This document provides an outline of topics covered in a grammar book, including:
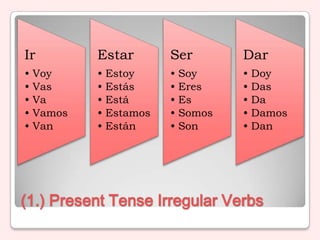
1) Present tense verbs and irregular forms
2) Stem-changing verbs
3) Verbs like saber vs conocer, reflexives, and impersonal se
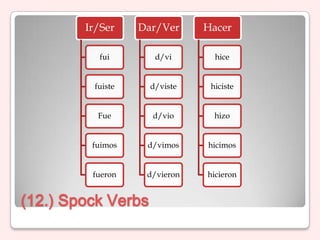
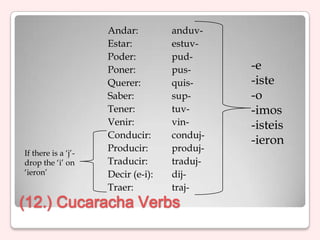
4) Verb conjugations, irregular verbs, and uses of hacer
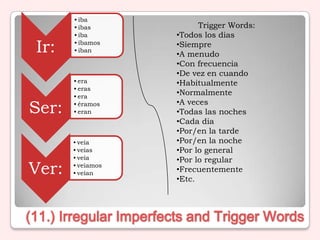
5) Imperfect, preterite, and future tenses along with comparative and superlative structures.
The document includes examples and explanations of grammatical structures and concepts.