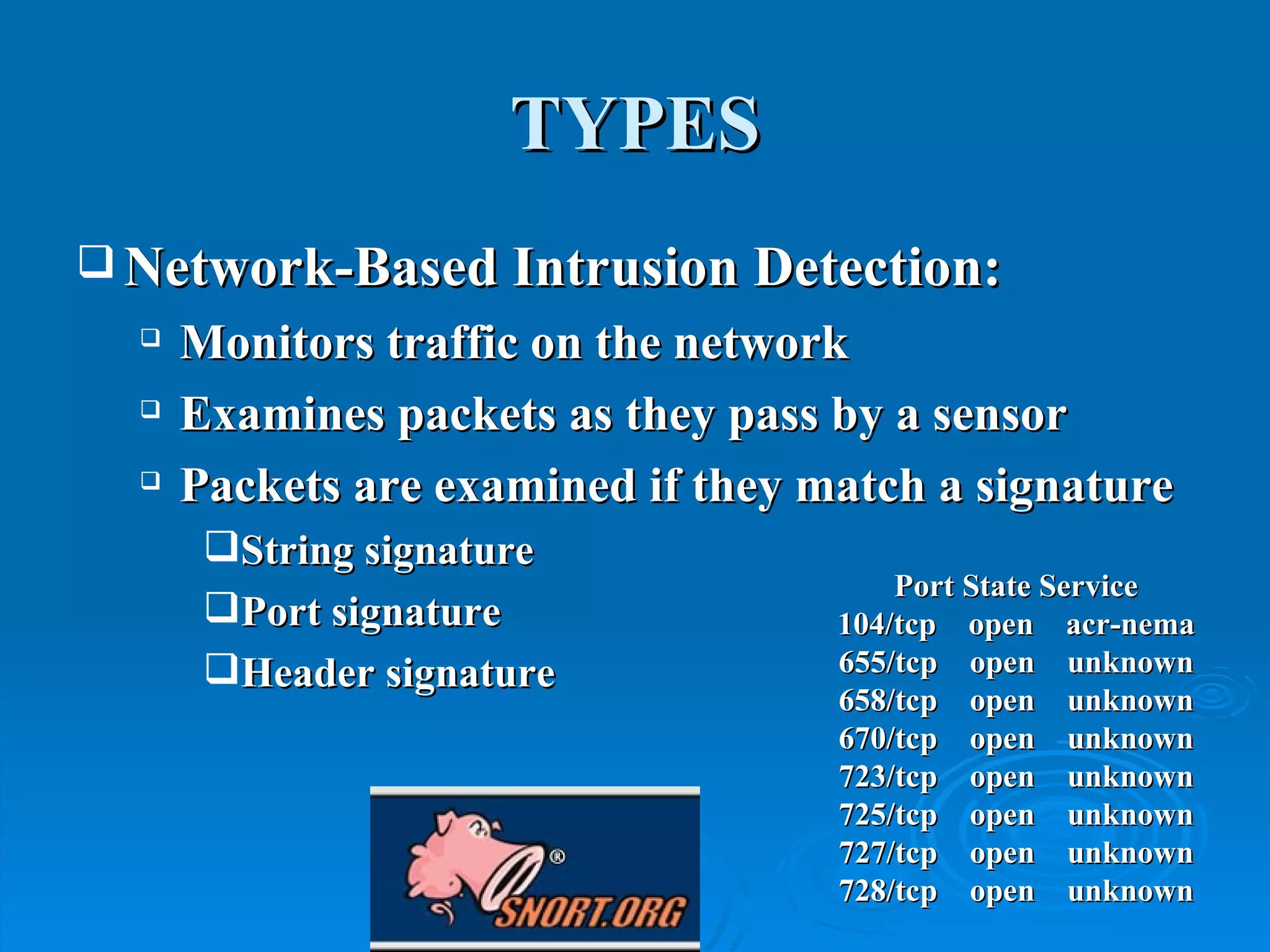
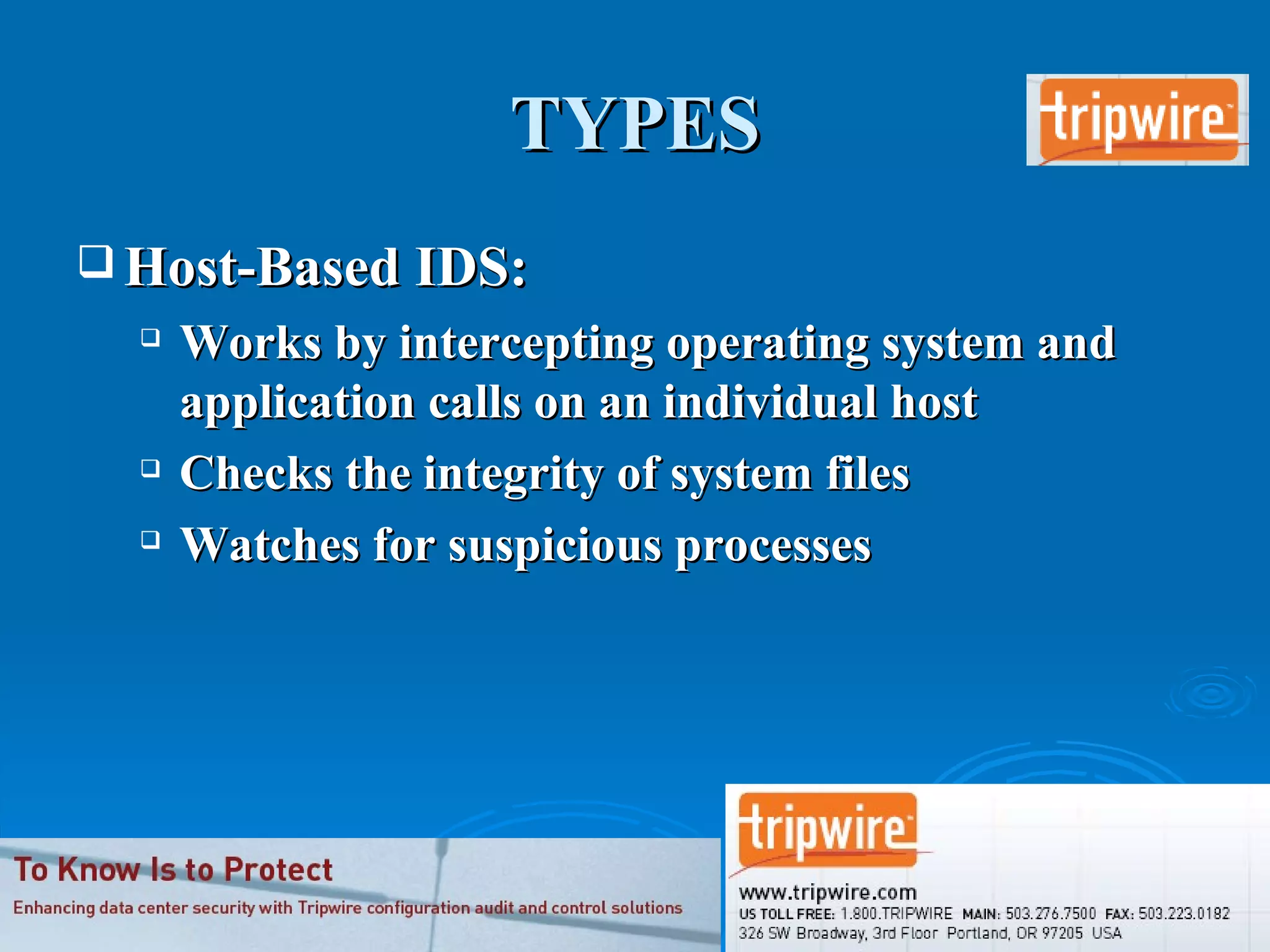
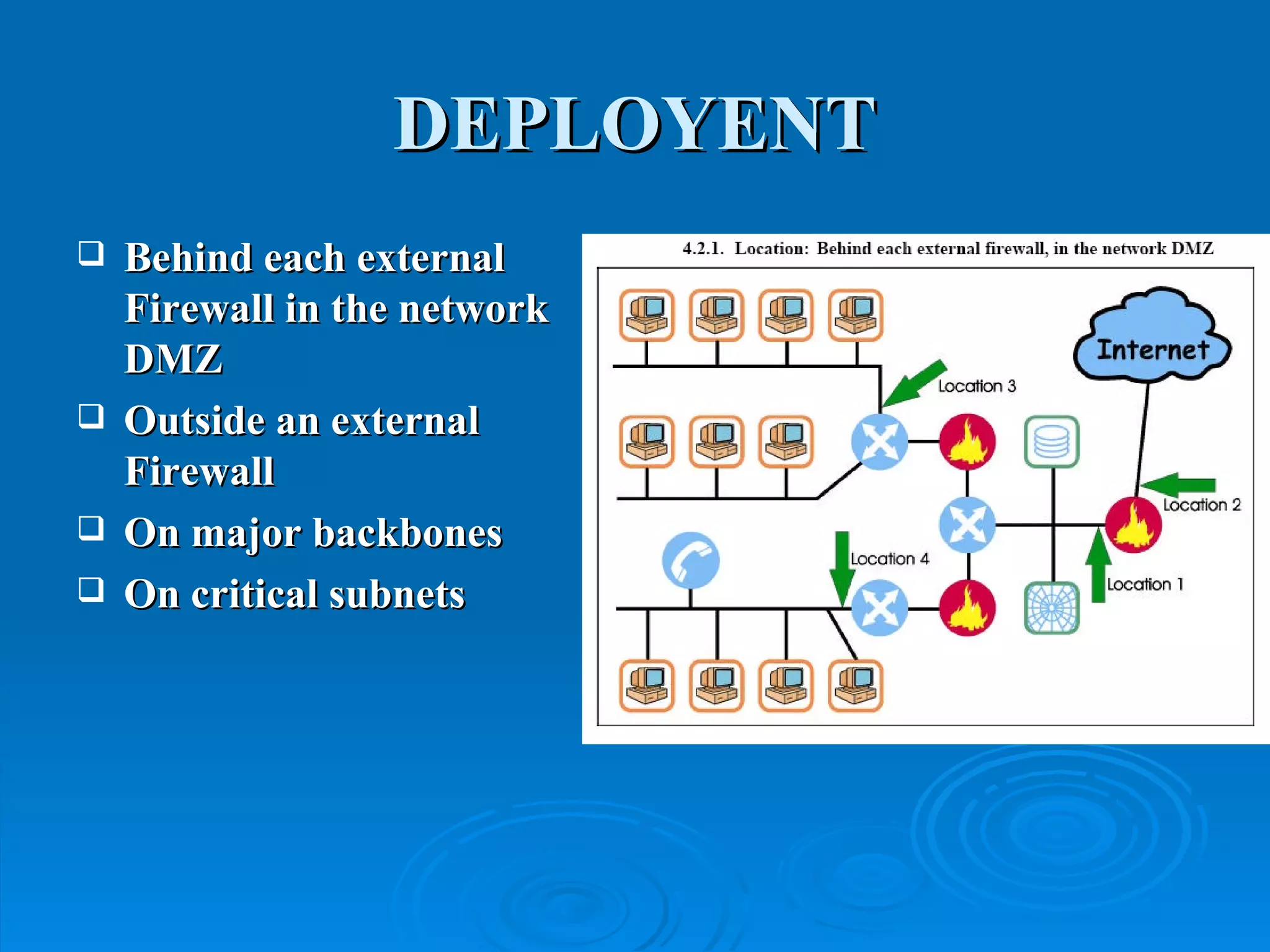
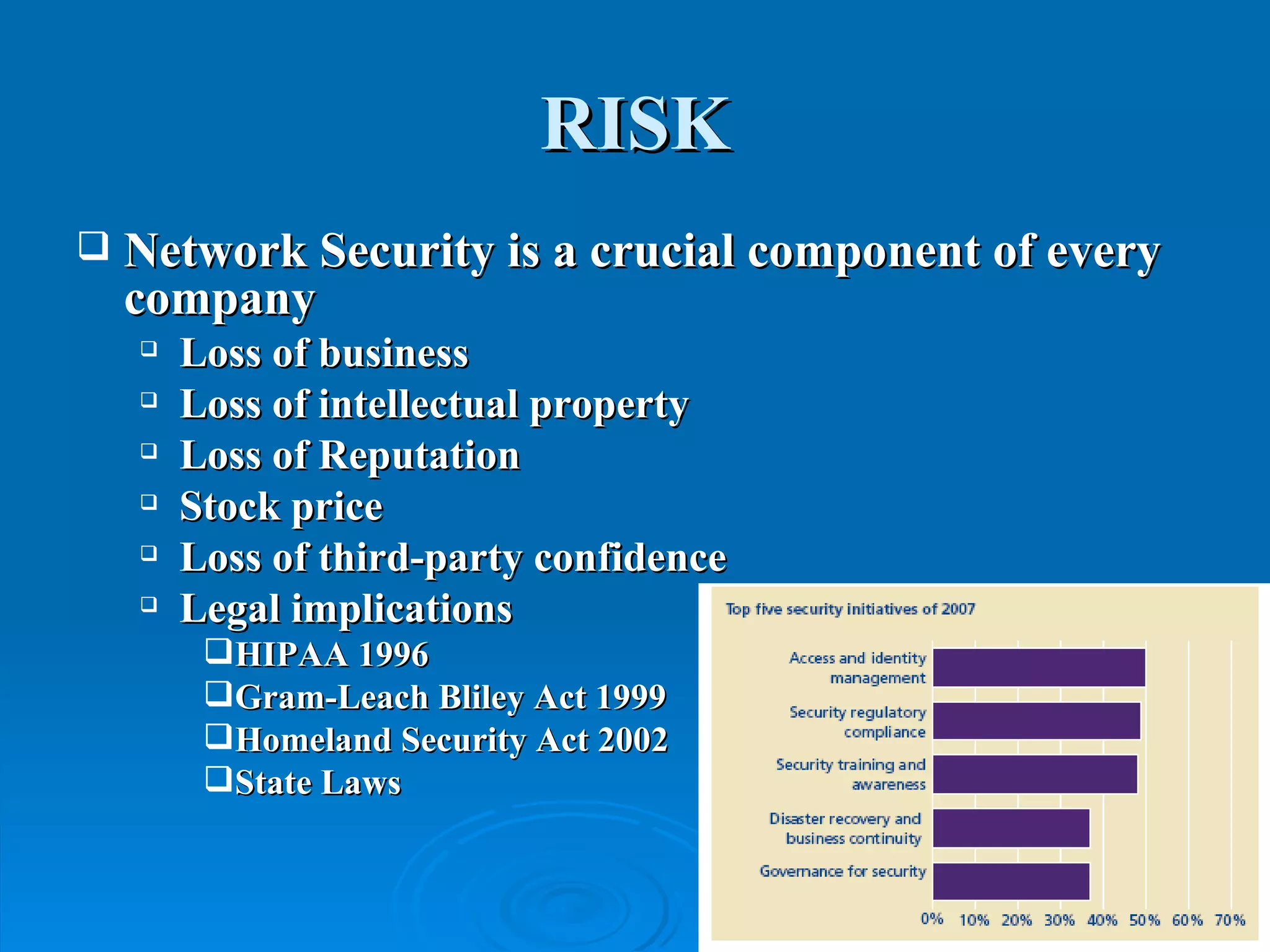
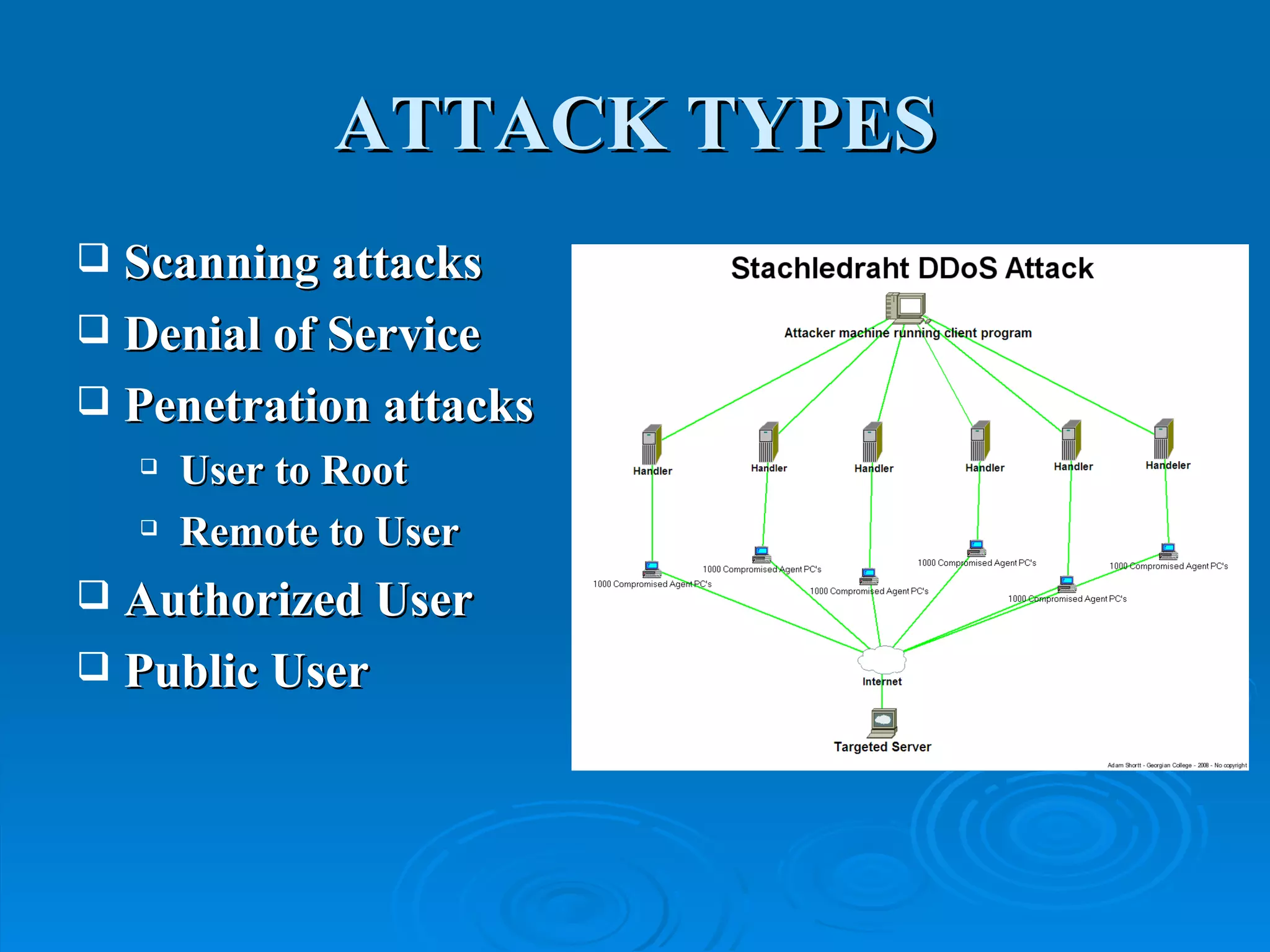
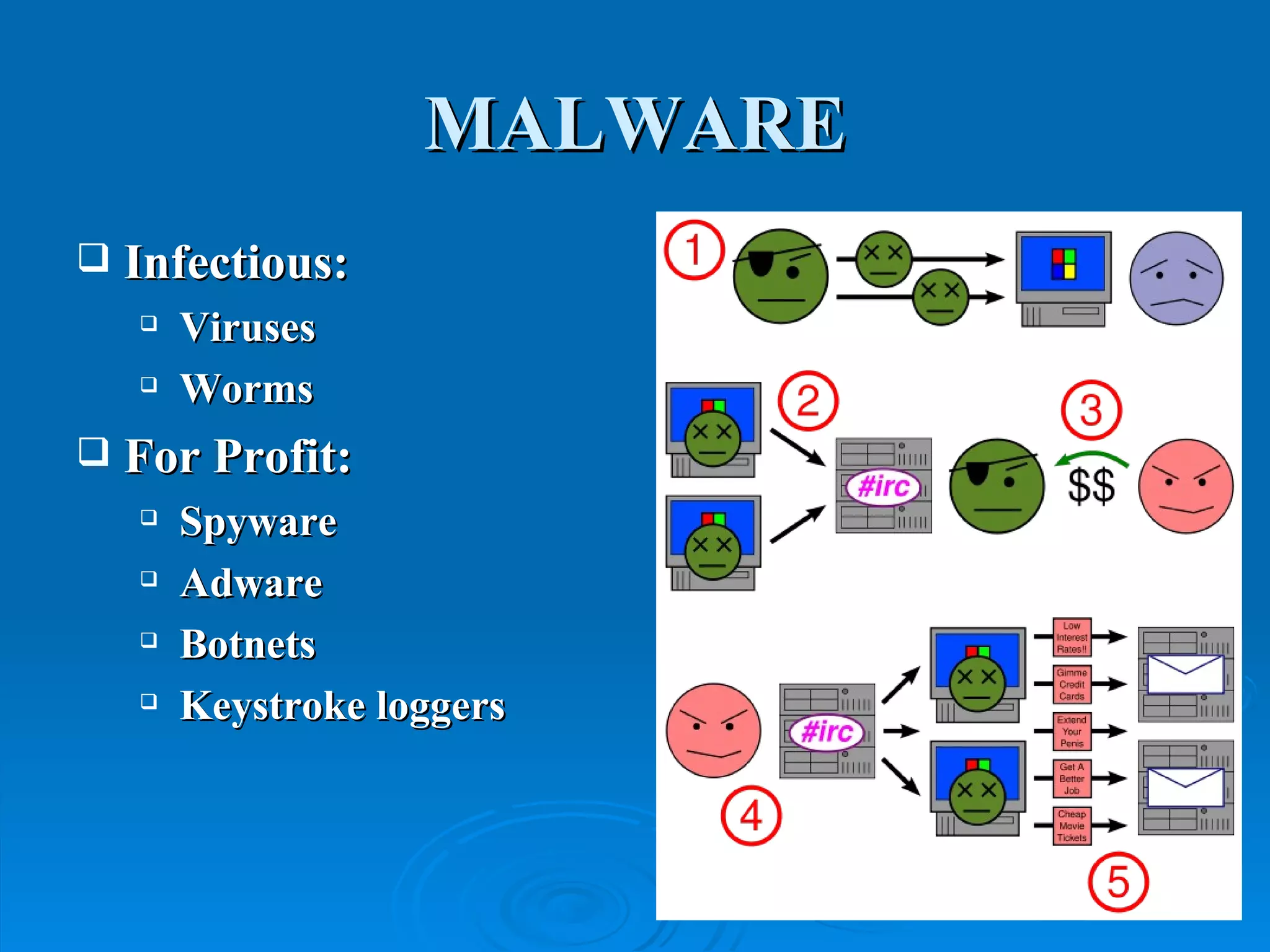
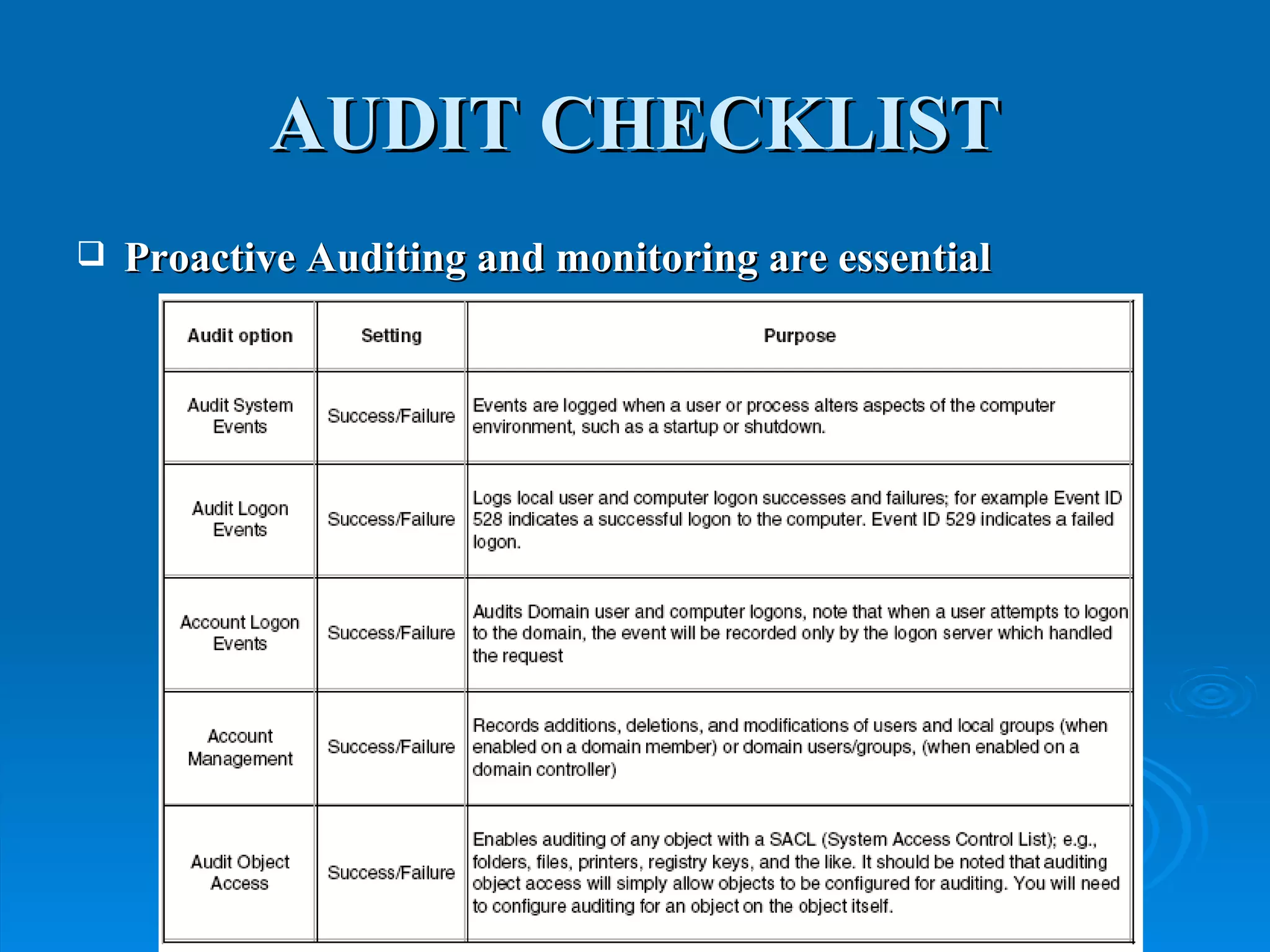
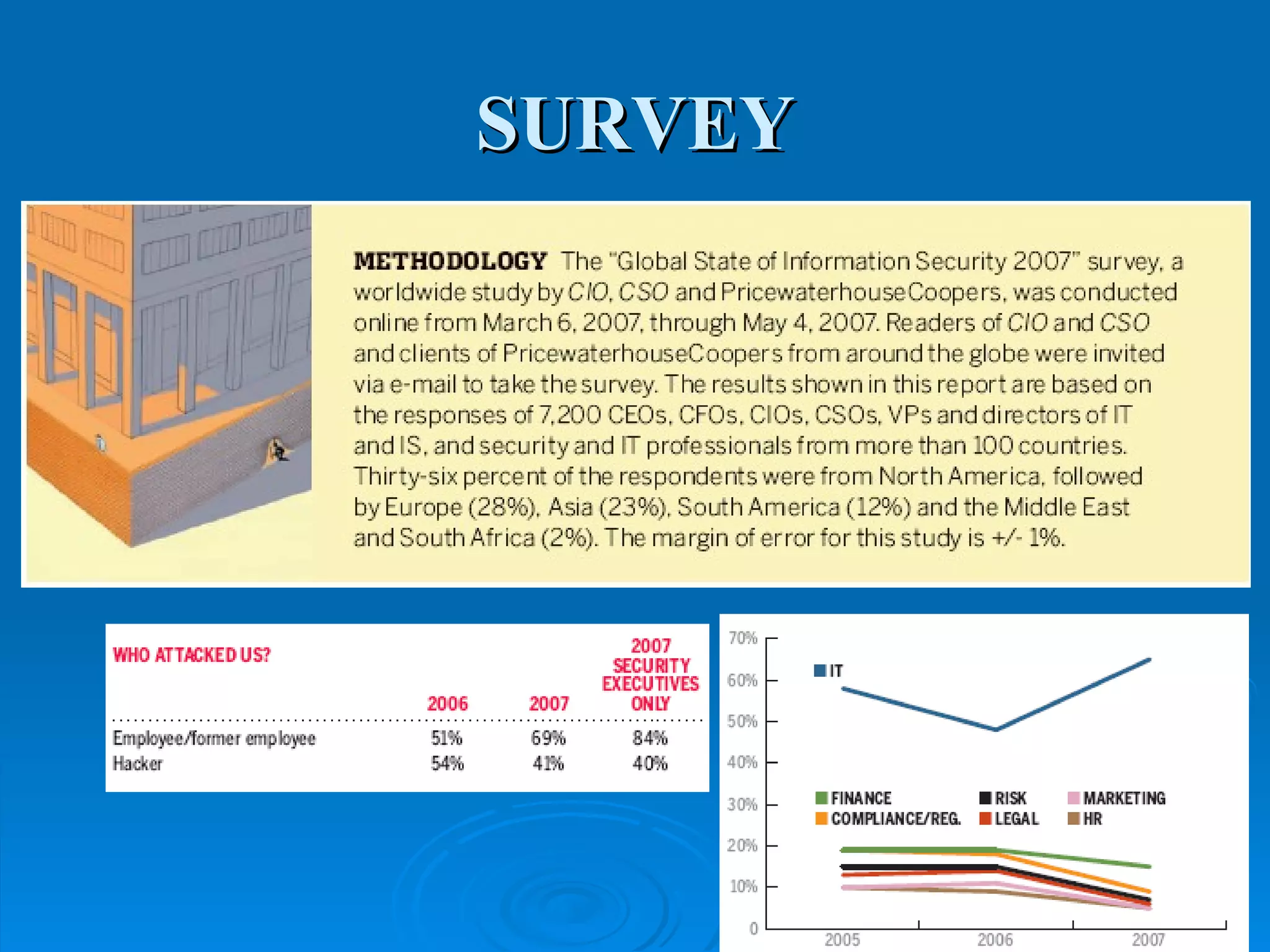
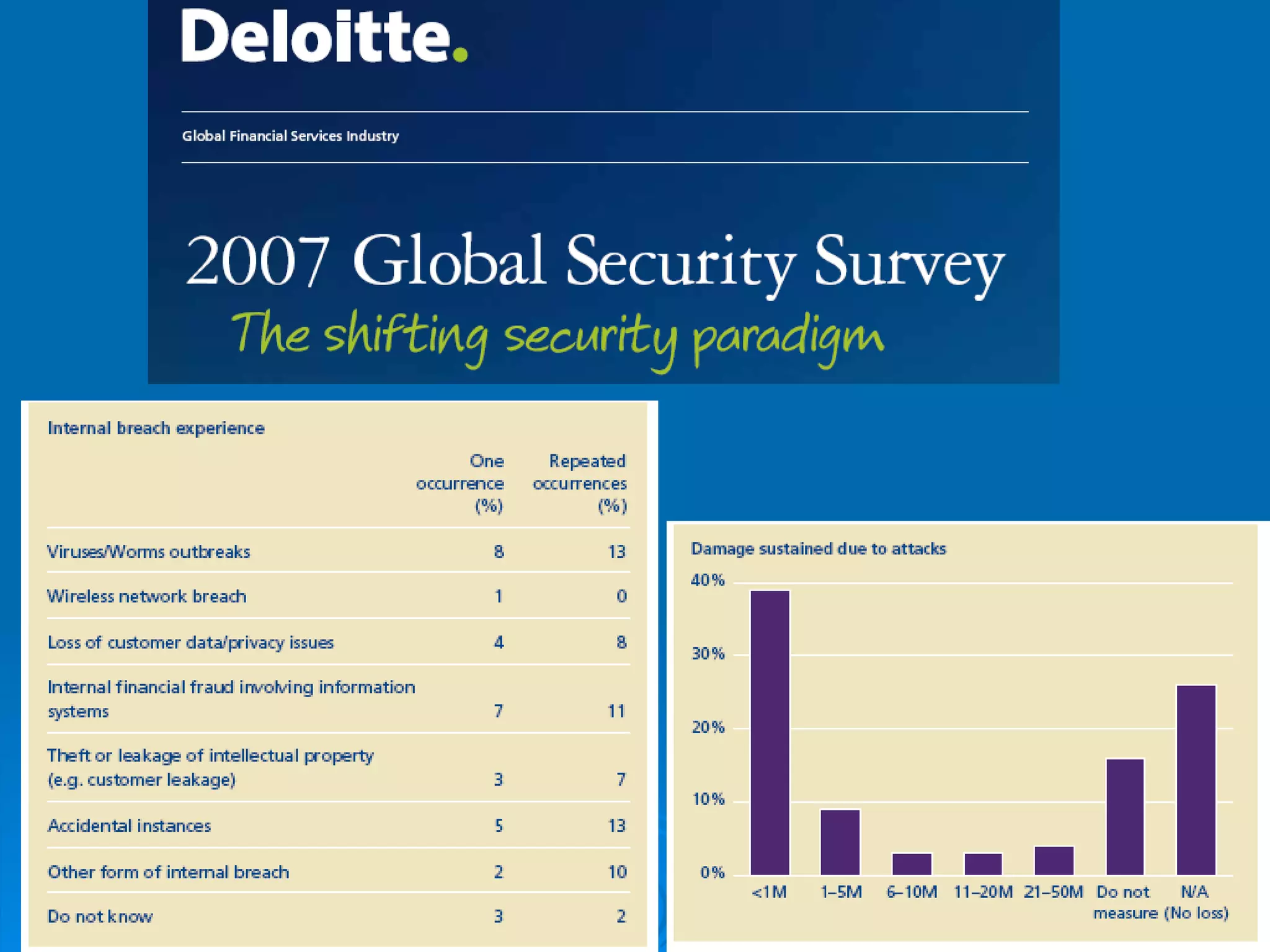
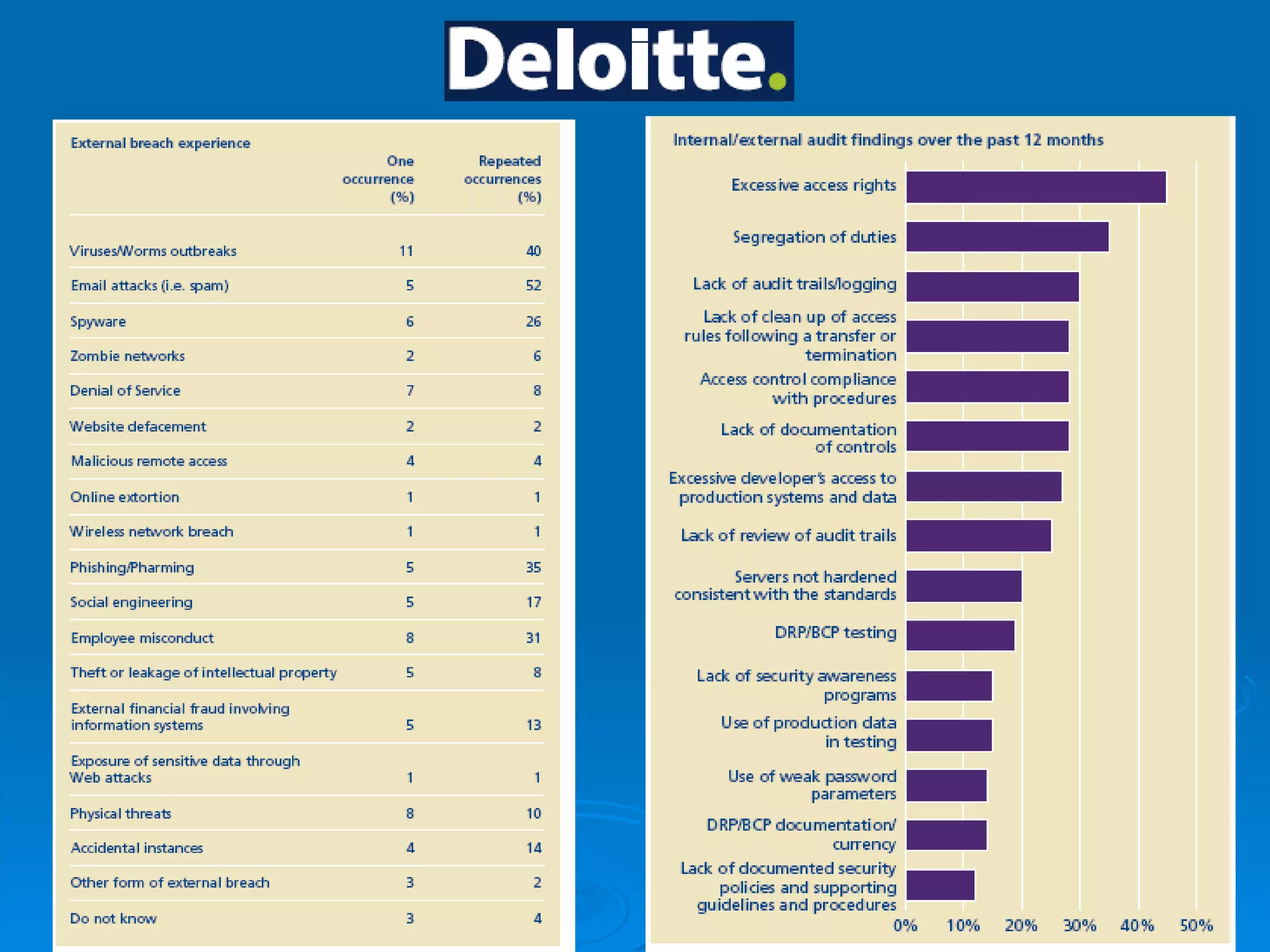
Intrusion detection systems monitor computer networks and systems for unauthorized access or activity. There are two main types: network-based systems examine network traffic for attacks, while host-based systems check the integrity of individual systems. Methods include knowledge-based systems that detect known attacks and behavior-based systems that identify deviations from normal usage profiles. Regular auditing of systems, logs, user rights and files is needed to detect intrusions. While intrusion detection is important for security, intrusion prevention systems that can block attacks in real-time are increasingly replacing detection-only systems.