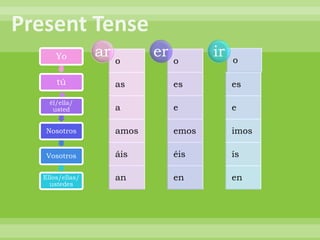
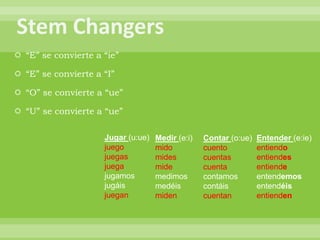
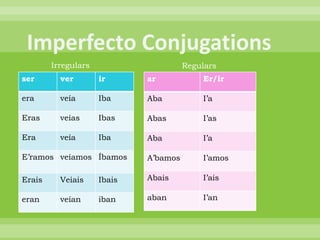
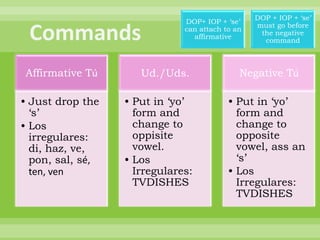
This document provides a summary of Spanish grammar topics in 18 numbered sections. It includes explanations of verb conjugations, stem changers, reflexive verbs, impersonal expressions, diphthongs, saber vs conocer, the preterite and imperfect tenses, por vs para, and other grammar concepts. Tables are included showing examples of conjugations and stem changes.