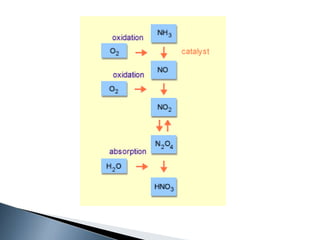
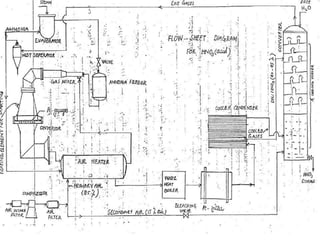
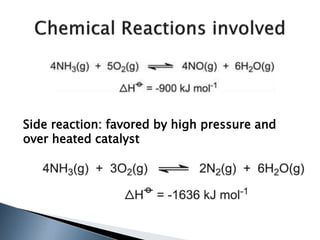
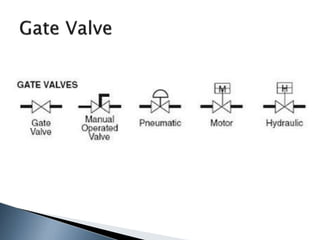
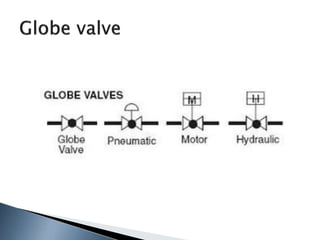
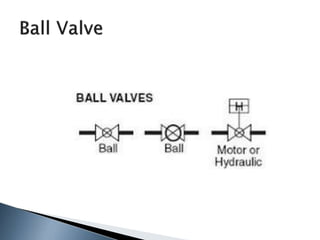
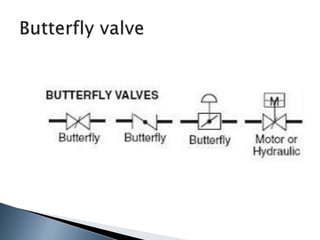
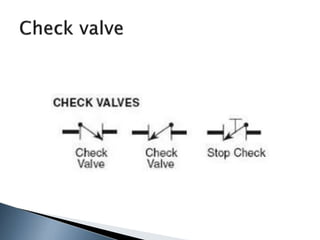
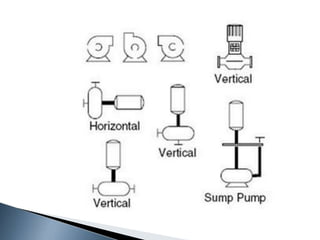
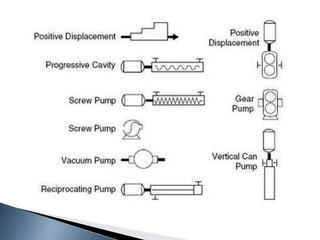
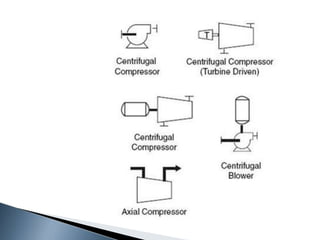
Here are two ways expenses are minimized in the Ostwald process:
1. The heat generated by the exothermic reactions is utilized to maintain the high temperature needed for the ammonia oxidation reaction, reducing energy costs.
2. Platinum-rhodium alloy is used as the catalyst. Platinum is very expensive but using it in an alloy with less costly rhodium allows the use of less platinum, lowering material costs.