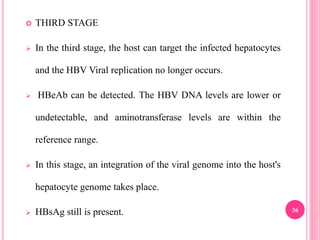
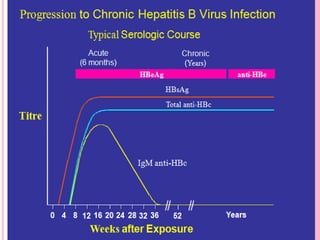
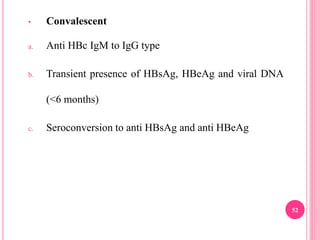
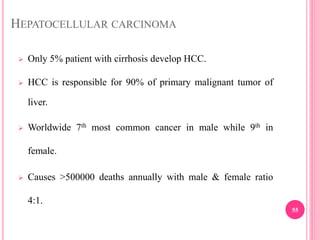
This document discusses hepatitis B, including its history, prevalence, transmission, clinical features, outcomes, and diagnosis. Key points include:
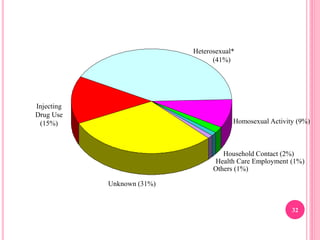
- Hepatitis B is a serious viral infection that affects the liver and can become chronic, increasing risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. It is transmitted through bodily fluids and from mother to child.
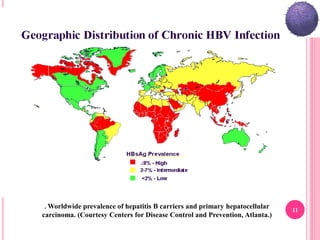
- Globally, over 350 million people have chronic hepatitis B infections, with prevalence highest in Asia and Africa.
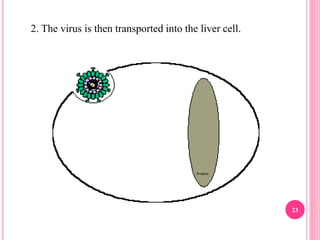
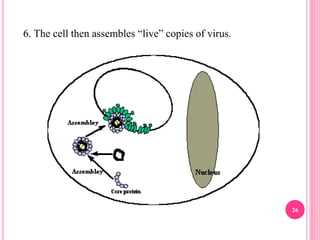
- The virus replicates in liver cells and can cause acute or chronic infection. Chronic carriers have a high risk of long-term liver damage.
- Symptoms of acute hepatitis B include jaundice and fatigue. Chronic infection often has no symptoms but increases cirrh