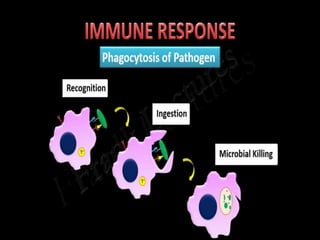
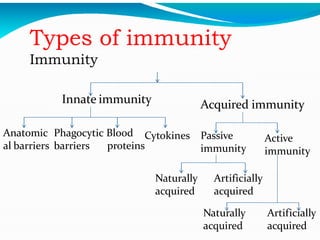
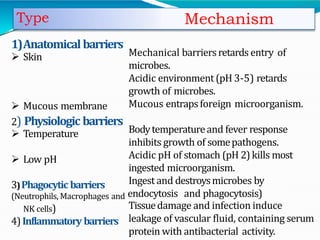
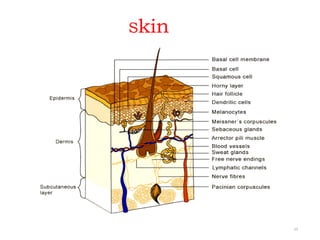
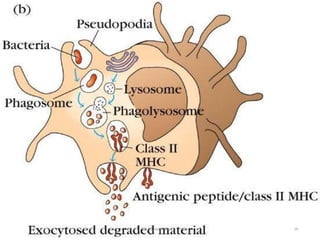
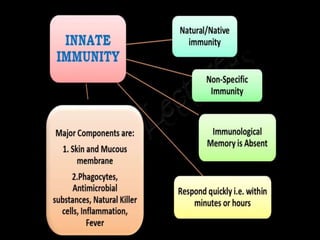
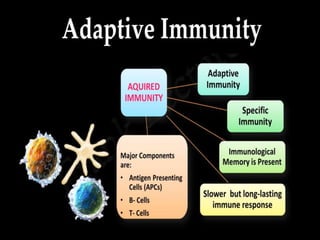
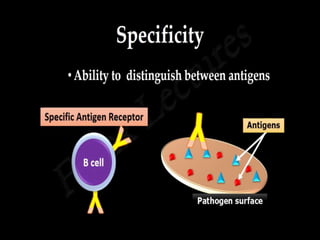
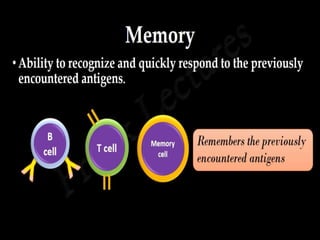
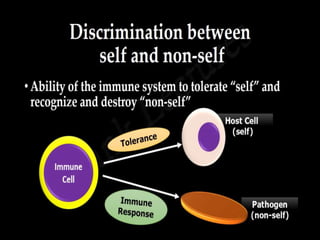
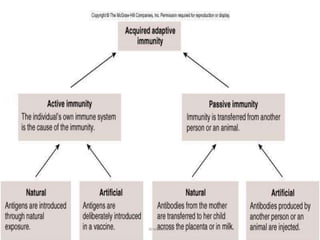
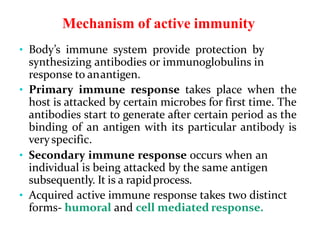
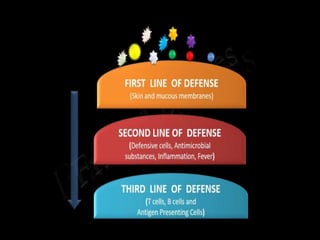
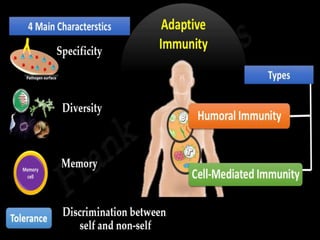
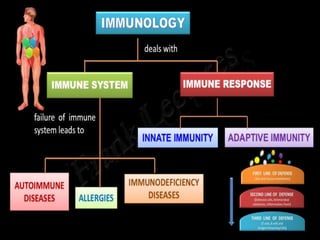
This document discusses the different types of immunity. It begins by defining immunity and describing the innate immunity system, which includes anatomical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, physiological barriers like low pH levels, and biological barriers like white blood cells. The document then explains acquired immunity, noting it is antigen specific, diverse, leads to immunological memory, and involves self/non-self recognition. Acquired immunity is divided into active immunity, which occurs from natural exposure or vaccination, and passive immunity, which results from transfer of antibodies or immune cells from another individual. Both active and passive immunity can be naturally acquired or artificially acquired.