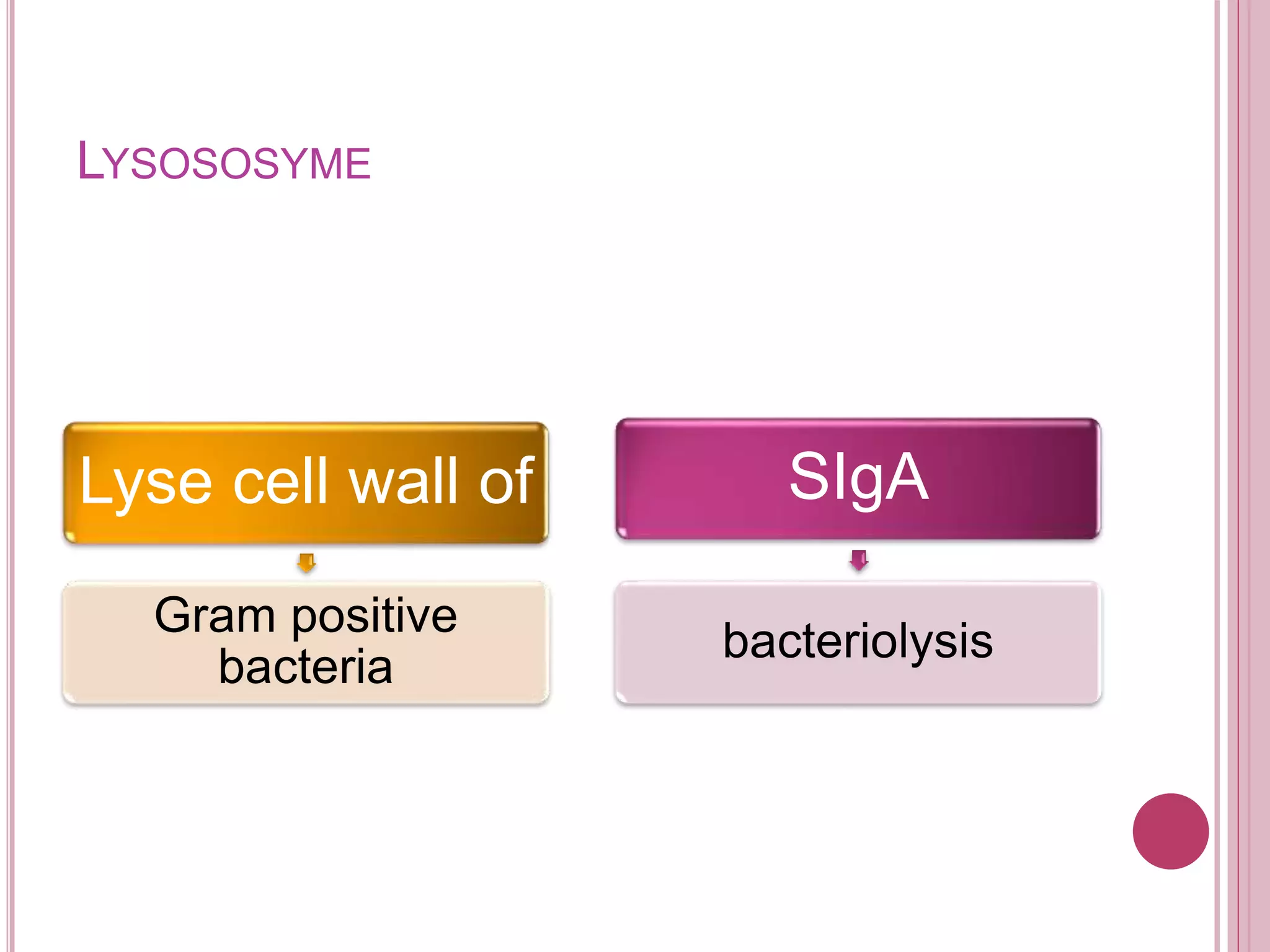
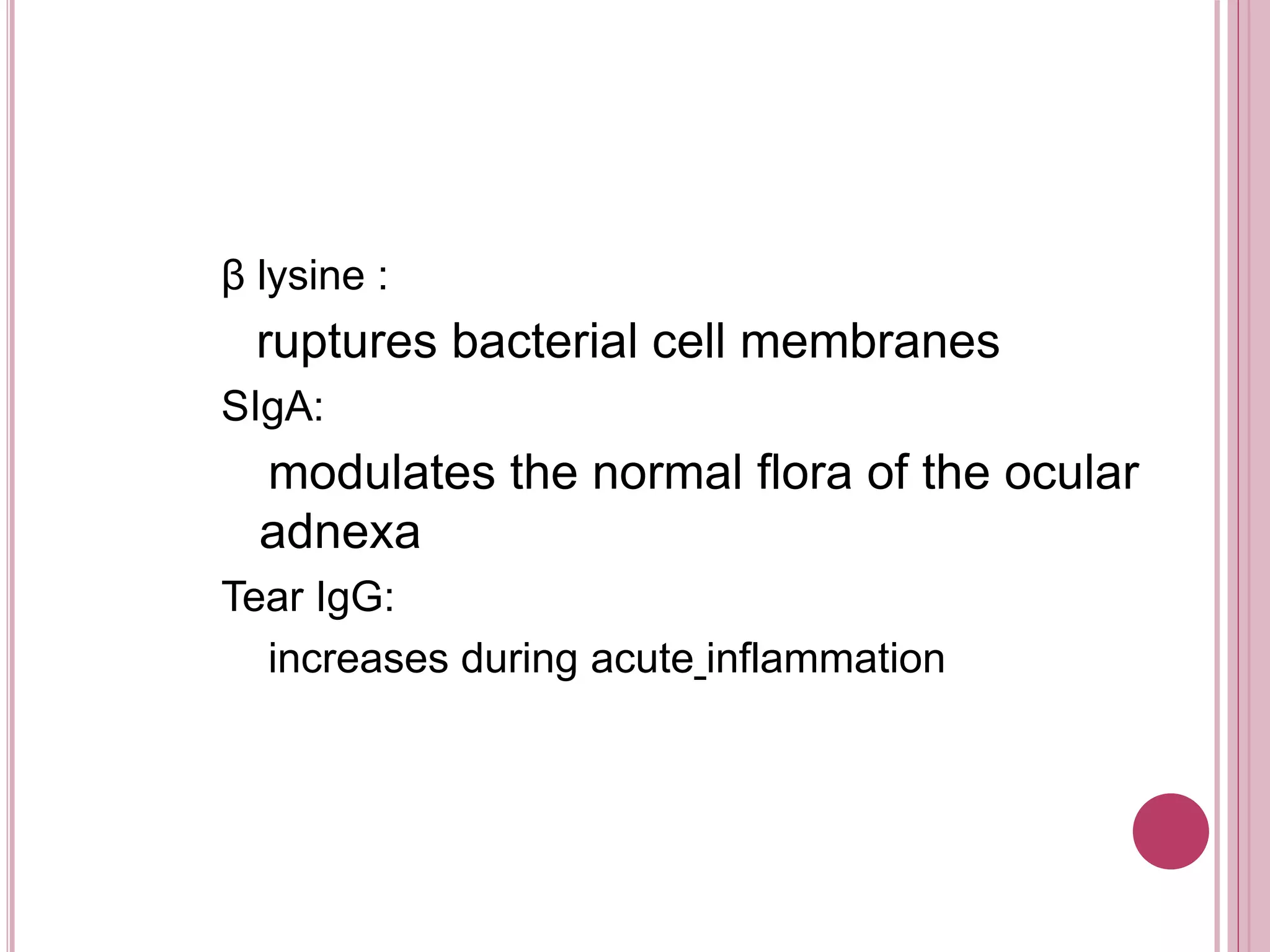
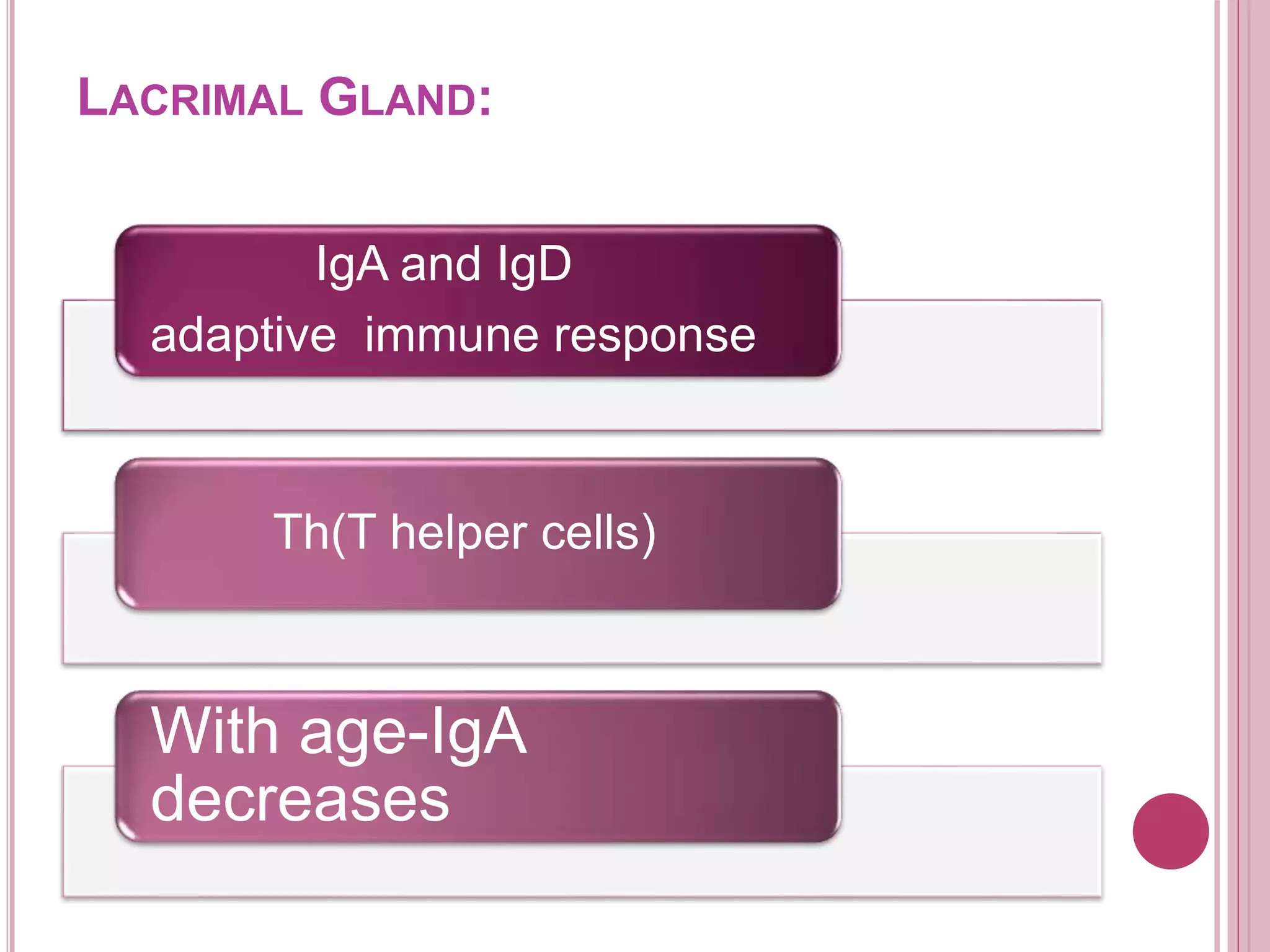
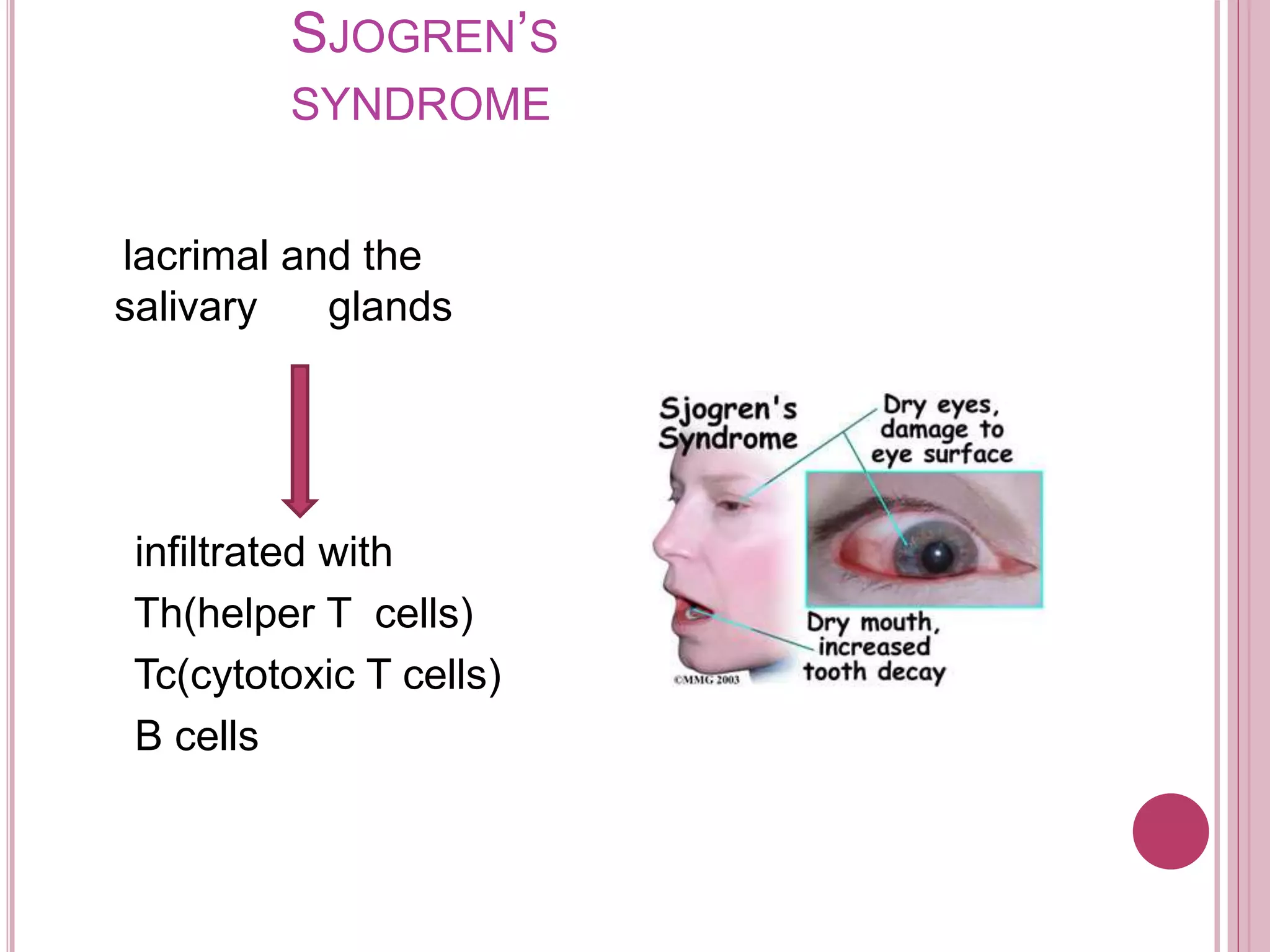
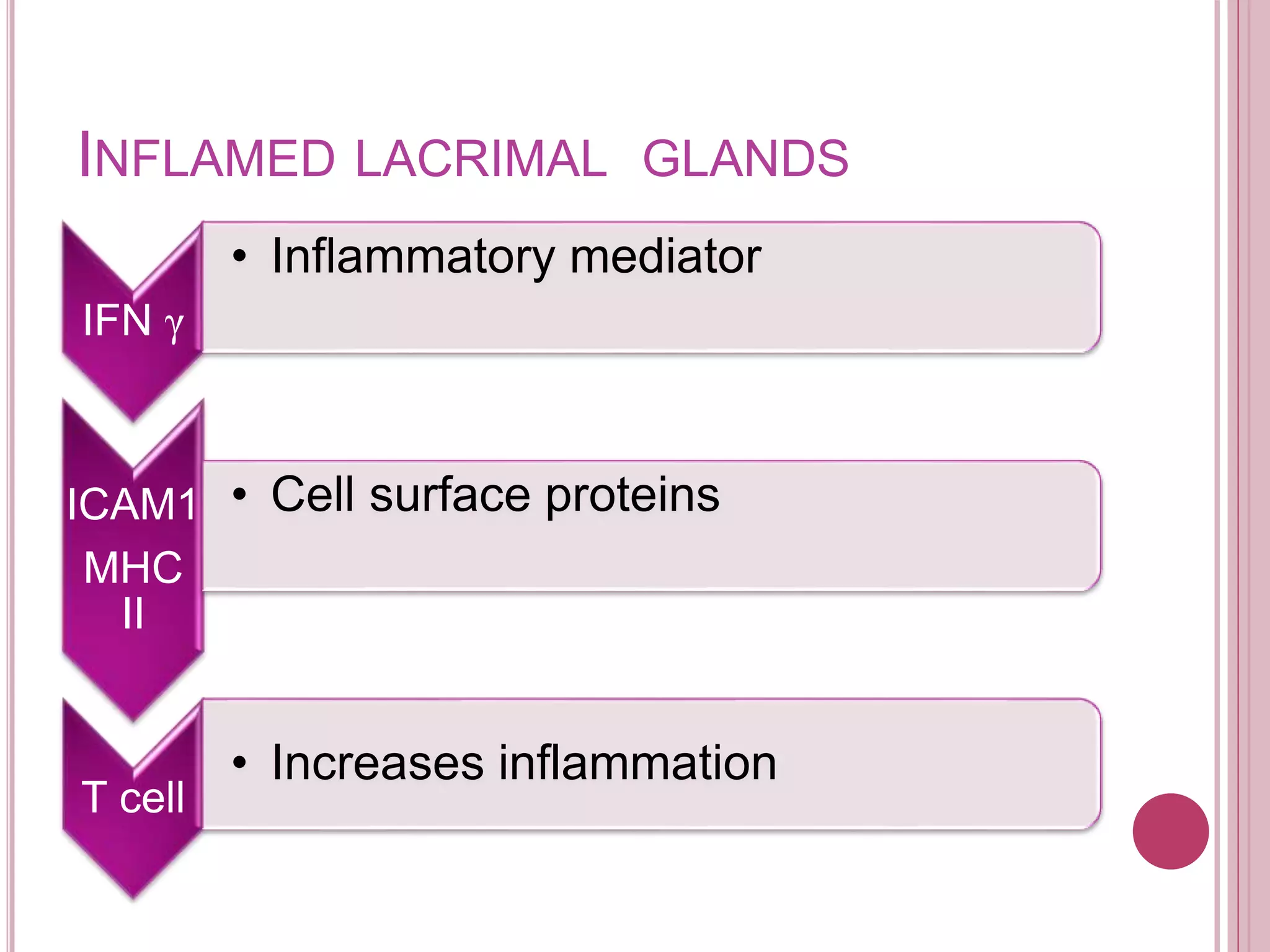
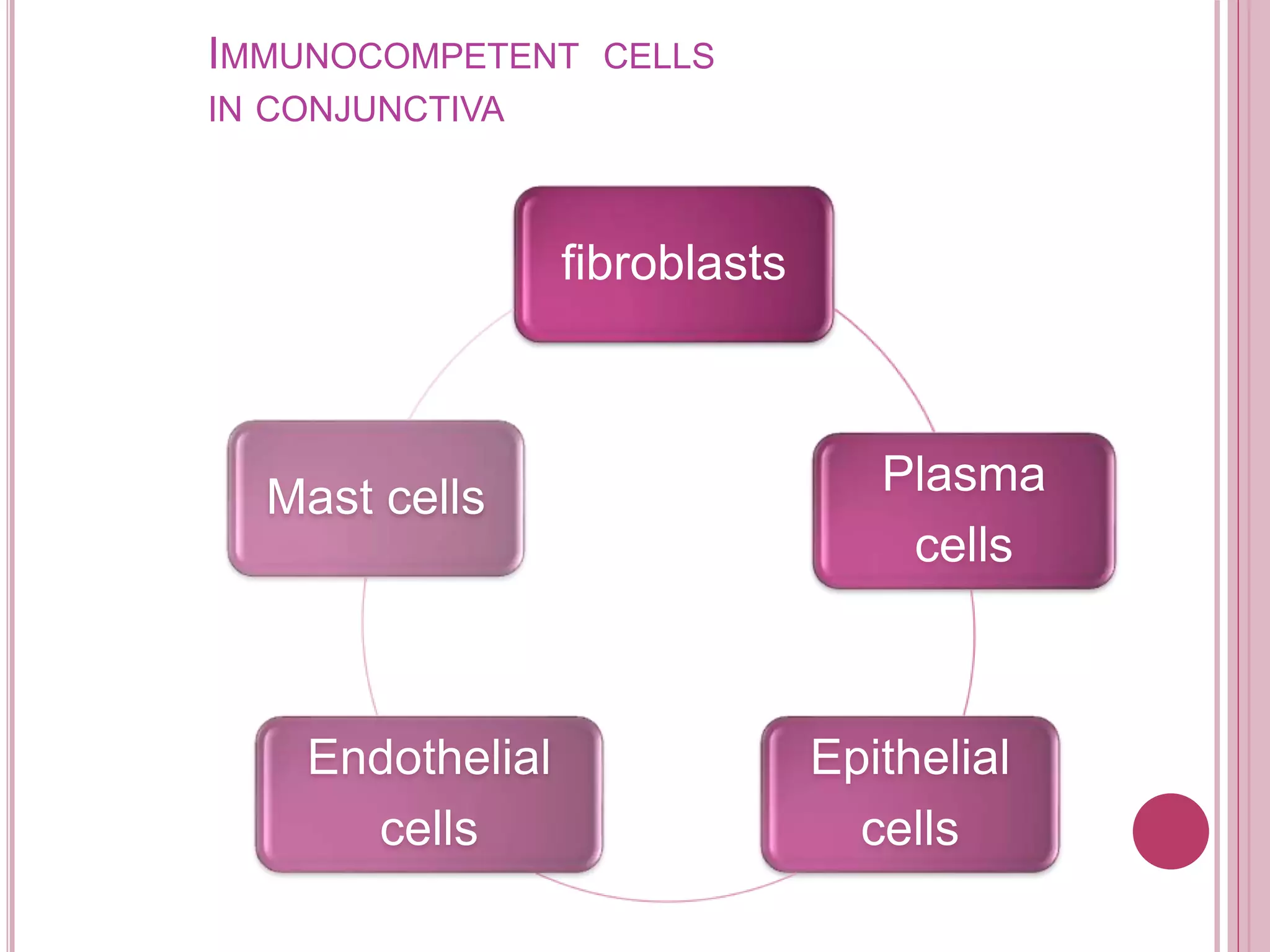
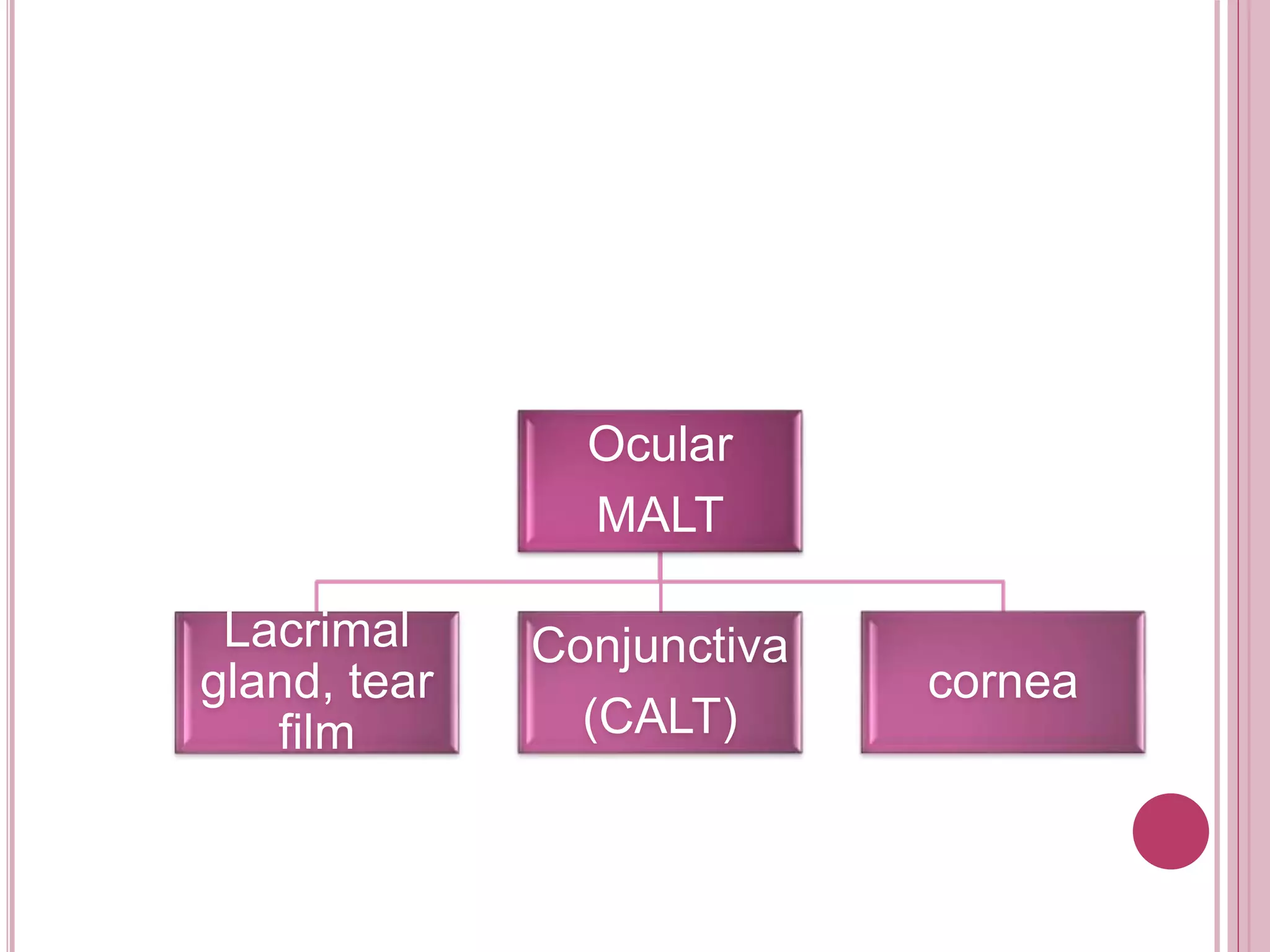
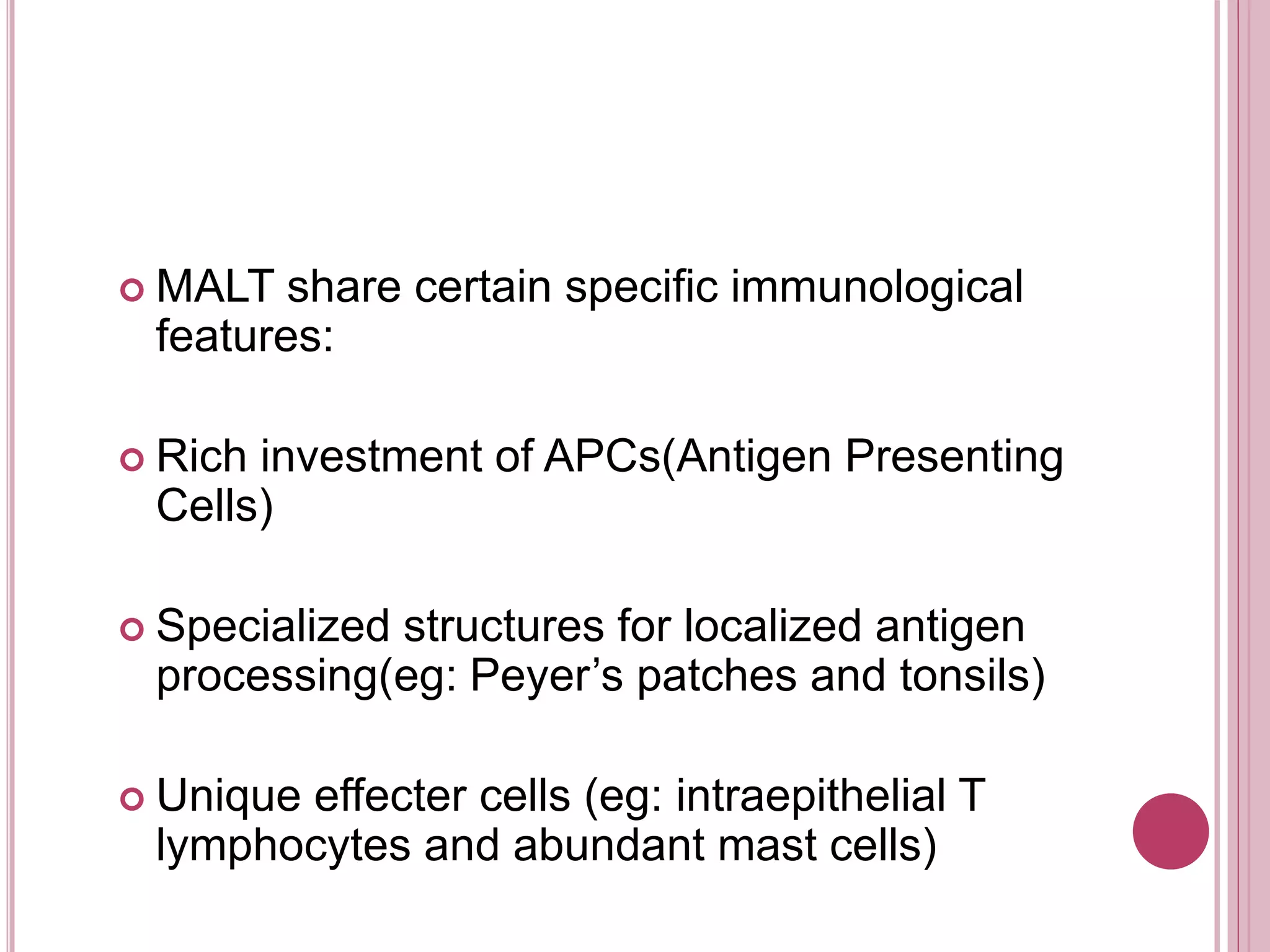
The ocular immune response involves local, regional, and systemic components. Locally, the conjunctiva, cornea, anterior chamber, and retina are involved. Regionally, the lacrimal gland and lymph nodes participate. Systemically, the spleen, thymus, and mucosal tissues are engaged. The tear film and its components, such as lysozyme, lactoferrin, and secretory IgA, play an important role in the ocular immune response by protecting the eye from pathogens. Specialized immune structures like the conjunctiva-associated lymphoid tissue (CALT) help regulate immunity in the eye. Dysregulation of the ocular immune system can lead to inflammatory conditions