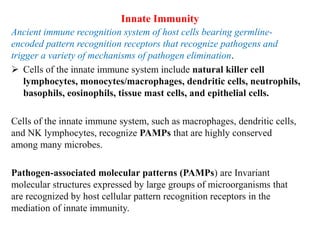
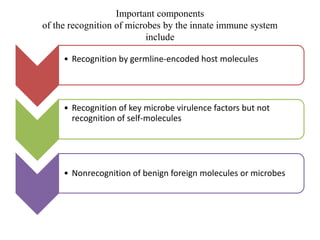
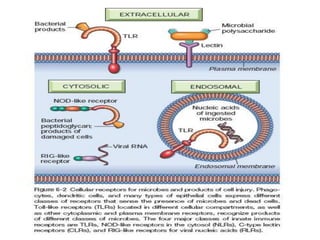
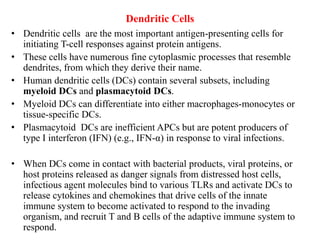
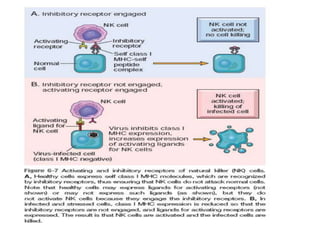
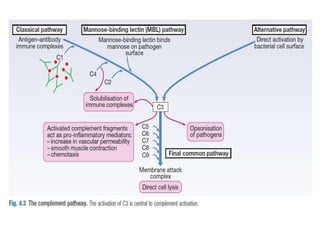
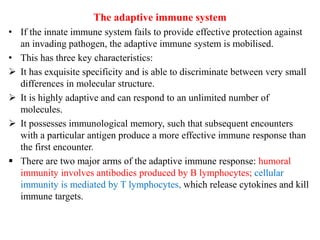
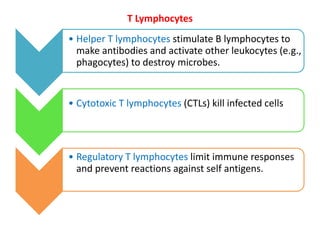
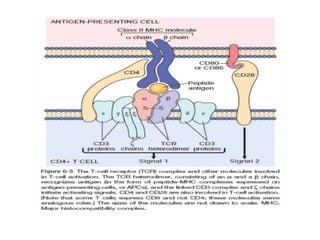
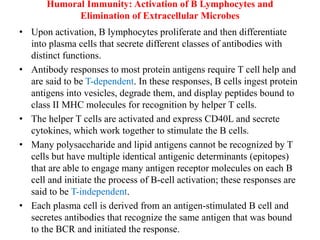
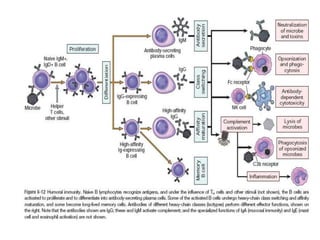
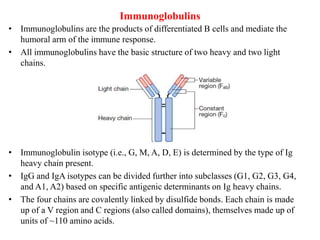
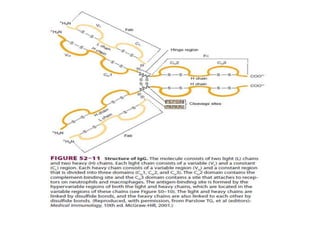
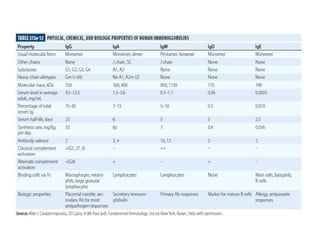
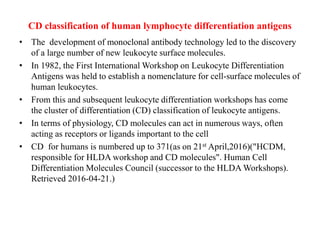
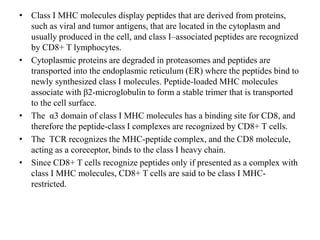
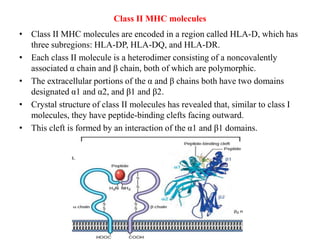
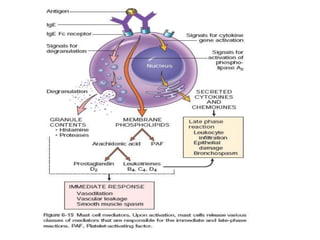
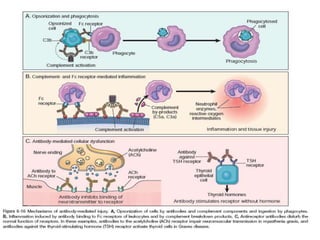
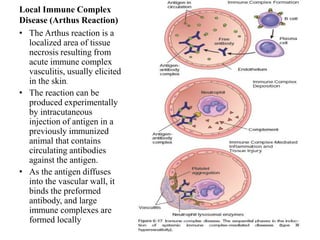
The immune system consists of cells, proteins, and lymphoid organs that work together to protect the body from infection. The immune system has two branches: innate immunity provides a general and immediate response, while adaptive immunity provides a tailored response after initial exposure. Innate immunity involves physical barriers and cells like macrophages that recognize pathogens. Adaptive immunity involves B and T cells that recognize specific pathogens and mount stronger responses upon reexposure. Cytokines are proteins that regulate immune cell growth and activation and mediate inflammatory responses.