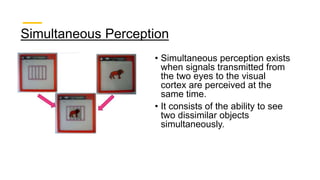
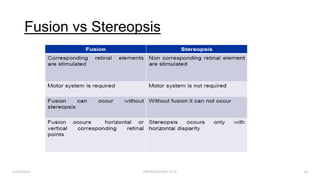
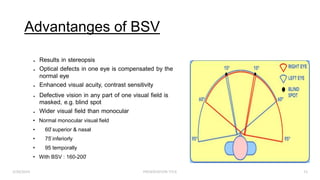
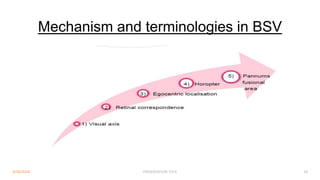
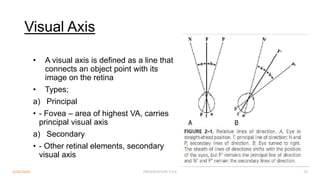
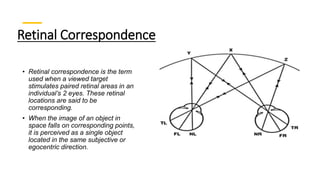
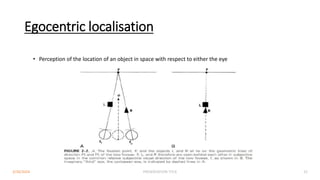
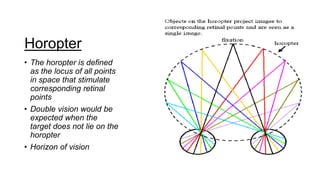
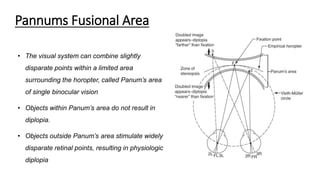
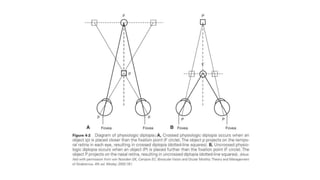
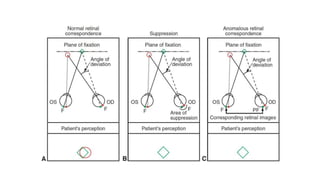
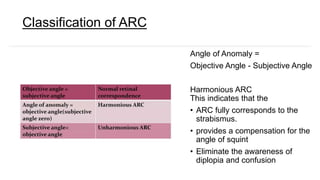
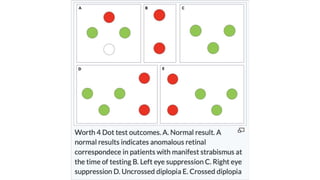
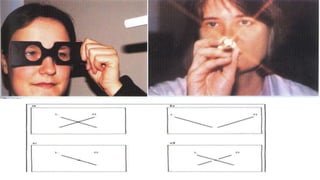
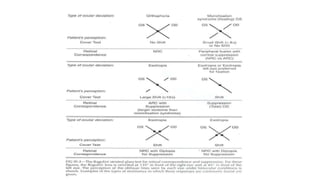
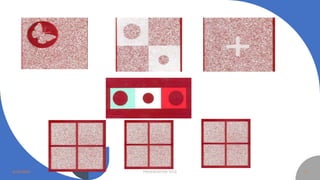
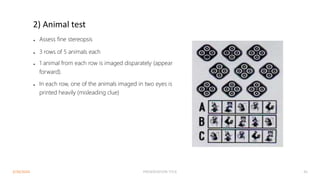
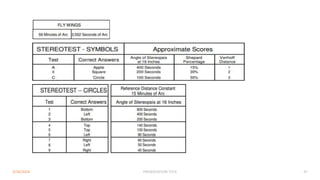
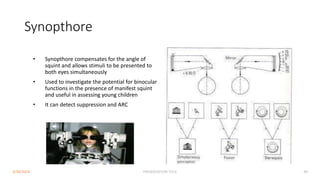
Binocular single vision refers to the state of simultaneous vision achieved through the coordinated use of both eyes to perceive a single image. It involves three main components: simultaneous perception, fusion, and stereopsis. Simultaneous perception is perceiving images from both eyes at the same time. Fusion is the cortical unification of the two retinal images into one percept. Stereopsis provides the highest level of binocular cooperation by producing a sensation of depth through the fusion of horizontally disparate retinal images. The development of binocular single vision occurs gradually in infancy and early childhood as the visual system matures and learns to coordinate the two eyes. Mechanisms such as retinal correspondence, the horopter, Panum's fusional area,