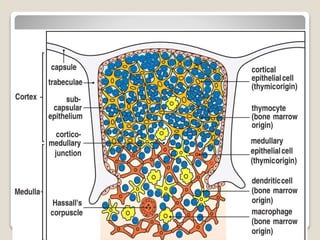
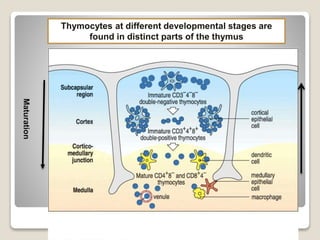
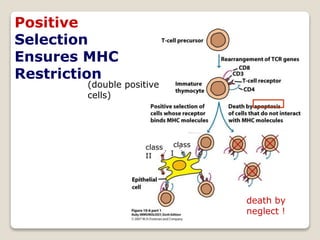
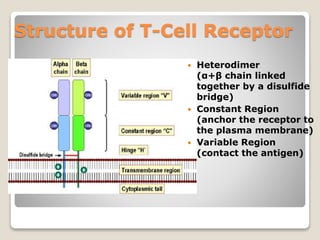
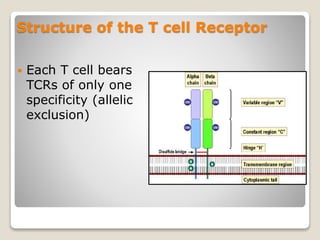
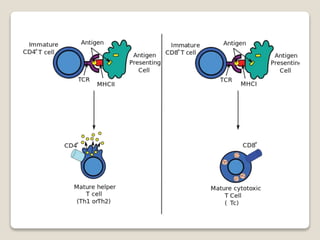
T-cells are a type of white blood cell that play a major role in the immune system by fighting infection. There are different types of T-cells that act in various ways to identify and destroy pathogens. T-cells mature in the thymus gland, where they develop receptors called TCRs that allow them to recognize antigens bound to MHC molecules on other cells. The MHC presents antigen fragments to T-cells to trigger an immune response against invading microbes.