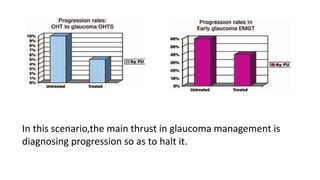
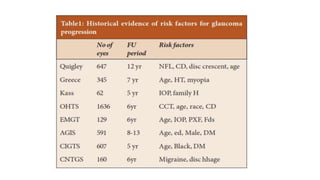
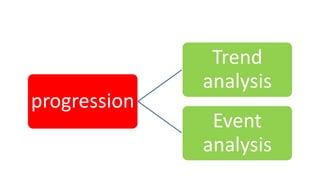
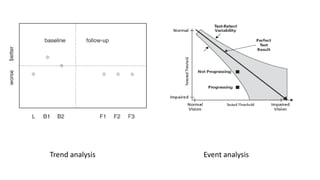
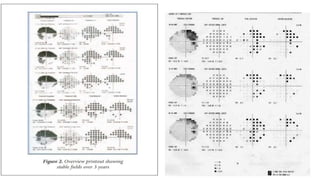
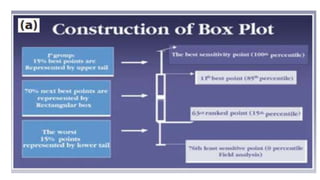
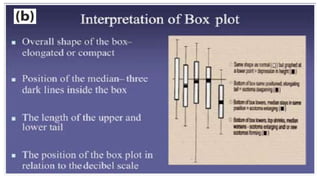
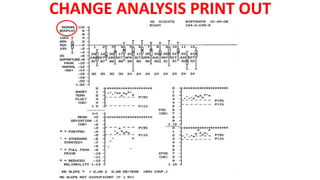
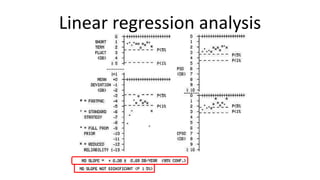
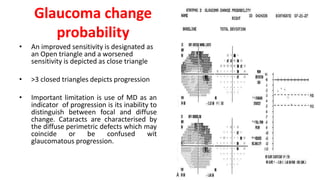
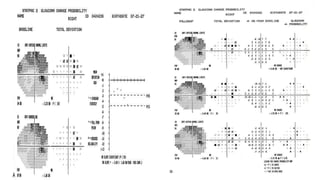
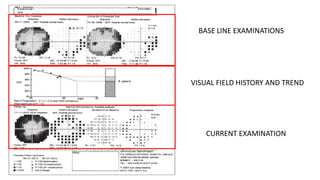
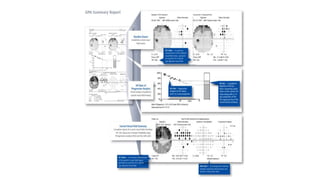
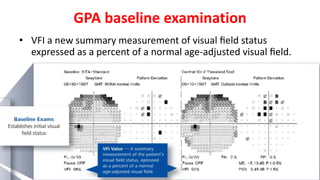
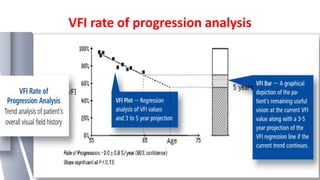
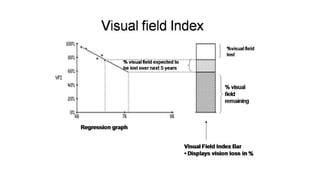
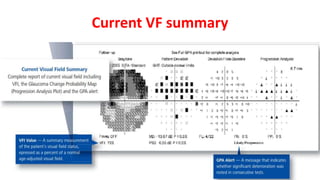
Glaucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy characterized by retinal ganglion cell loss. Progression is irreversible, so diagnosis and monitoring are important for management. Progression can be monitored structurally with HRT, GDX, and OCT, or functionally with perimetry. Clinical evaluation and perimetry are standard for detecting progression, but have limitations like subjectivity. Trend and event analysis of visual fields are used to objectively detect progression over time. Various programs analyze parameters like TD, MD, and CPSD for trend analysis or look for deteriorating thresholds beyond baseline levels for event analysis. HVF STATPAC provides overview prints, change analysis, GCP plots, and GPA to facilitate interpretation of visual field changes