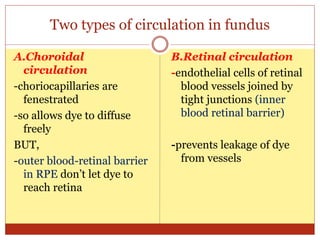
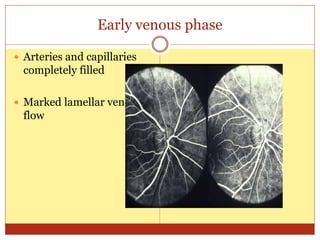
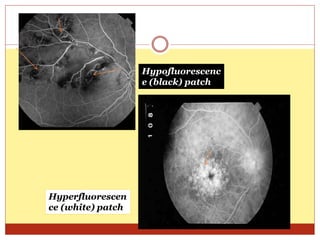
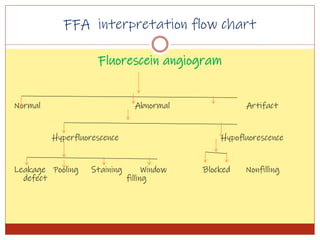
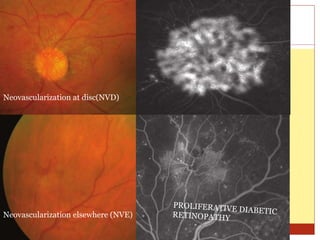
Fluorescein angiography uses fluorescence to evaluate the integrity of retinal and choroidal vessels. Fluorescein dye is injected and its movement through the eye is photographed. Normally, dye fills the choroidal and retinal vessels without leaking. Abnormalities appear as hyperfluorescence, where dye leaks, or hypofluorescence, where filling is blocked. Fluorescein angiography helps diagnose and monitor retinal diseases by detecting breaks in the blood-retinal barrier and assessing the extent of damage. It remains useful for evaluating conditions like age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusions.