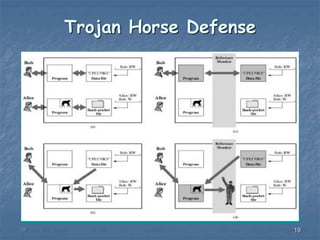
This document discusses trusted systems and the concept of a Trojan horse. It defines trusted systems as systems used to enhance security defenses against intruders and malware. It describes multilevel security as allowing multiple data classification levels, with mandatory access control enforcing that information does not flow to unauthorized users. The document also discusses how Trojan horses can provide unauthorized remote access if installed on a user's computer.