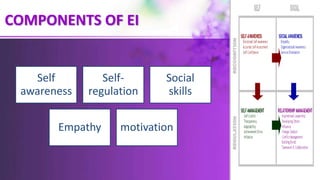
The document discusses the importance of assessment in nursing education, highlighting the assessment of both students and teachers as crucial for maintaining educational standards. It outlines essential teacher qualities, various teaching styles, types of learners, and factors affecting learning and motivation. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of emotional intelligence in learning and the need for educators to create supportive environments to enhance student engagement and success.