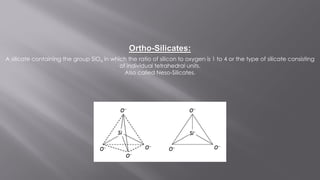
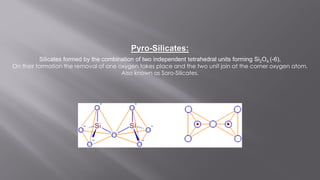
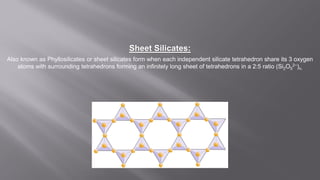
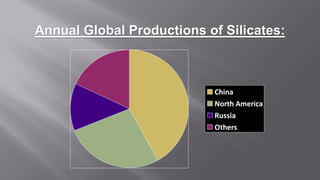
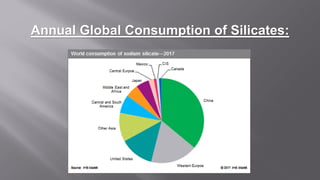
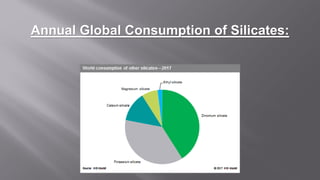
Silicates are minerals consisting of silica combined with metal oxides, forming a major component of the earth's crust. They have a basic tetrahedral structure and comprise 40% of common minerals. The main types are ortho, pyro, sheet, ring, and chain silicates. Silicates have many important uses including in microchips, quartz crystals, glass, ceramics, and as allied products such as sodium silicate, aluminum silicate, and potassium silicate. China is the world's largest producer and consumer of silicates.