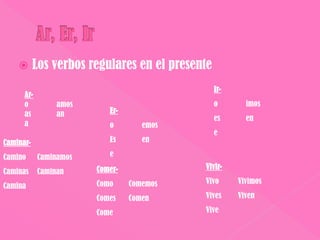
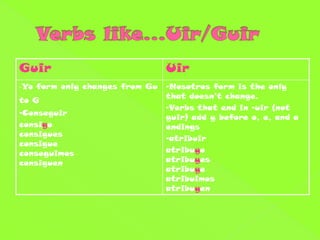
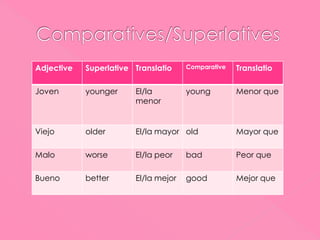
1. The document discusses Spanish verb conjugations in the present tense for regular -ar, -er, and -ir verbs. It provides examples of stem changes and spelling changes in verbs.
2. Irregular verbs are discussed such as saber, conocer, tener, poner, and hacer. Reflexive, impersonal "se", and diphthongs are also covered.
3. Verb tenses like the preterite, imperfect, and future are introduced along with examples of irregular conjugations in those tenses.