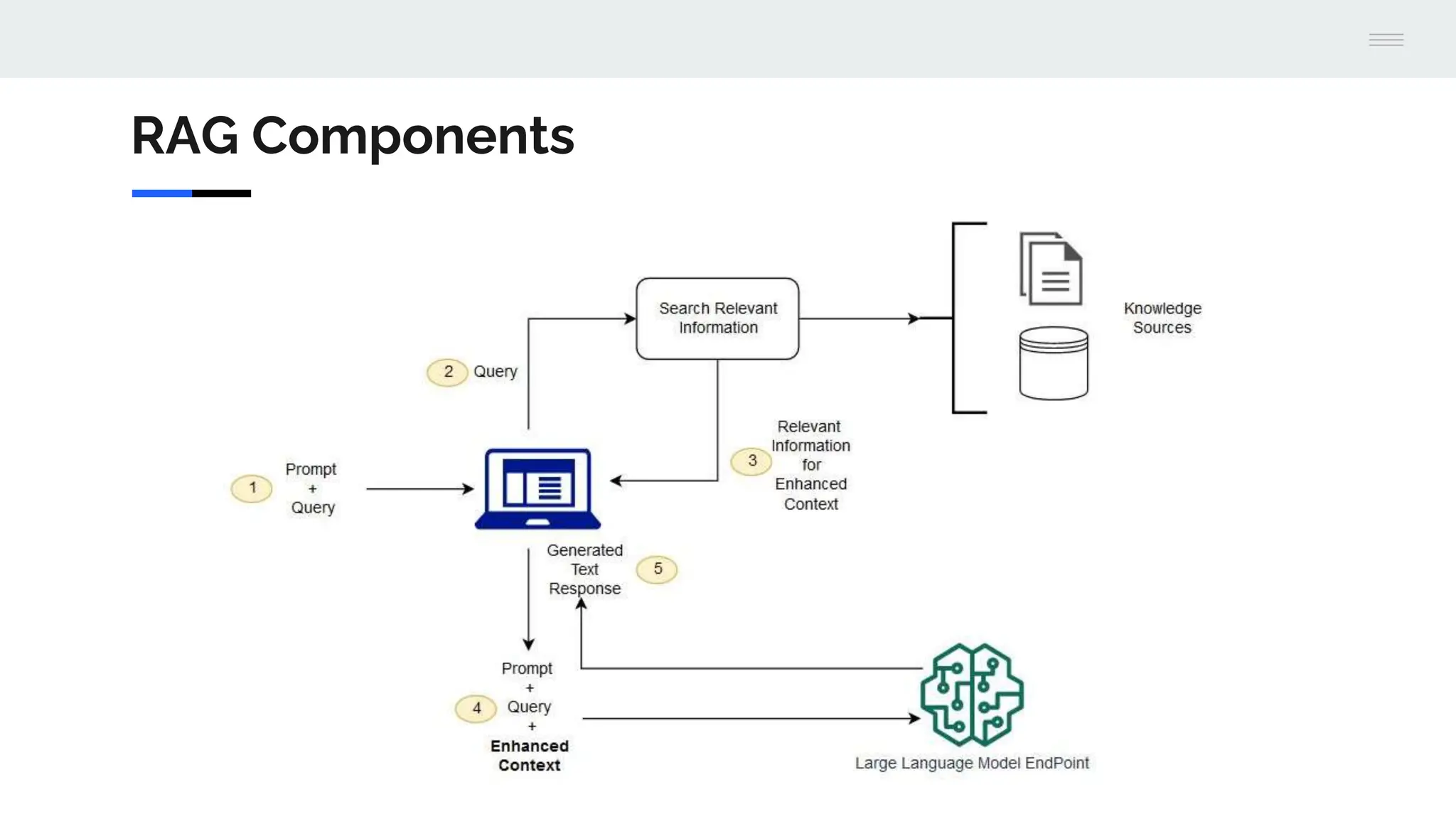
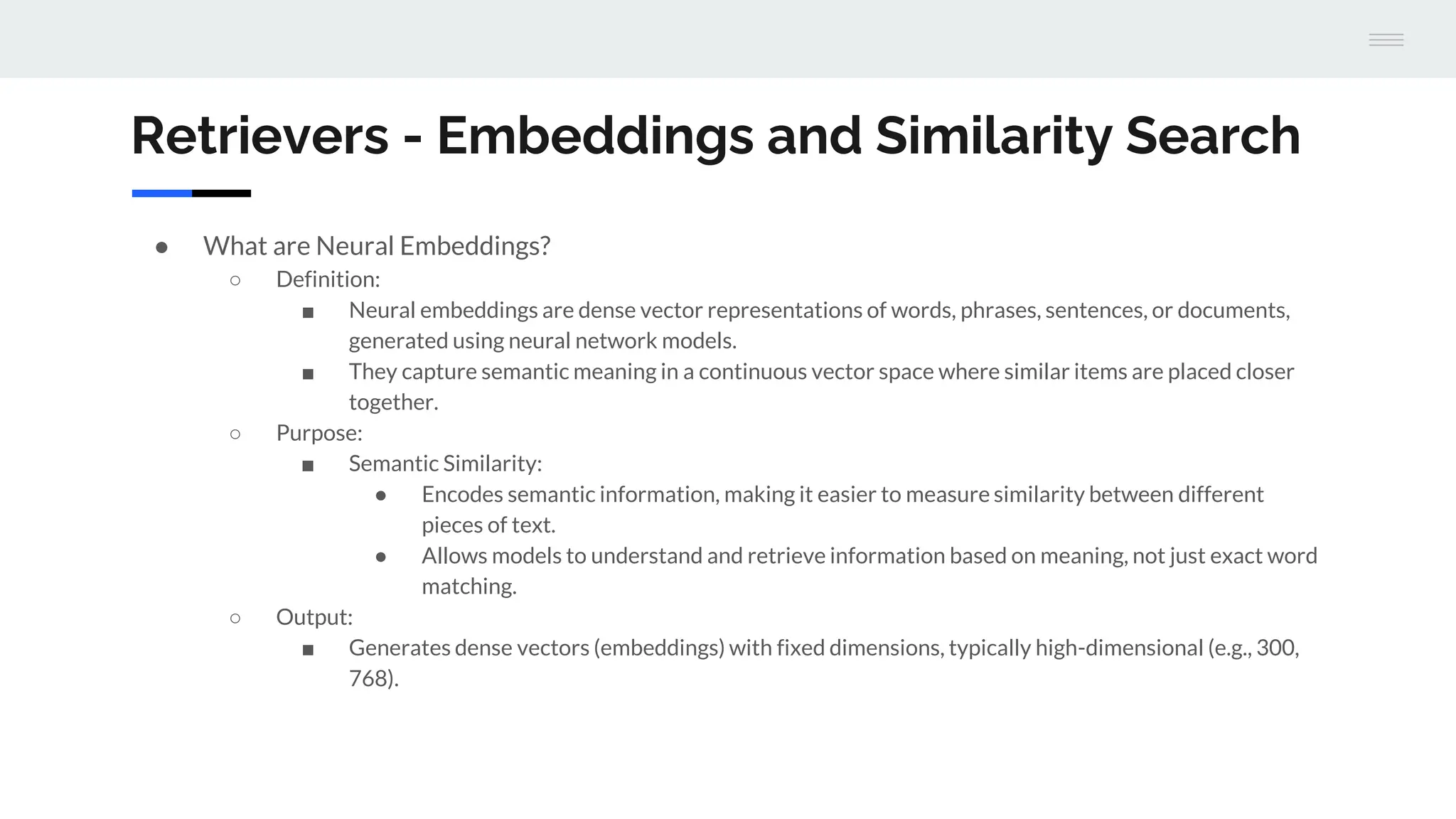
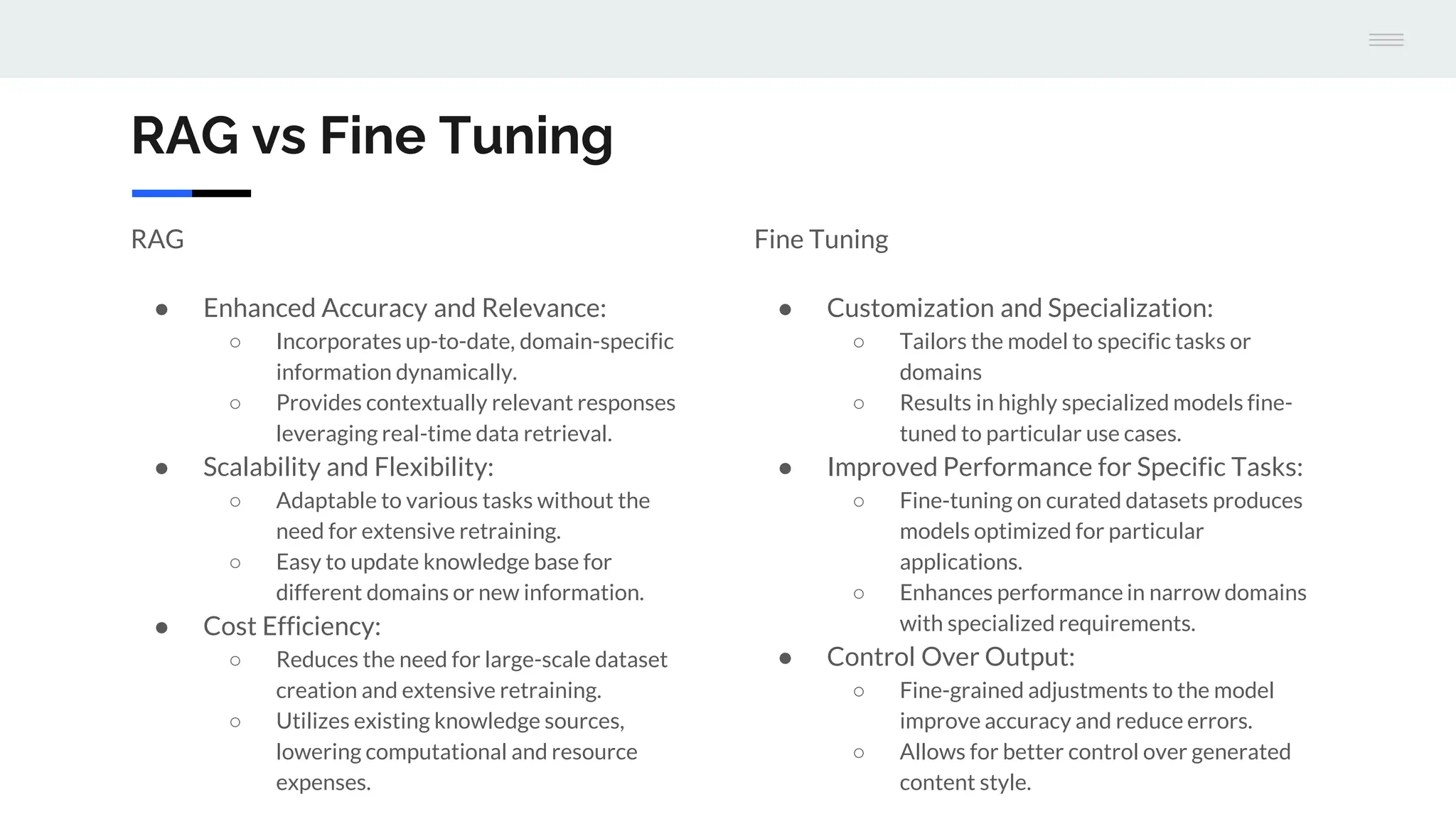
The document discusses a version 1.0 fine-tuning of the Llama 2 model using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), emphasizing its hybrid approach that combines information retrieval with text generation to enhance accuracy and relevance. It outlines the mechanisms of how RAG works, the benefits it offers over traditional language models, and the importance of external knowledge sources for generating informed responses. The evaluation framework for performance assessment is aligned with established benchmarks for both traditional language models and RAG models.