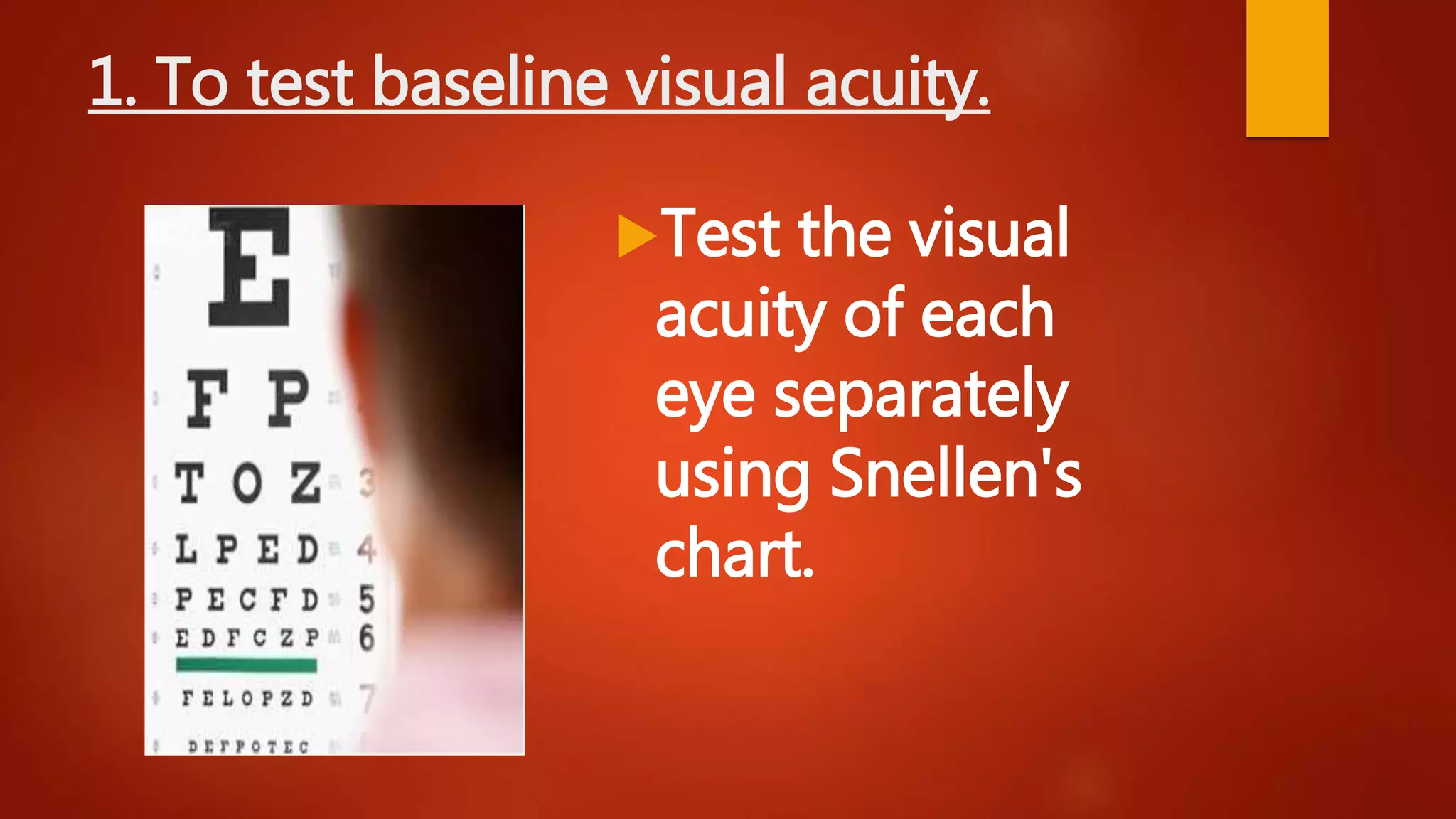
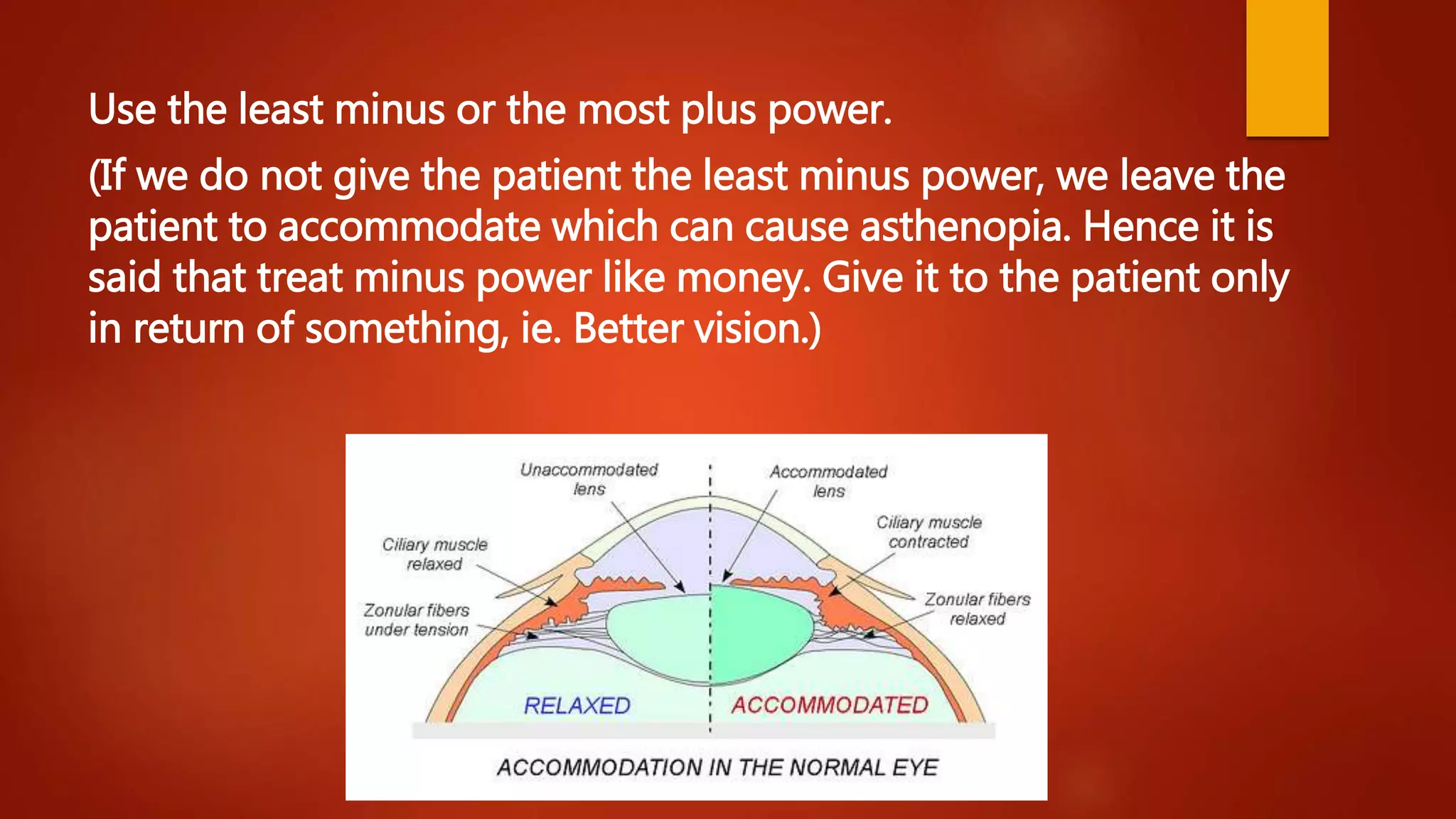
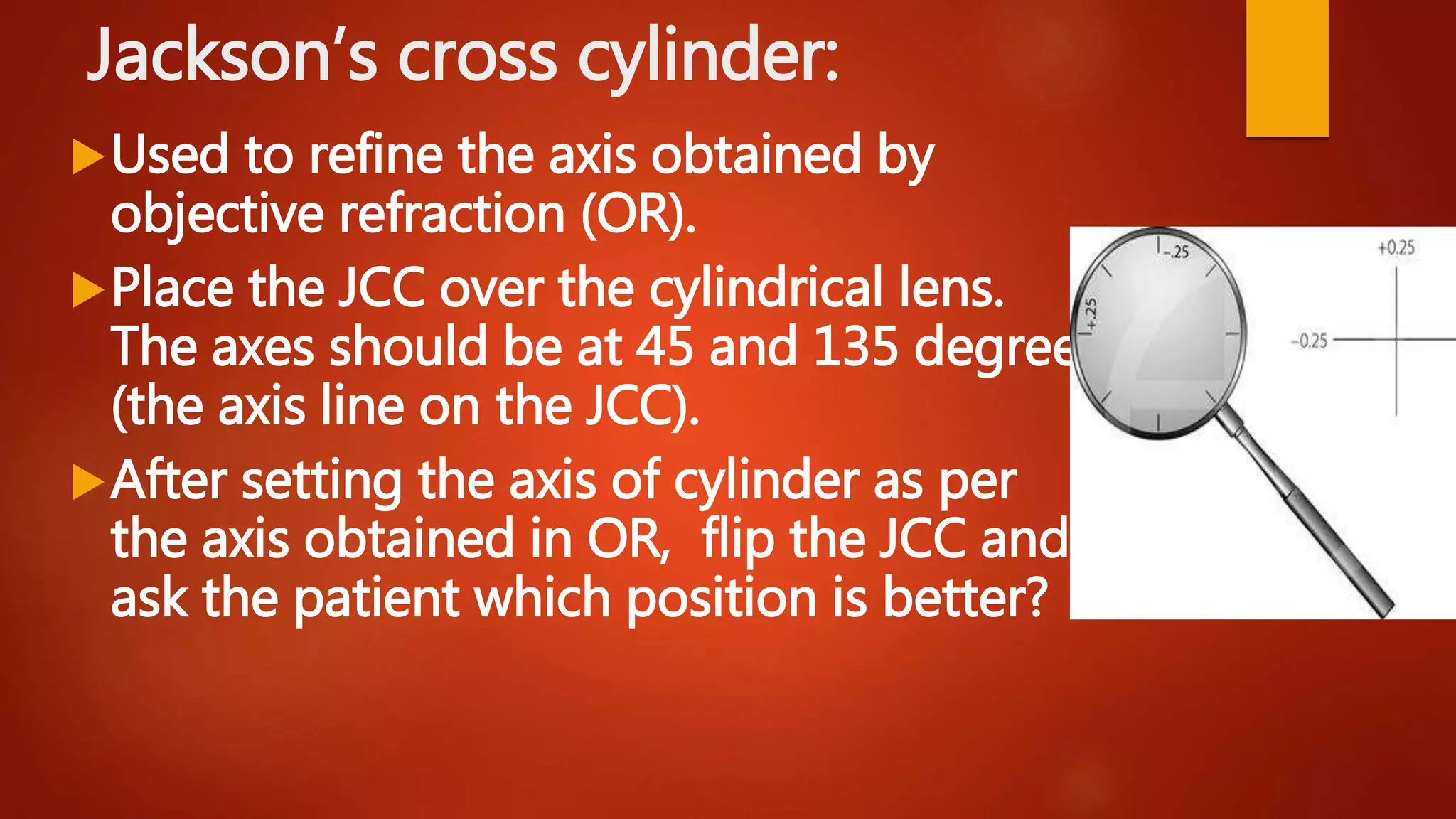
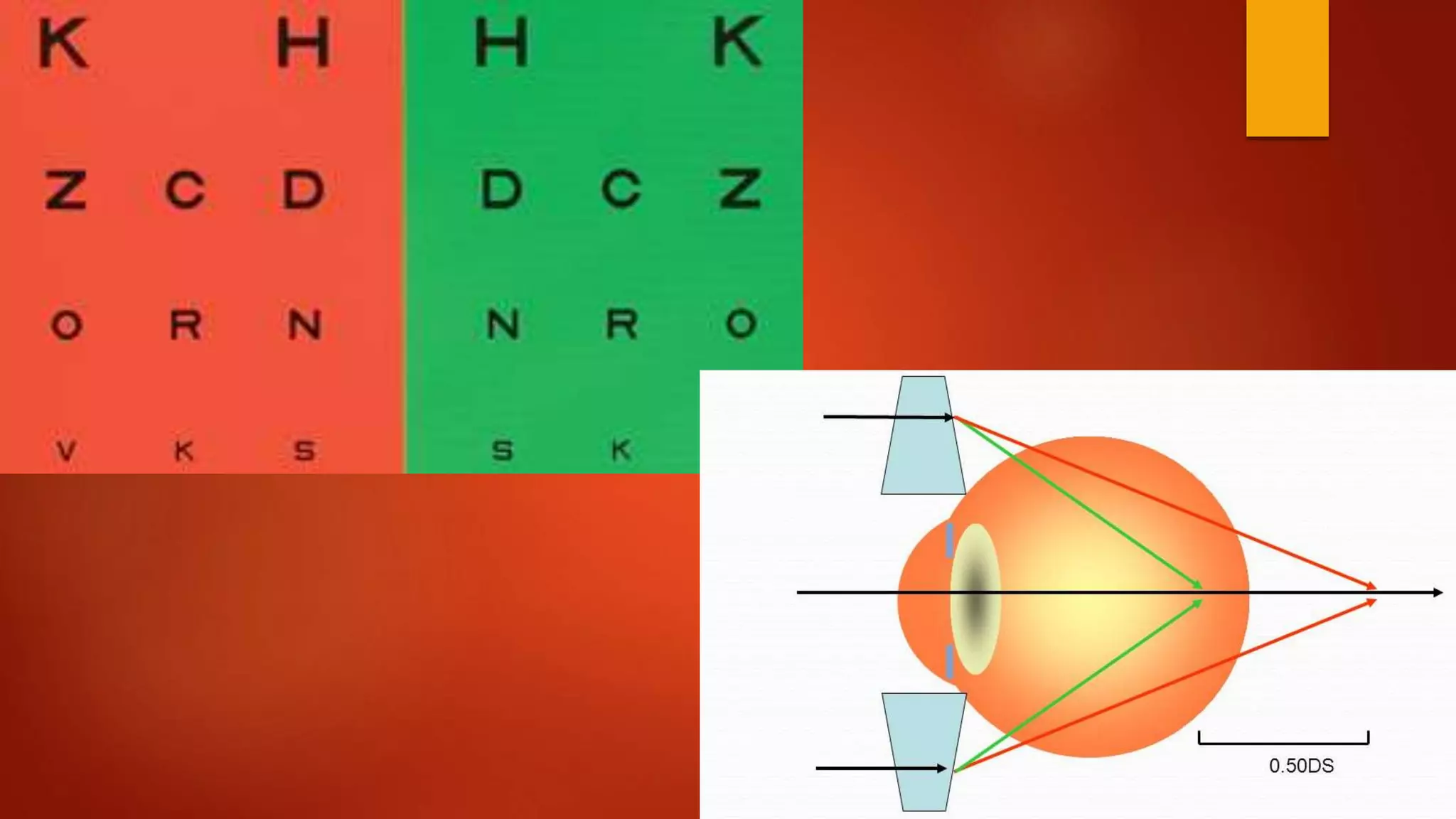
This document describes the process of refraction using a phoropter. A phoropter is an ophthalmic testing device used to measure refractive error and determine eyeglass prescriptions. It contains different lenses. The summary describes the preliminary steps, which include positioning the patient and adjusting the device. It then outlines the 6 steps of subjective refraction: 1) test visual acuity, 2) establish spherical power, 3) refine cylindrical axis, 4) refine cylindrical power, 5) refine spherical power, and 6) perform binocular balancing.