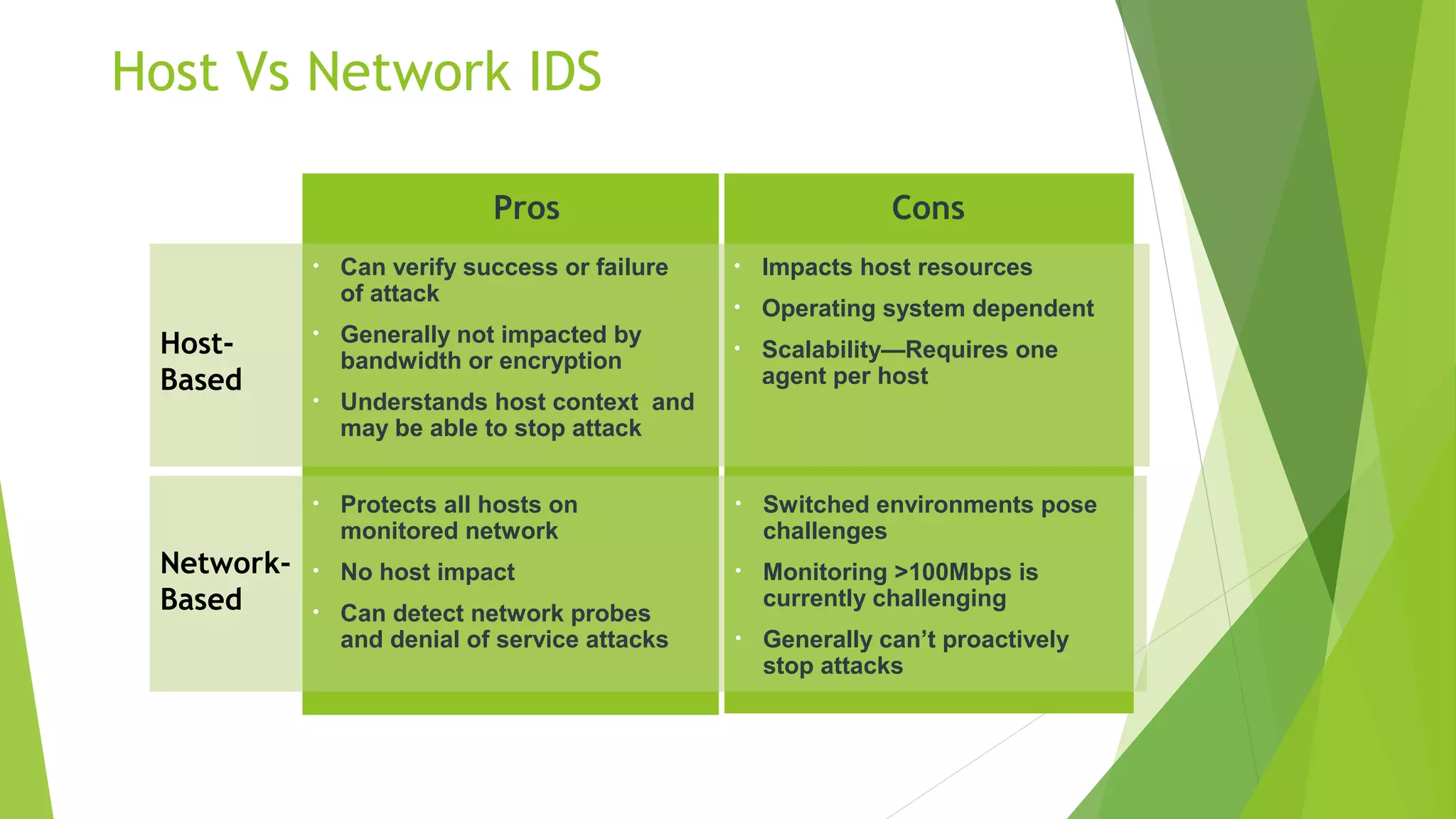
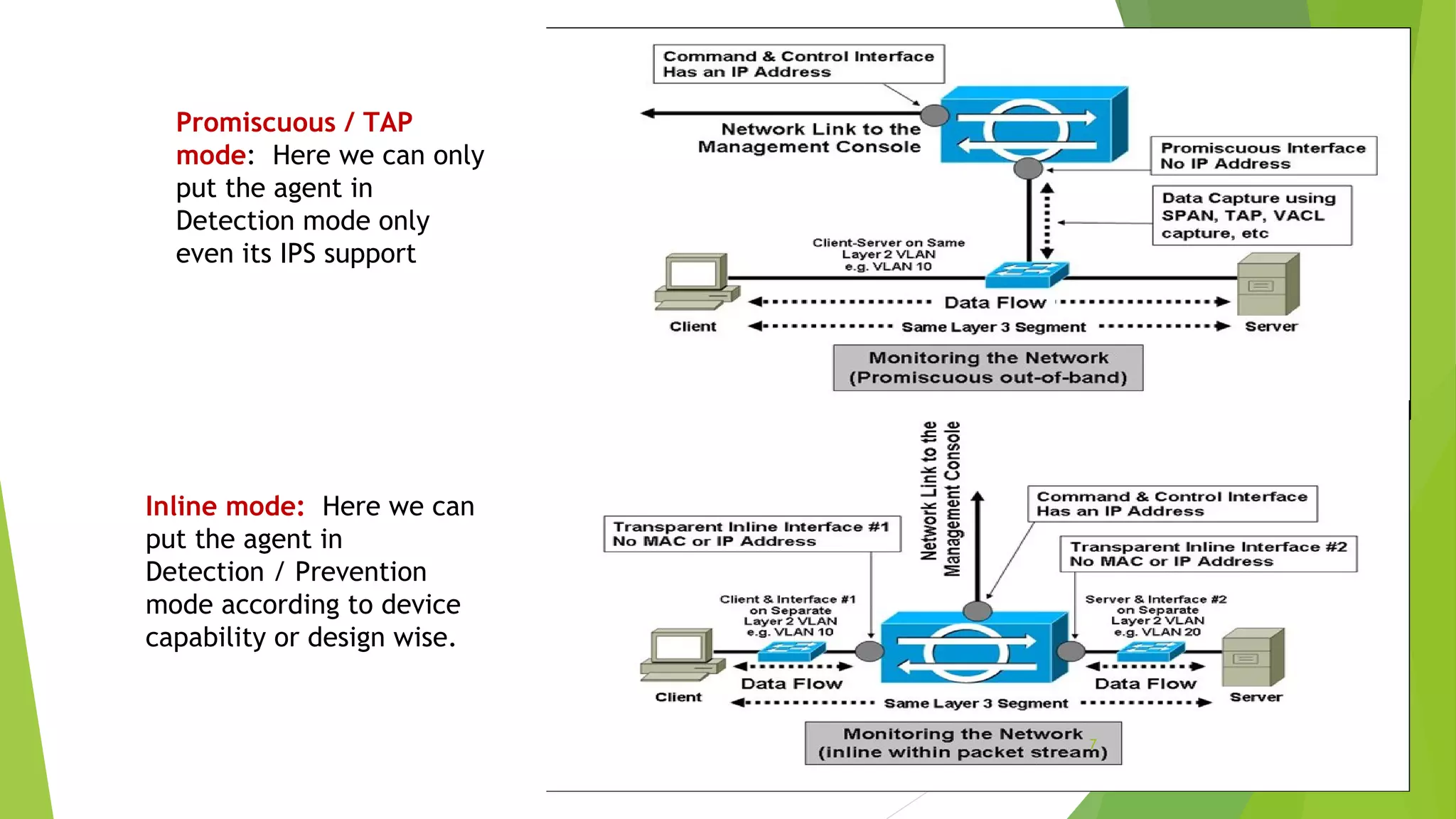
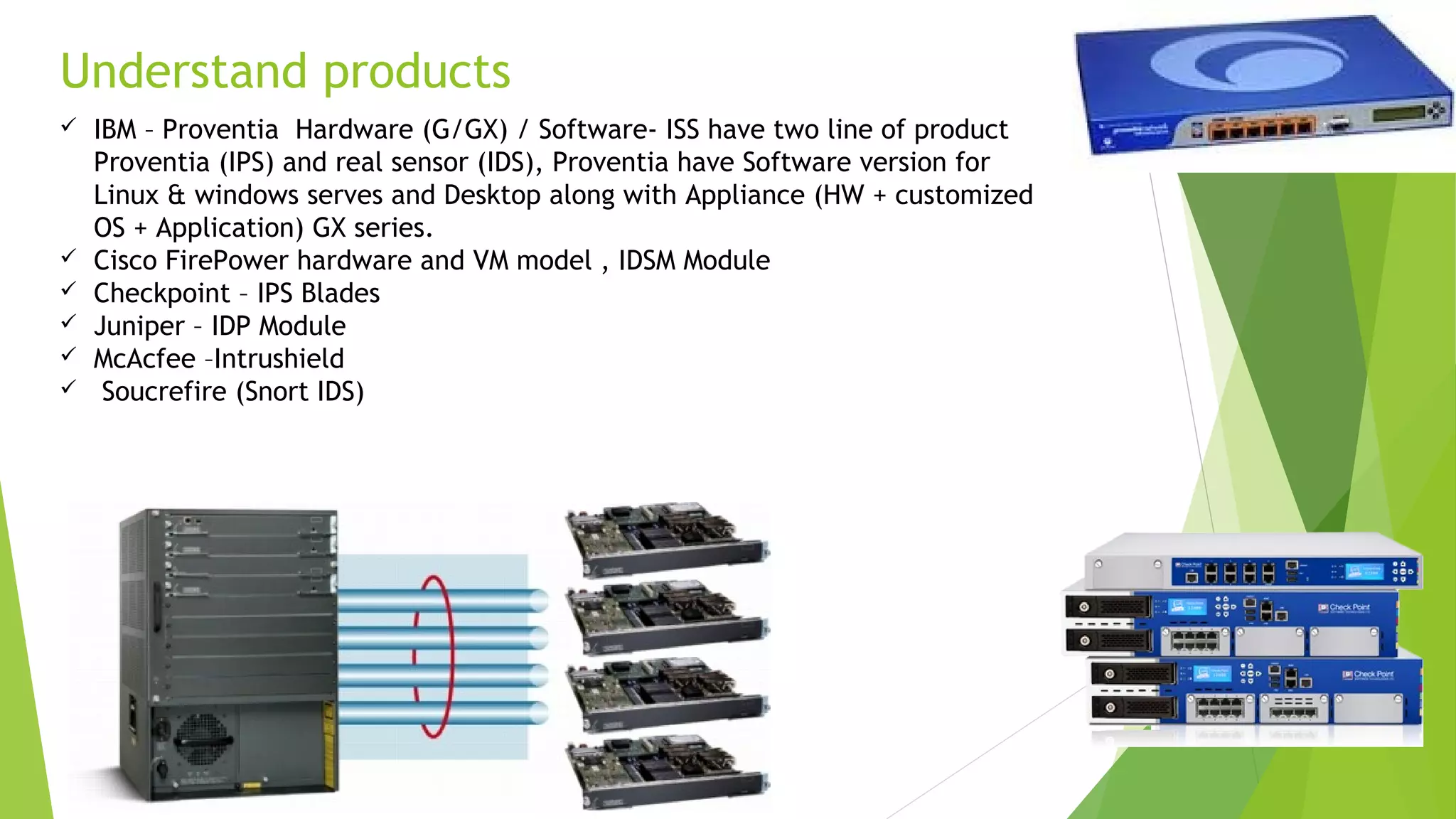
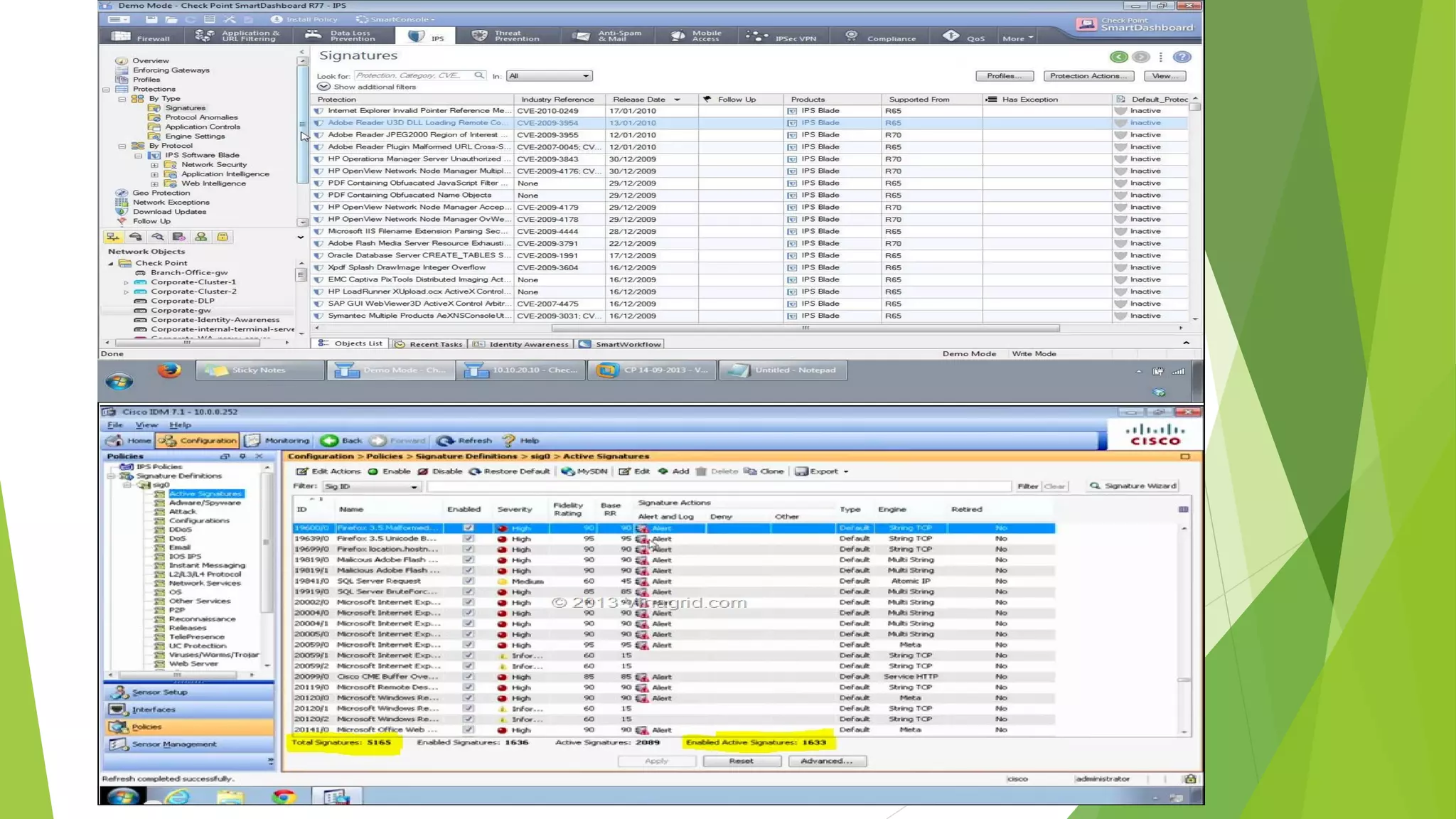
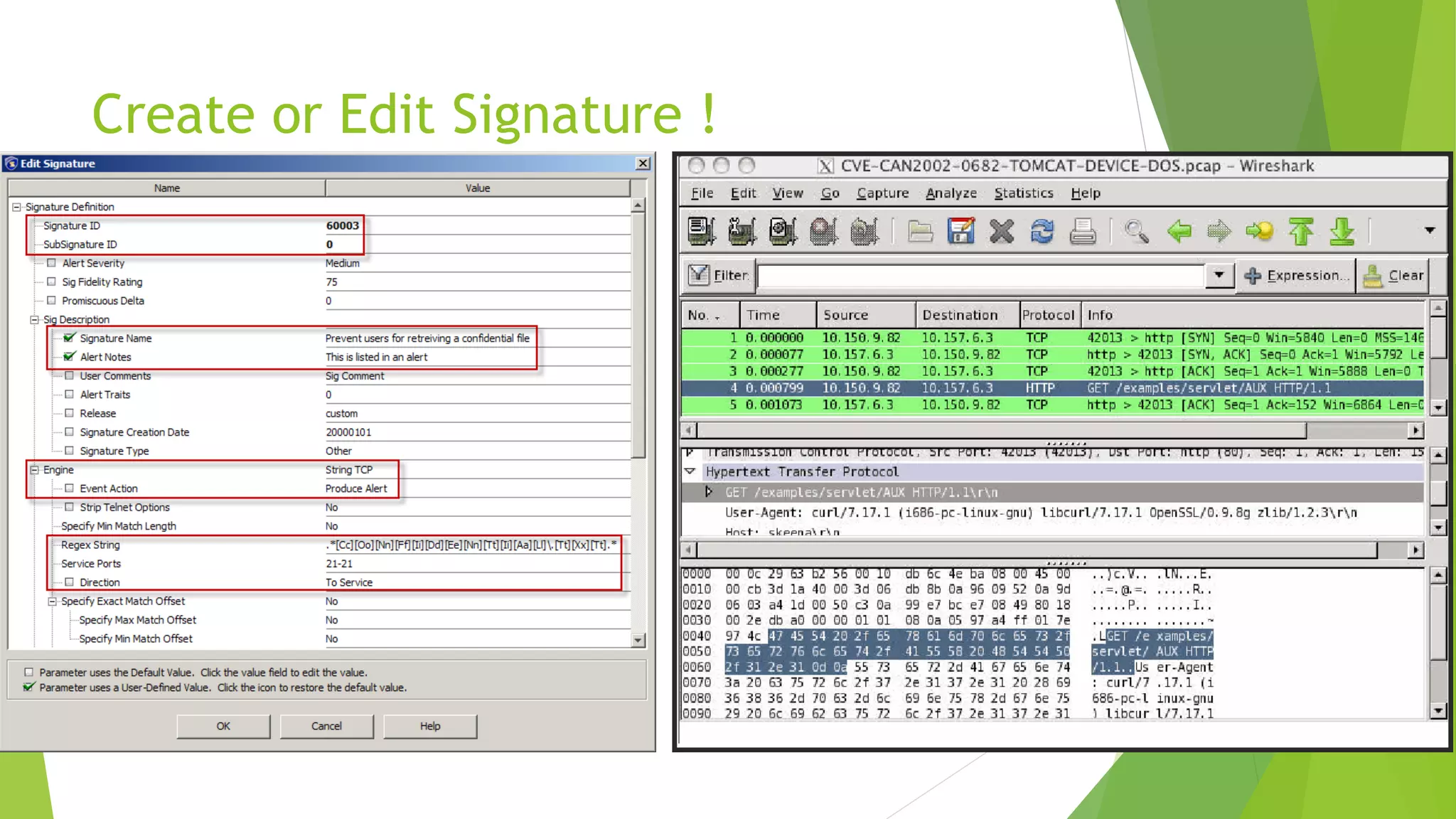
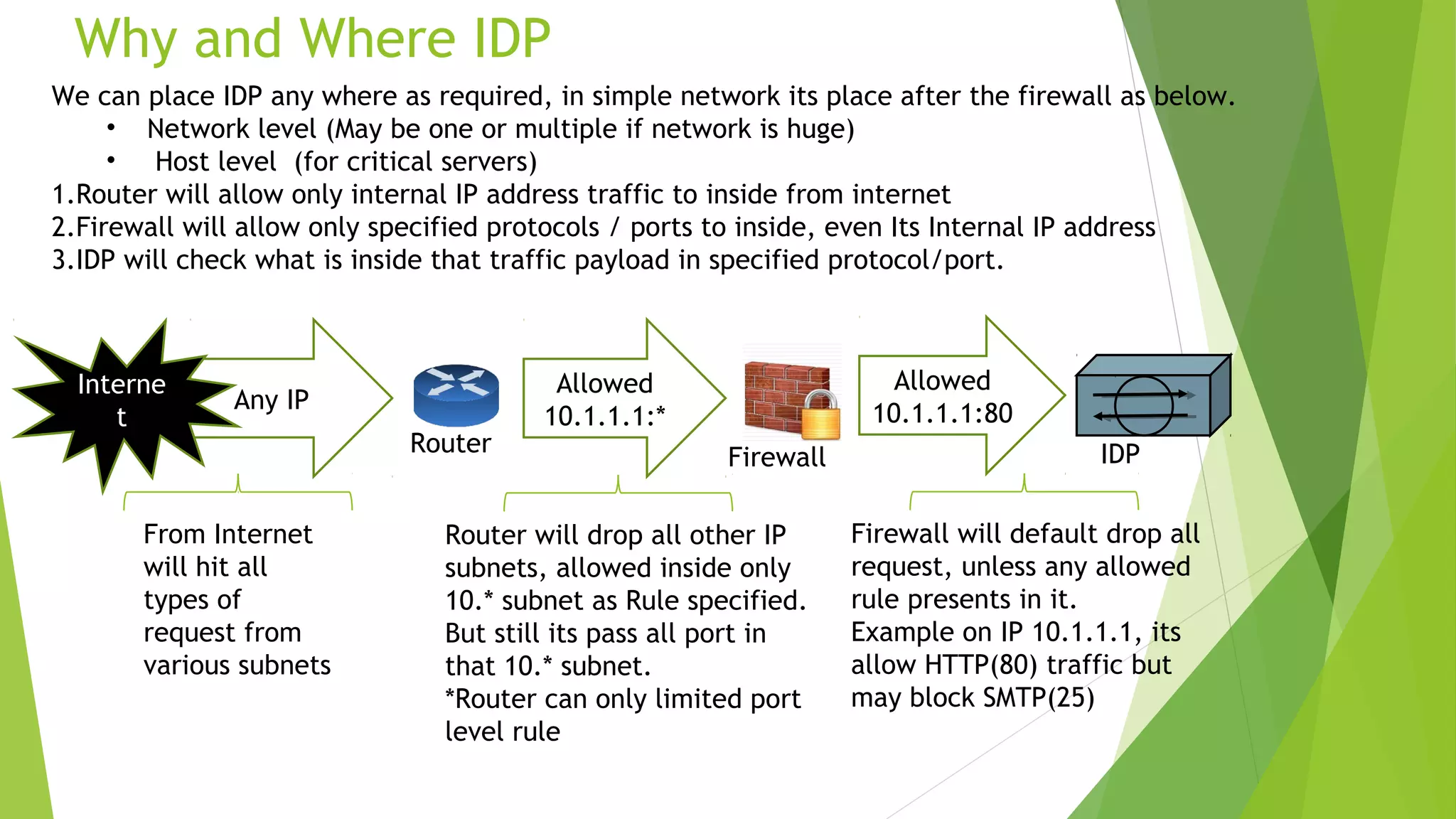
This document discusses intrusion detection and prevention systems. It defines intrusion detection as detecting inappropriate, incorrect, or anomalous activity. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) can be used to determine if a network or server has experienced an unauthorized intrusion. IDS and IPS systems work by using network sensors to detect intrusions or host agents to detect intrusions on individual systems. The document discusses different IDS and IPS products and how to implement them, including in network or host modes. It also covers signature tuning and different deployment models.