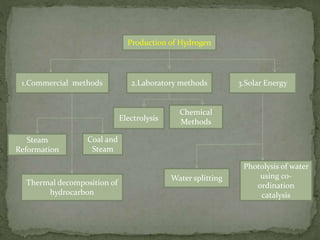
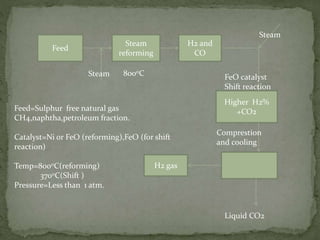
There are three main commercial methods for hydrogen production: steam reformation, coal gasification, and thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons. Steam reformation involves reacting hydrocarbons like natural gas with steam at high temperatures over a catalyst to produce hydrogen and carbon oxides. The mixture is then shifted to increase hydrogen concentration before purification. Coal gasification uses superheated steam to gasify coal, producing water gas that is further reacted to hydrogen. Thermal decomposition produces hydrogen as a byproduct when cracking hydrocarbons at high heat.