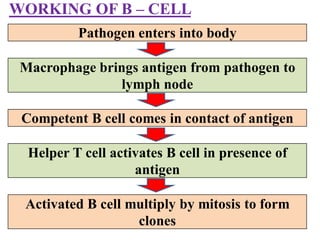
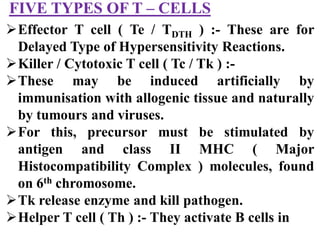
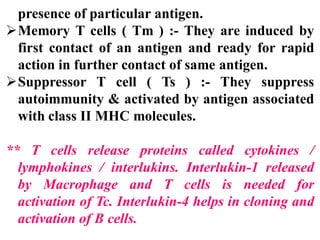
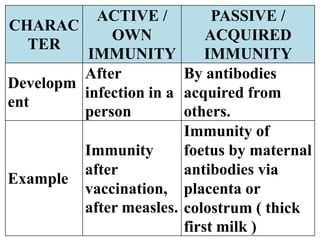
Immunity is the body's resistance or action against invaders or harmful substances. There are two types of immunity - innate (non-specific) and acquired (specific). The innate immunity provides first and second line of defense through physical barriers and white blood cells. The acquired immunity provides third line of defense through humoral immunity via B cells and antibodies or cell-mediated immunity via T cells. Edward Jenner is considered the father of immunology. Vaccines help develop acquired immunity by introducing weakened pathogens.