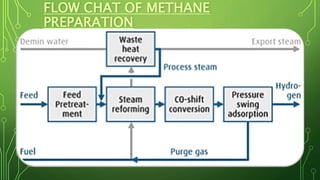
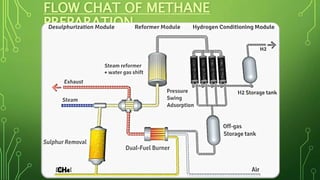
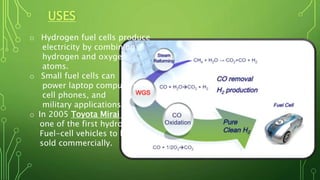
The document discusses the introduction, preparation, and properties of hydrogen gas. It begins by introducing hydrogen and how it was first artificially produced. It then discusses various methods of preparing hydrogen gas, including the reaction of metals with acids or water, electrolysis of water, and from hydrocarbons like methane. The document outlines the process for producing hydrogen from methane, including desulfurization, reforming, shift reactions, and methanation. It concludes by discussing the physical and chemical properties of hydrogen gas and its various industrial uses such as in rockets, fuel cells, and ammonia production.