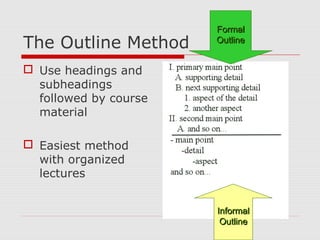
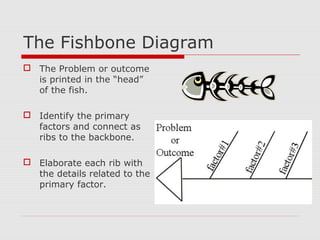
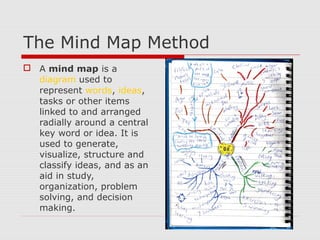
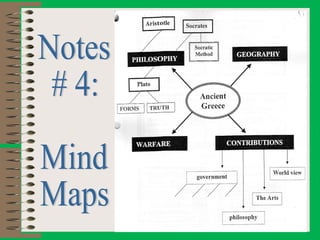
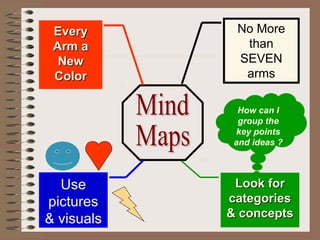
The document discusses effective note-taking strategies. It recommends taking notes for the purposes of remembering, examining, preparing, organizing, and reviewing material to think critically. The "5 C's of note-taking" are outlined as taking charge of lectures, concentrating, listening critically, connecting ideas, and capturing key points. Various note-taking styles like outlining, Cornell method, paragraph method, and fishbone diagrams are presented. The document emphasizes choosing a style that works best for the individual and provides other tips for effective note-taking.