The document provides an overview of key Spanish 4 grammar concepts including:
1. The present tense and its regular conjugations as well as irregular yo forms.
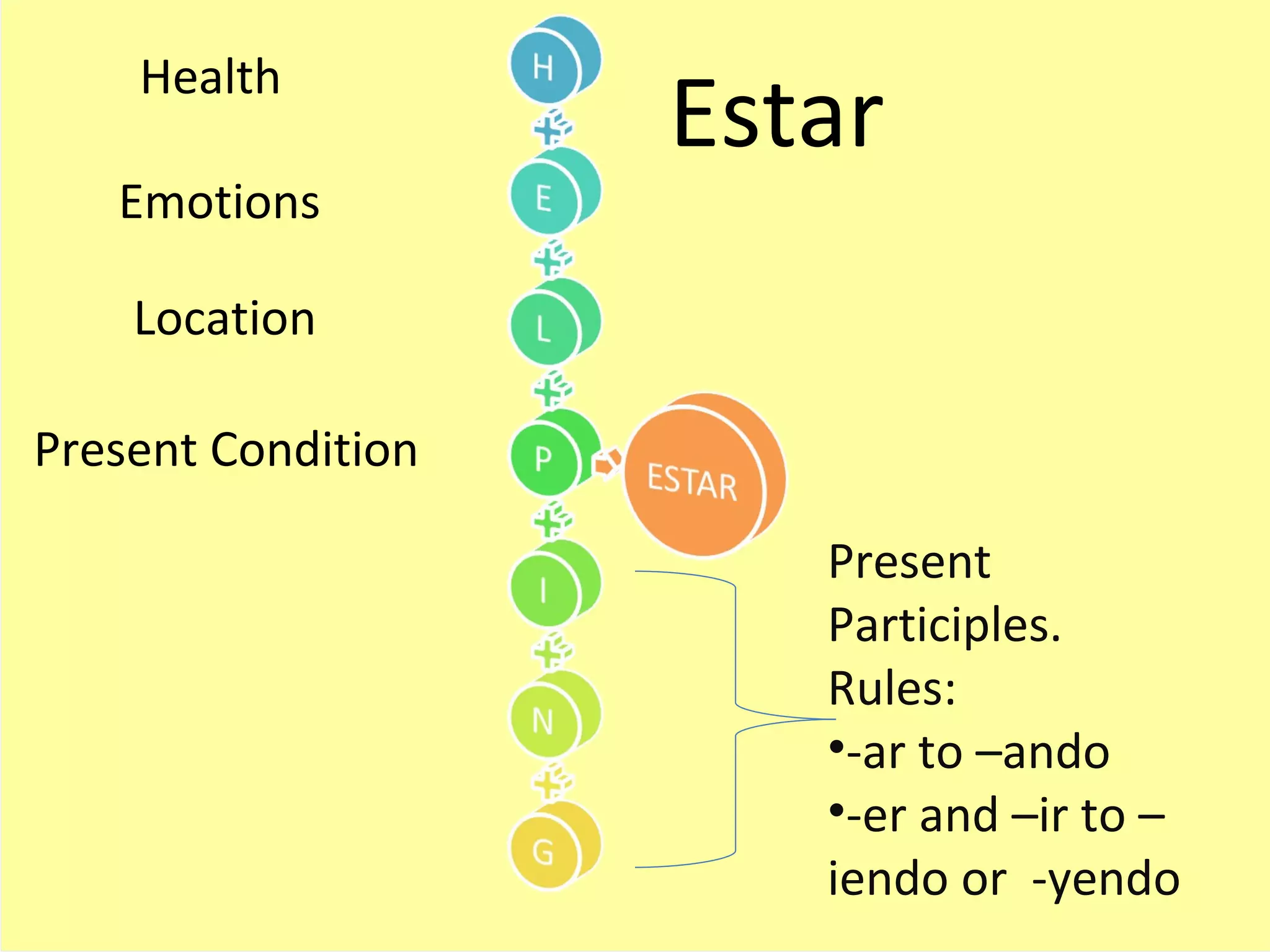
2. Ser and estar and how they are used with adjectives.
3. Gustar and similar verbs like gustar that follow the same conjugation.
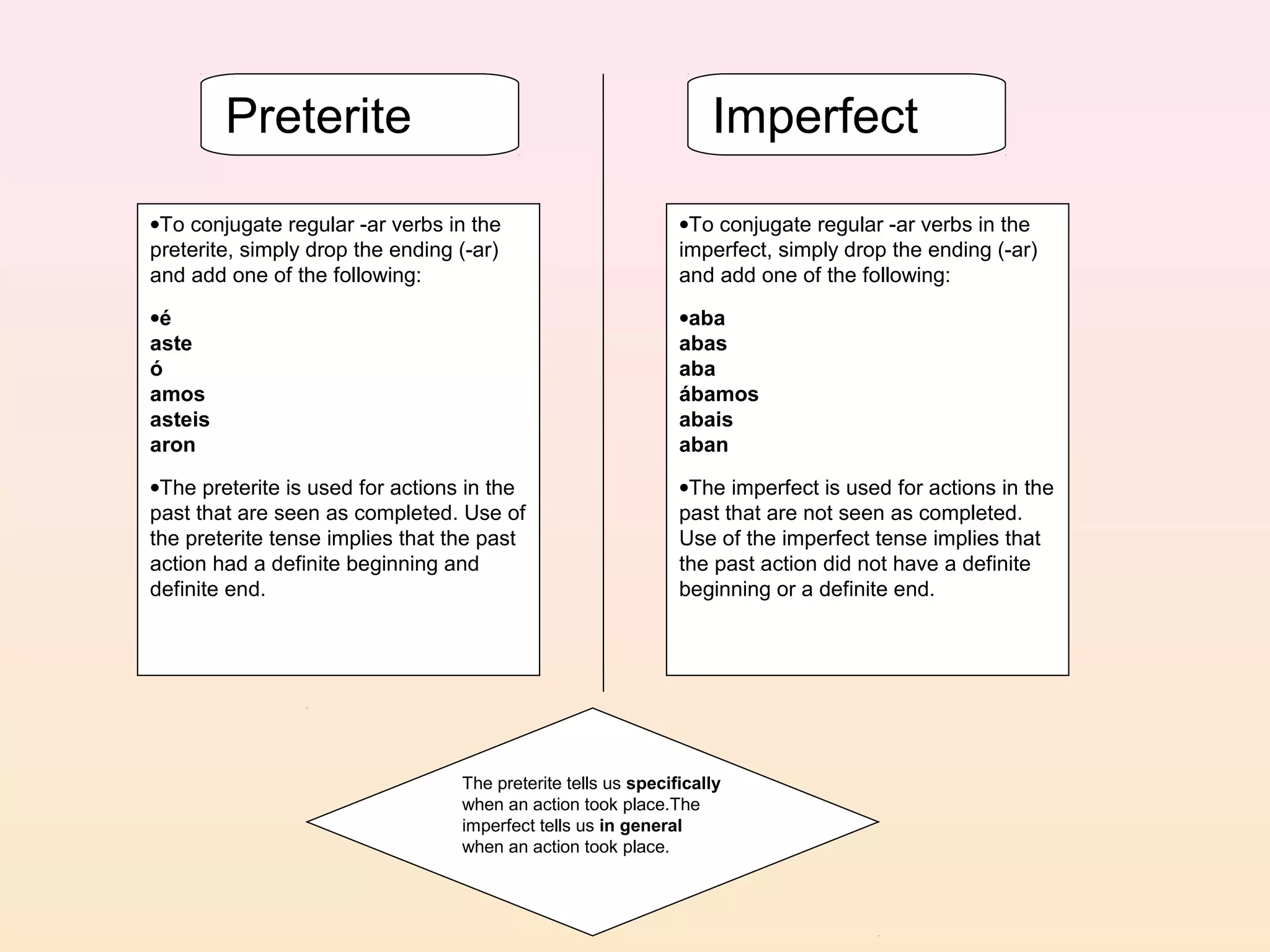
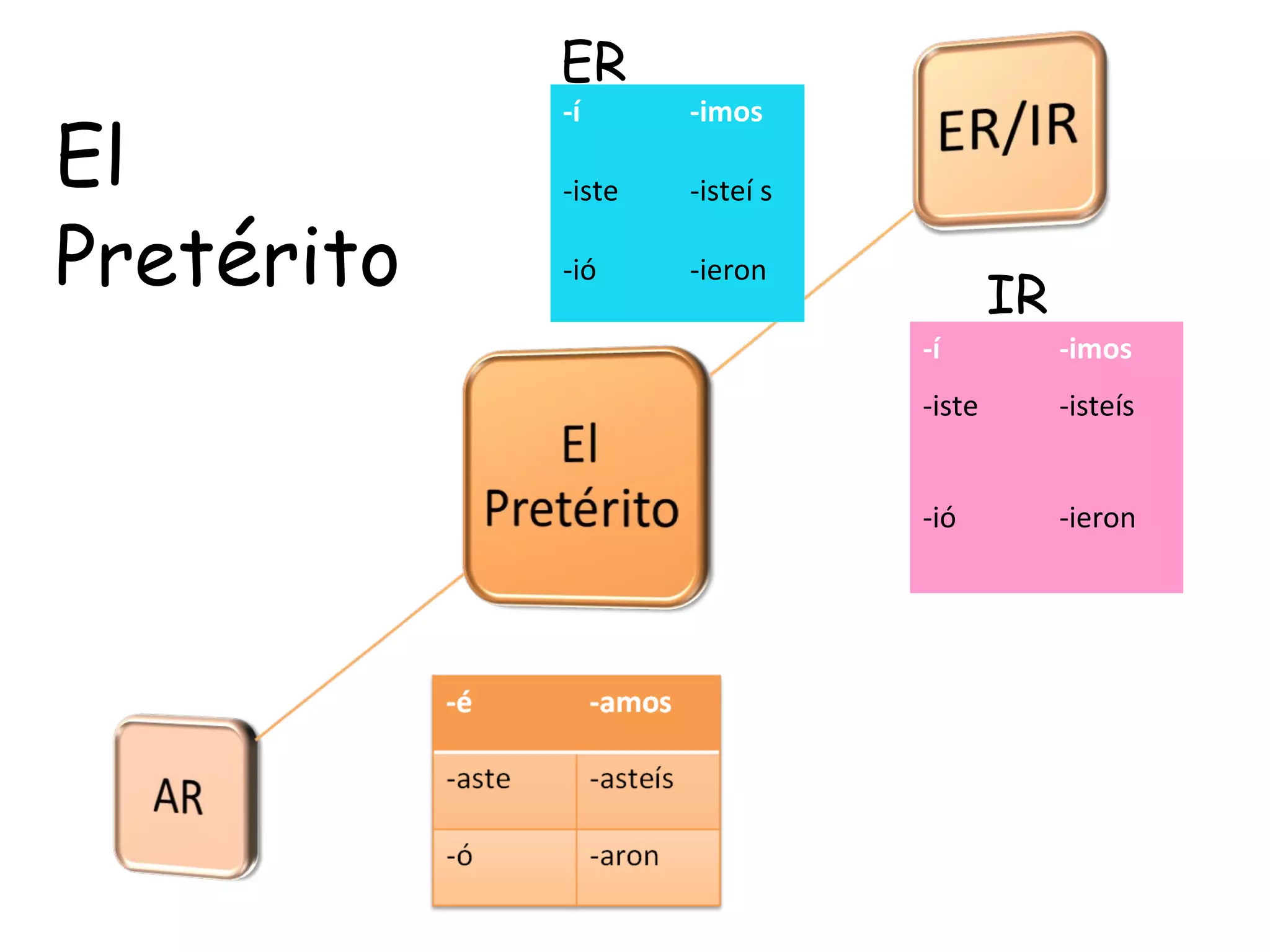
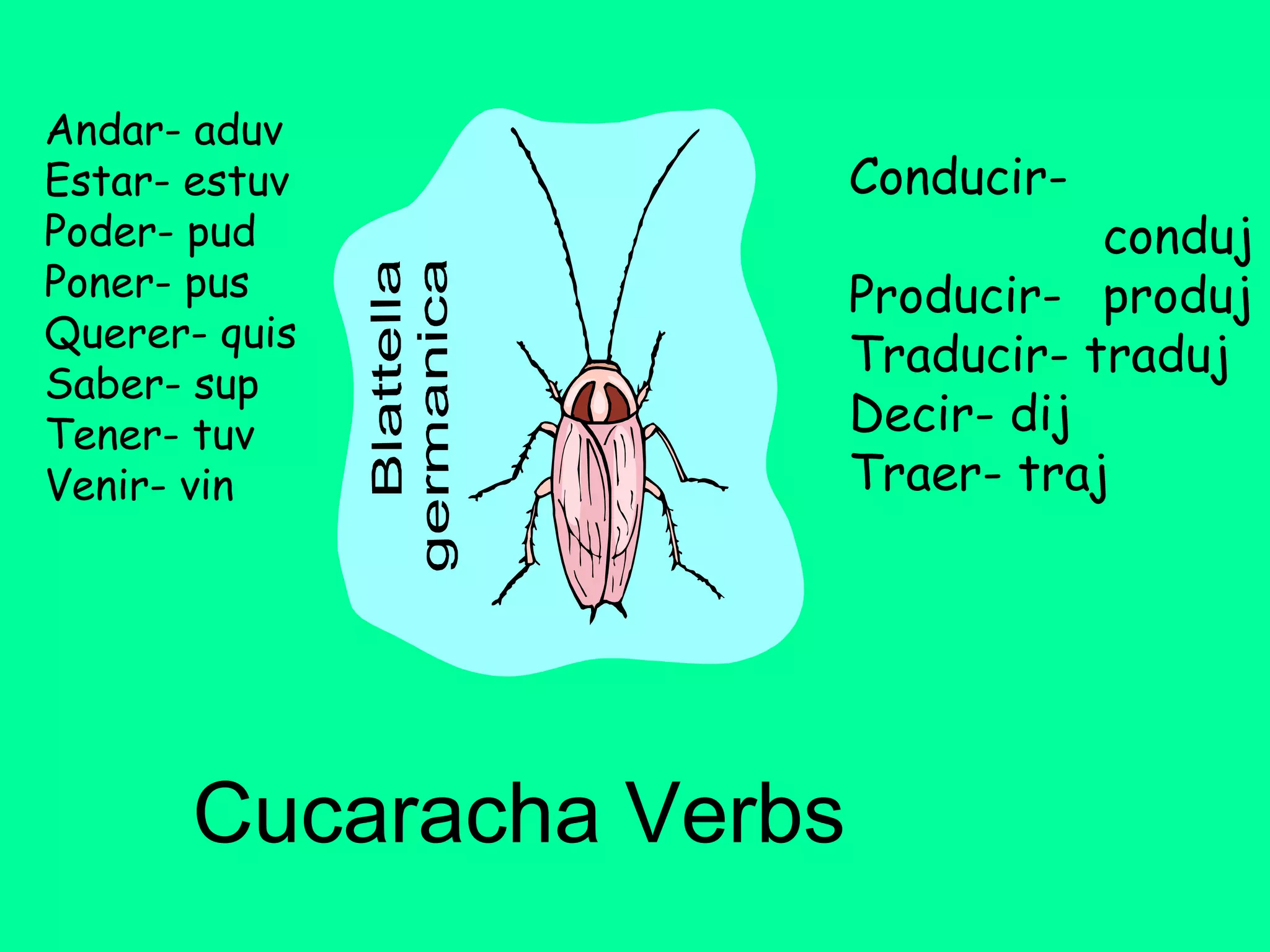
4. The preterite and imperfect tenses, including how to identify them using "trigger words" and their regular and irregular conjugations.