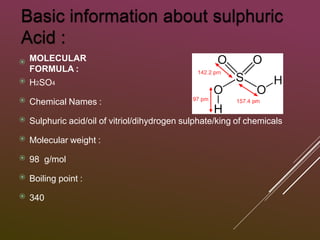
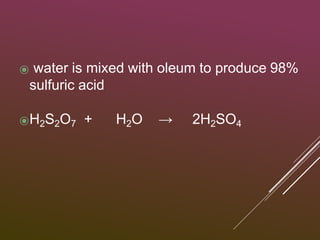
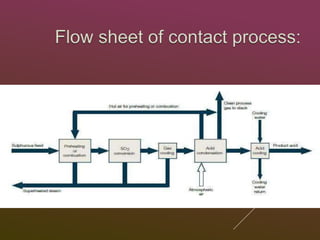
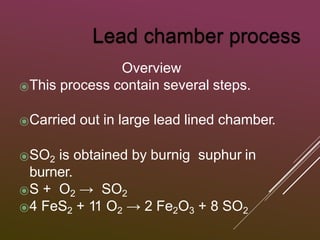
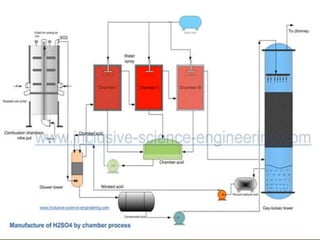
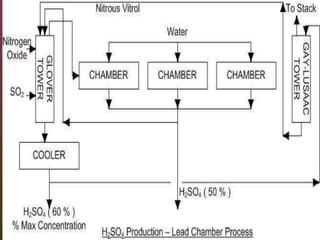
Sulfuric acid is produced via the contact process, which involves three main steps:
1) Sulfur is burned to produce sulfur dioxide gas.
2) Sulfur dioxide is converted to sulfur trioxide gas over a vanadium pentoxide catalyst.
3) Sulfur trioxide is dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid to form oleum, which is then diluted with water to produce 98% sulfuric acid.