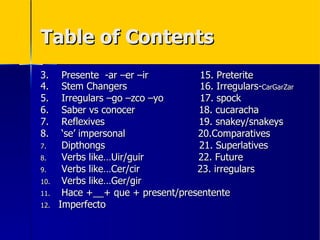
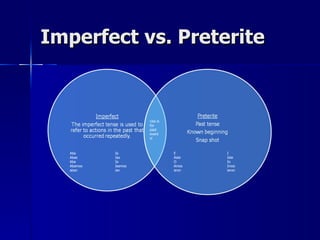
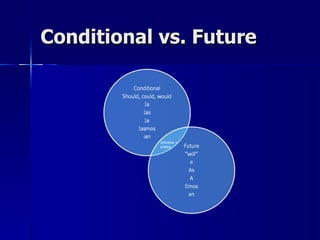
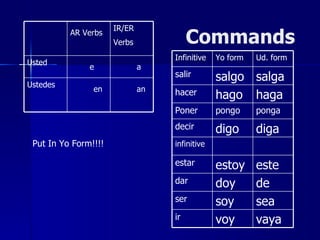
This document contains a summary of Spanish grammar concepts across various tenses and verb types. It includes explanations of regular verbs in the present tense (-ar -er -ir), stem changing verbs, irregular verbs like -go -zco -yo, reflexives, the impersonal 'se', diphthongs, verbs like -uir/-guir and -cer/cir, comparisons, the future tense, commands, the present perfect, double object pronouns, the subjunctive, and progressive tenses using ir, andar and seguir. The document provides examples and explanations of how to conjugate verbs in different tenses and with various concepts in Spanish grammar.