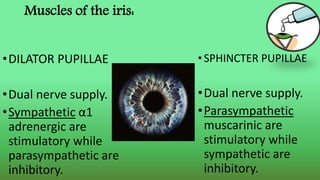
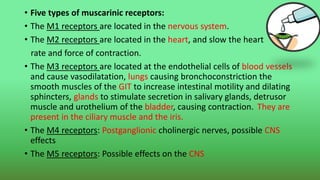
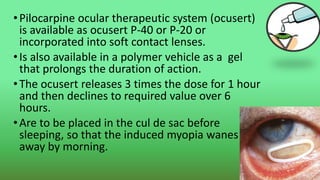
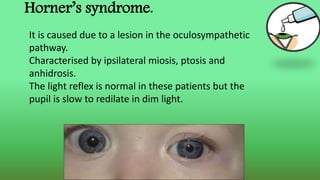
This document discusses miotics and mydriatics used in ophthalmology. Miotics like pilocarpine are parasympathomimetic drugs that cause pupil constriction (miosis) by stimulating muscarinic receptors. Common miotics discussed include pilocarpine, acetylcholine, and carbachol. Mydriatics like phenylephrine and atropine cause pupil dilation (mydriasis) by stimulating adrenergic receptors or blocking cholinergic receptors. Uses, mechanisms of action, and side effects of various miotics and mydriatics are provided. Diagnostic tests for conditions like Horner's syndrome using these agents are also summarized.