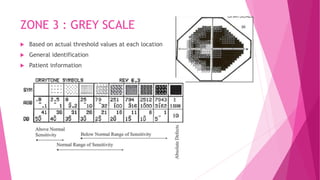
This document provides an overview of Humphrey visual field (HVF) testing. HVF uses static perimetry to measure threshold sensitivity values across the visual field and compare them to normative data. It uses white stimuli on a white background presented for 0.2 seconds. Common testing programs include 30-2, 24-2, and 10-2 patterns. The results are analyzed using global indices, total and pattern deviation plots, and the Glaucoma Hemifield Test. Test quality must be ensured through reliability indices and proper patient preparation. Visual field defects are evaluated based on probability plots and Anderson's criteria to determine if they are outside normal limits. Progression is monitored by frequent testing, especially if mean deviation is changing