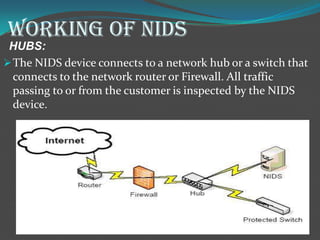
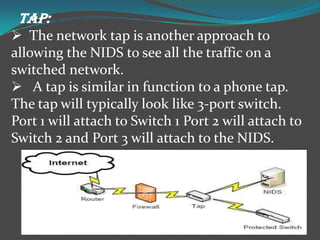
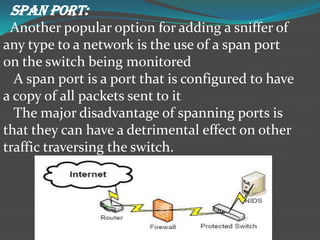
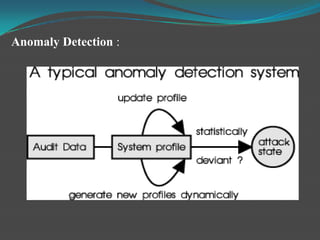
Network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) monitor network traffic for malicious activity by analyzing network packets at choke points like borders or the demilitarized zone. NIDS identify intrusions by comparing traffic patterns to known attack signatures or by detecting anomalies from established baselines. While NIDS can detect both previously known and unknown attacks, they require frequent signature database updates and may generate false positives. NIDS provide visibility without affecting network performance but cannot inspect encrypted traffic or all traffic on very large networks.














![IMPLEMENTED APPROACHES
IEEE 802.11
a) Open System Authentication.
b) Shared Key Authentication.
Secure key generation and distribution
Mitigating Routing Misbehavior:( Sergio
Marti et al. [19])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/579b-120127061045-phpapp01/85/Intrusion-detection-system-22-320.jpg)




