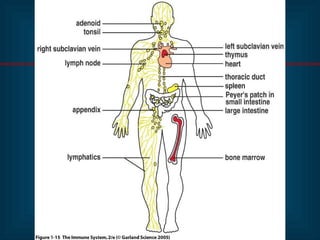
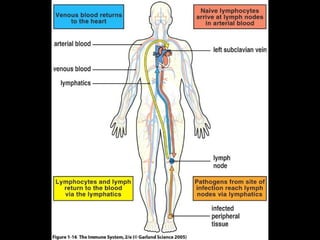
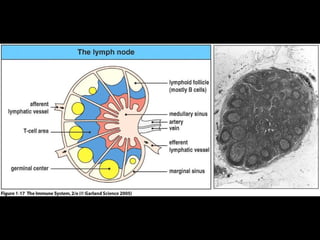
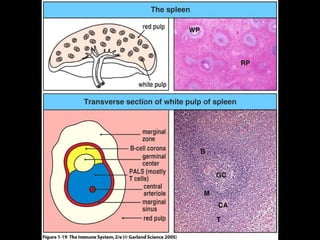
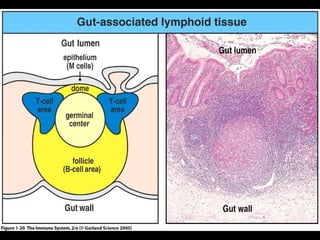
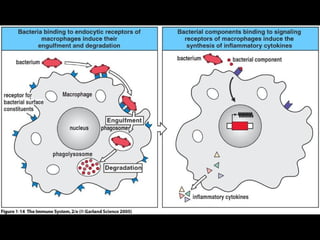
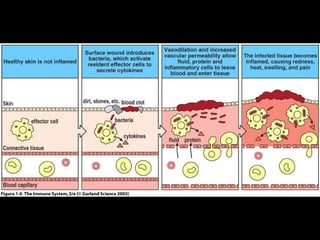
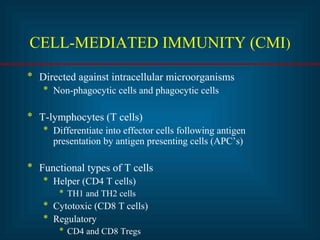
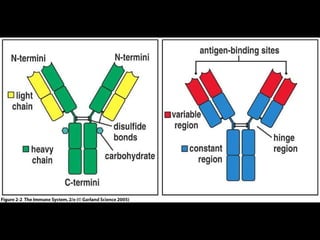
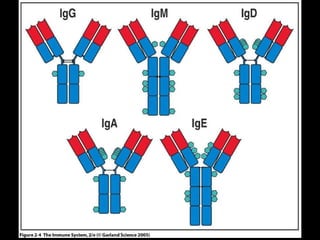
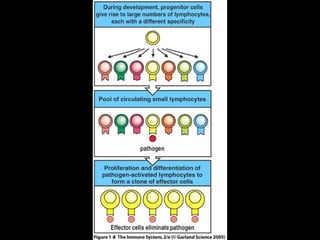
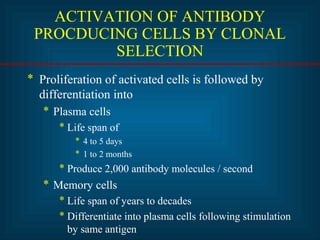
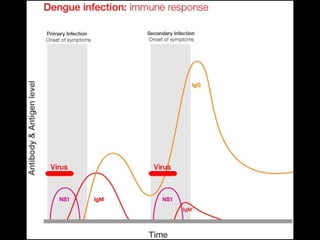
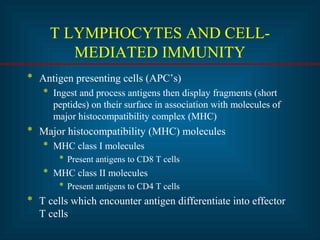
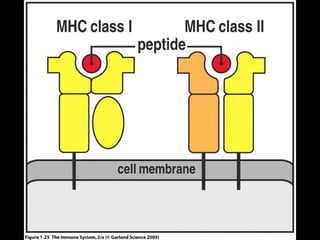
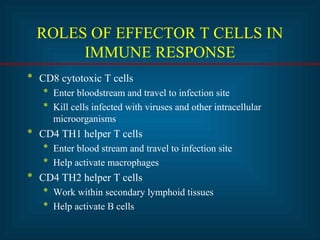
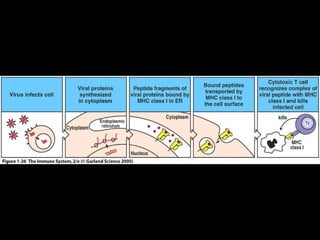
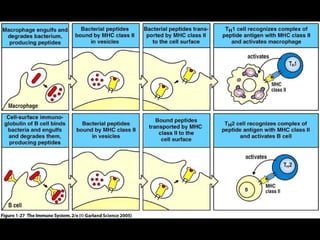
This document provides an introduction to immunology and the immune system. It discusses the study of immunology and defines the immune system. It also describes the innate and adaptive immune responses, natural and artificial immunity, the roles of antibodies and lymphocytes in humoral and cell-mediated immunity, and the functions of the lymphatic system. Key cell types like phagocytes, B cells, T cells, and antigens are also introduced.