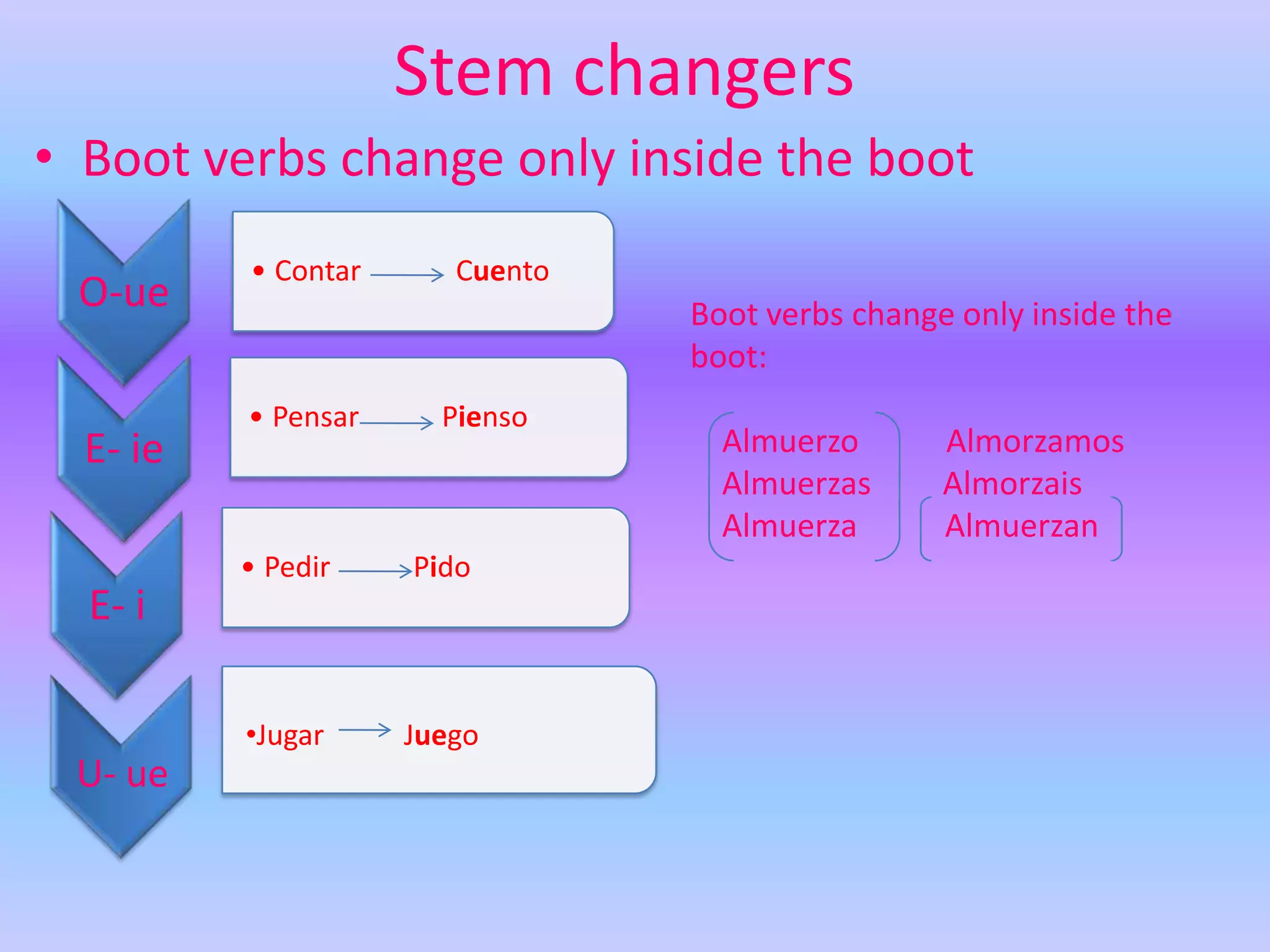
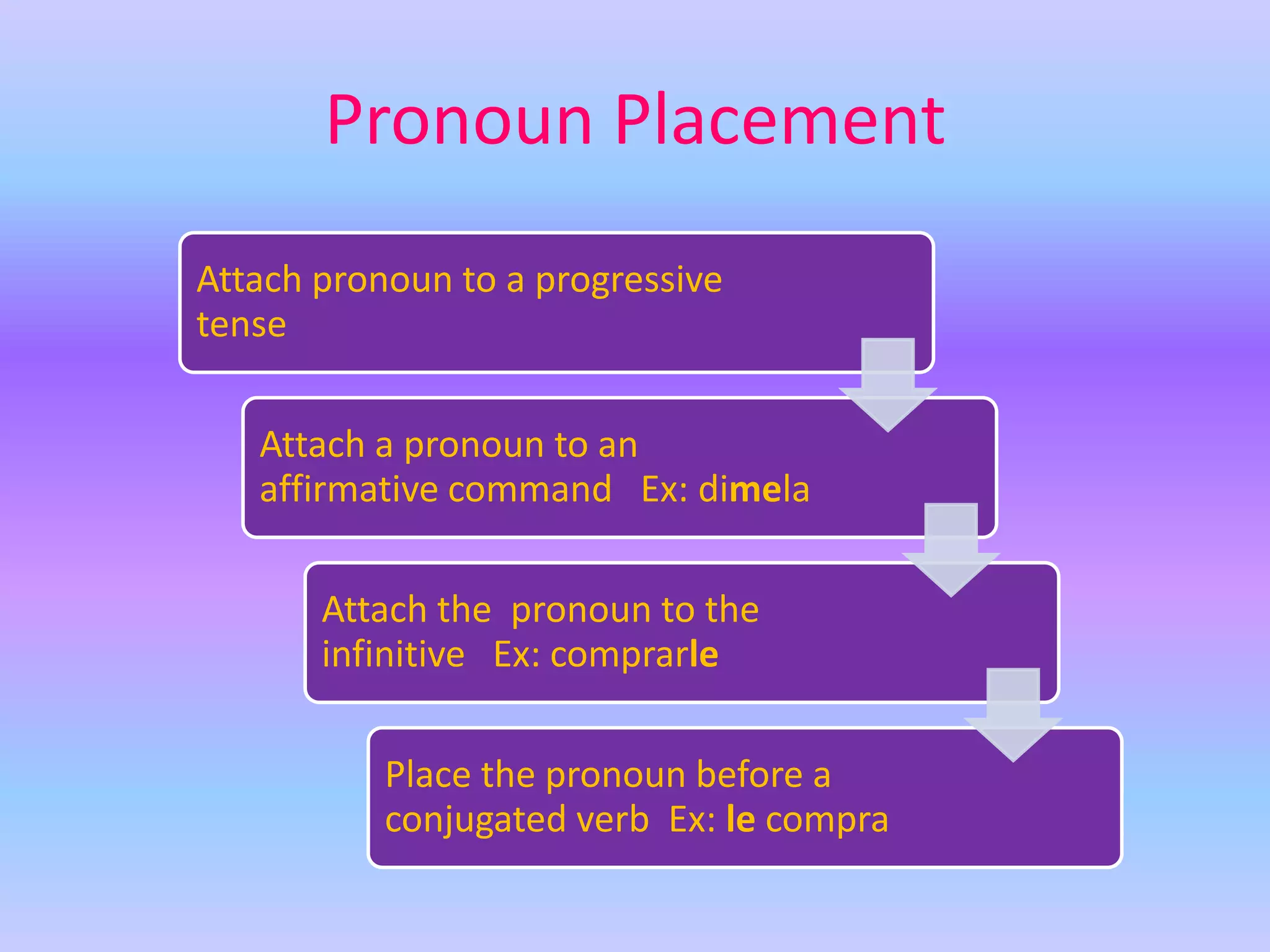
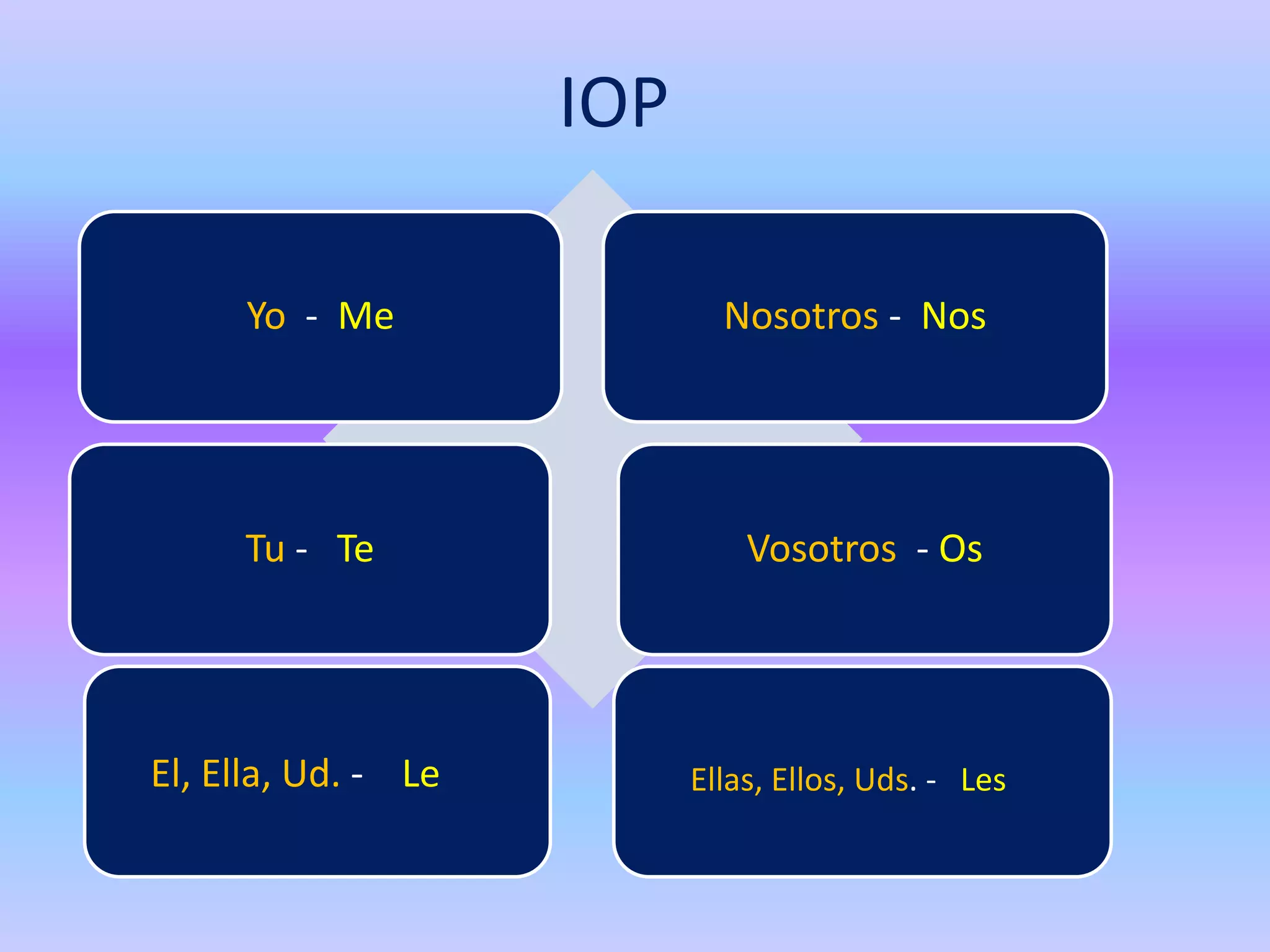
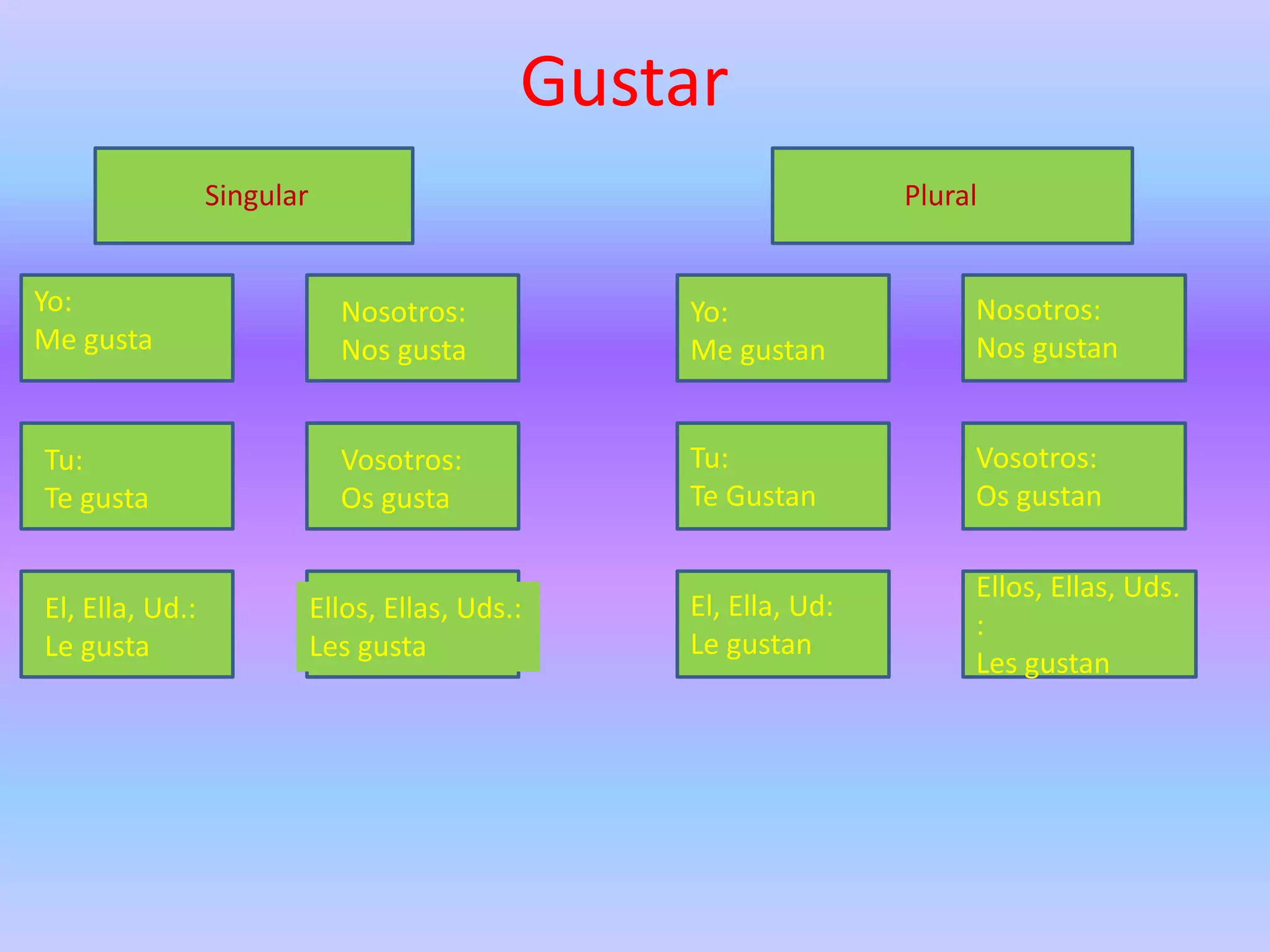
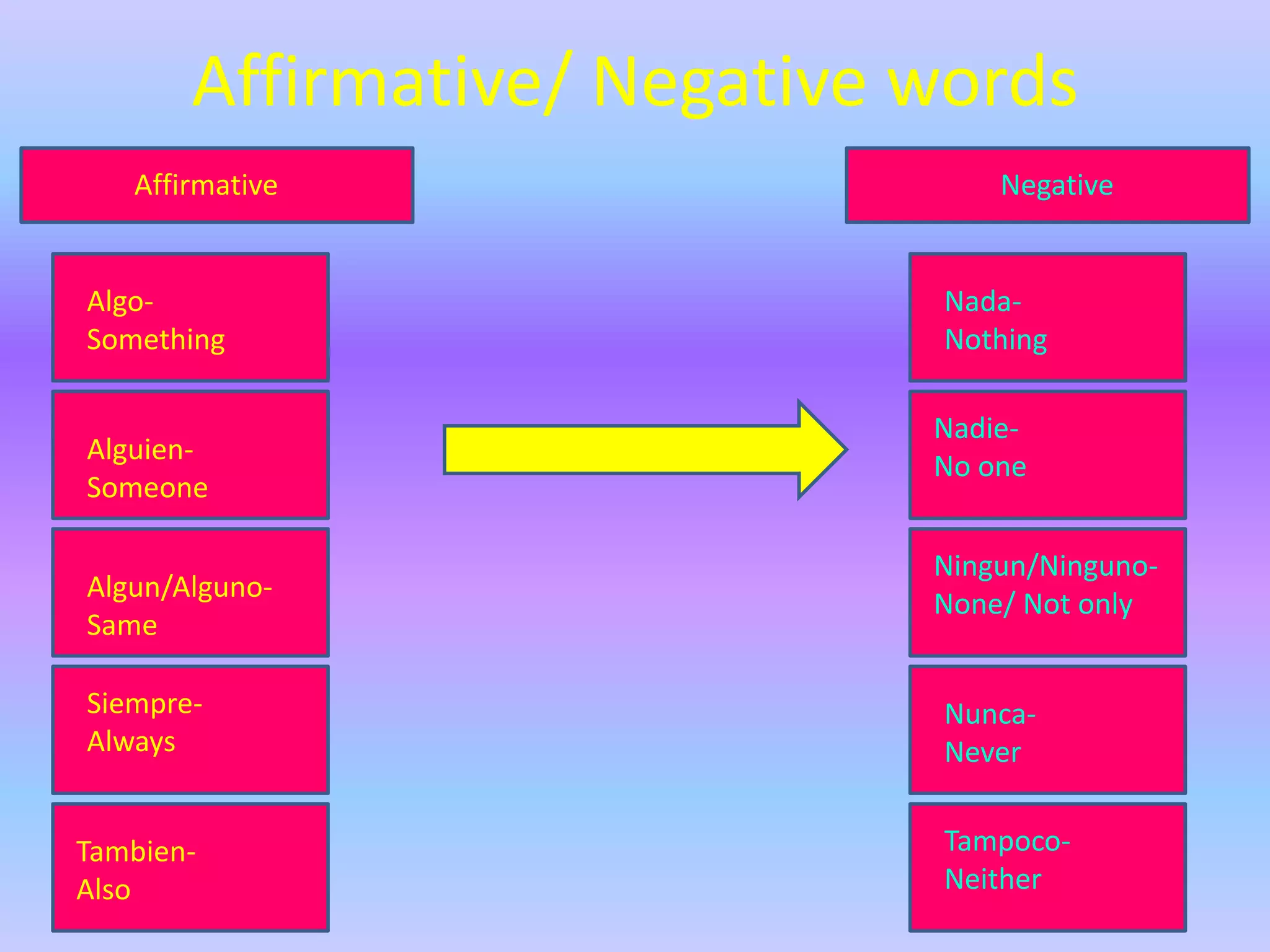
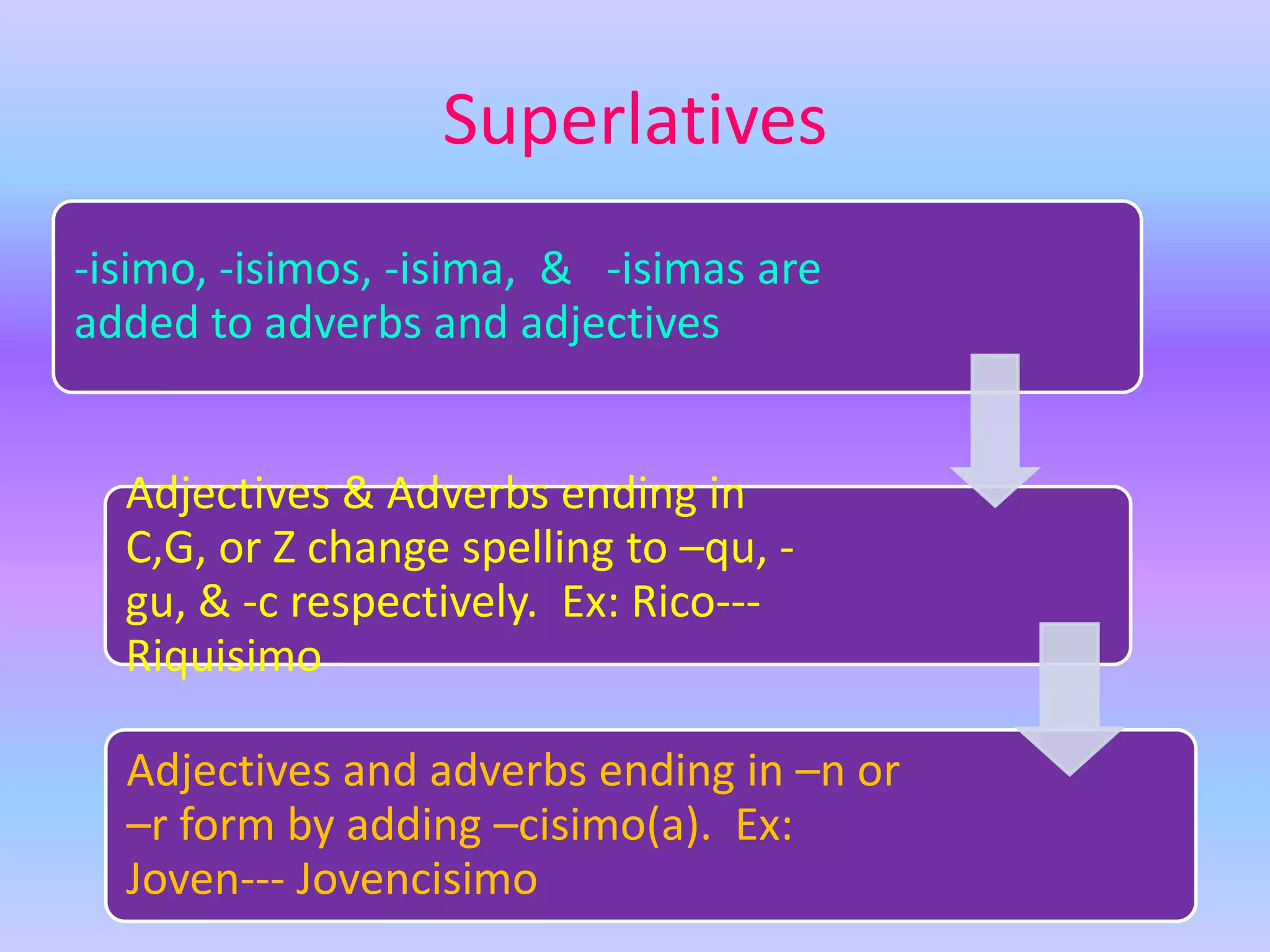
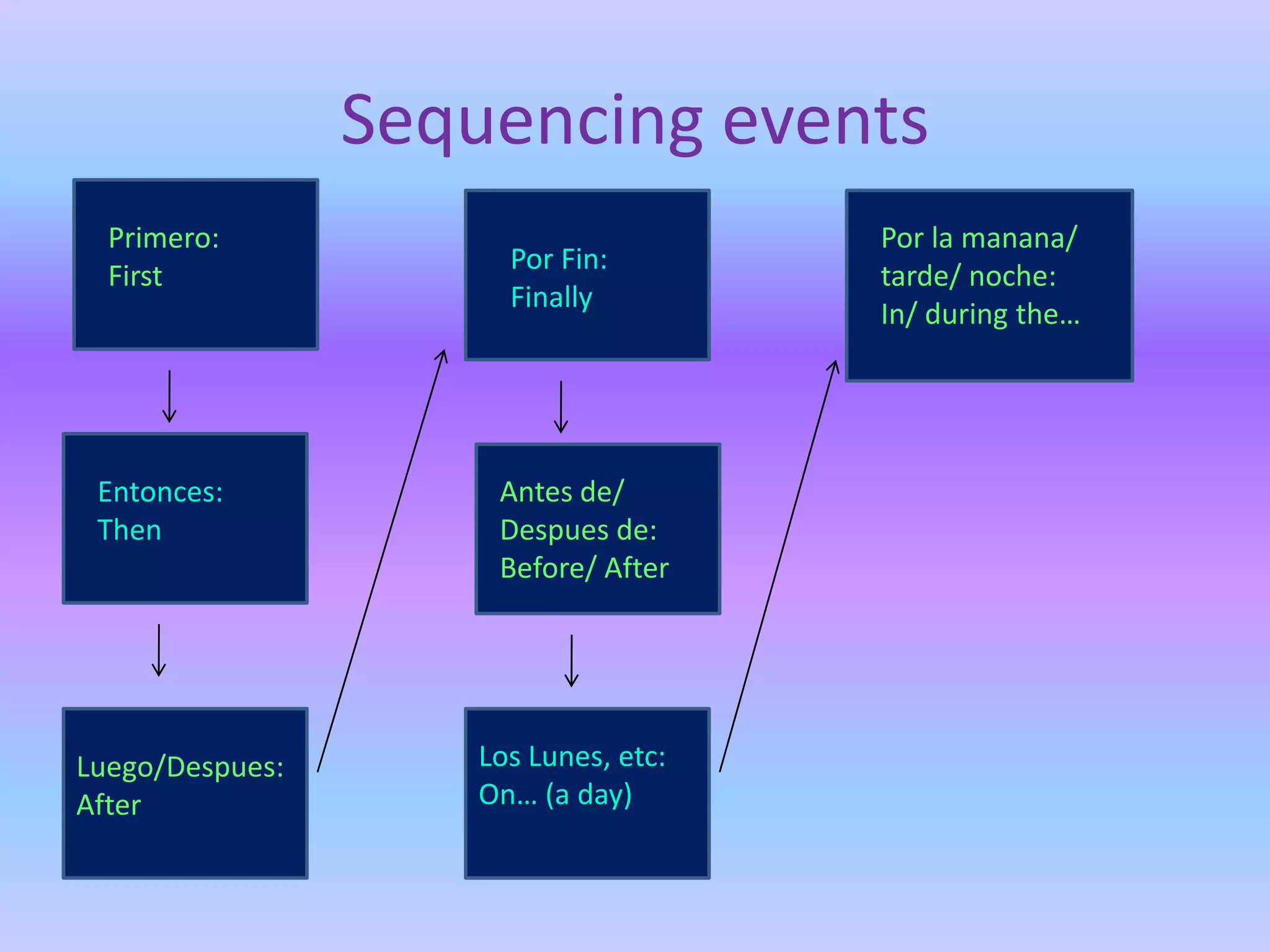
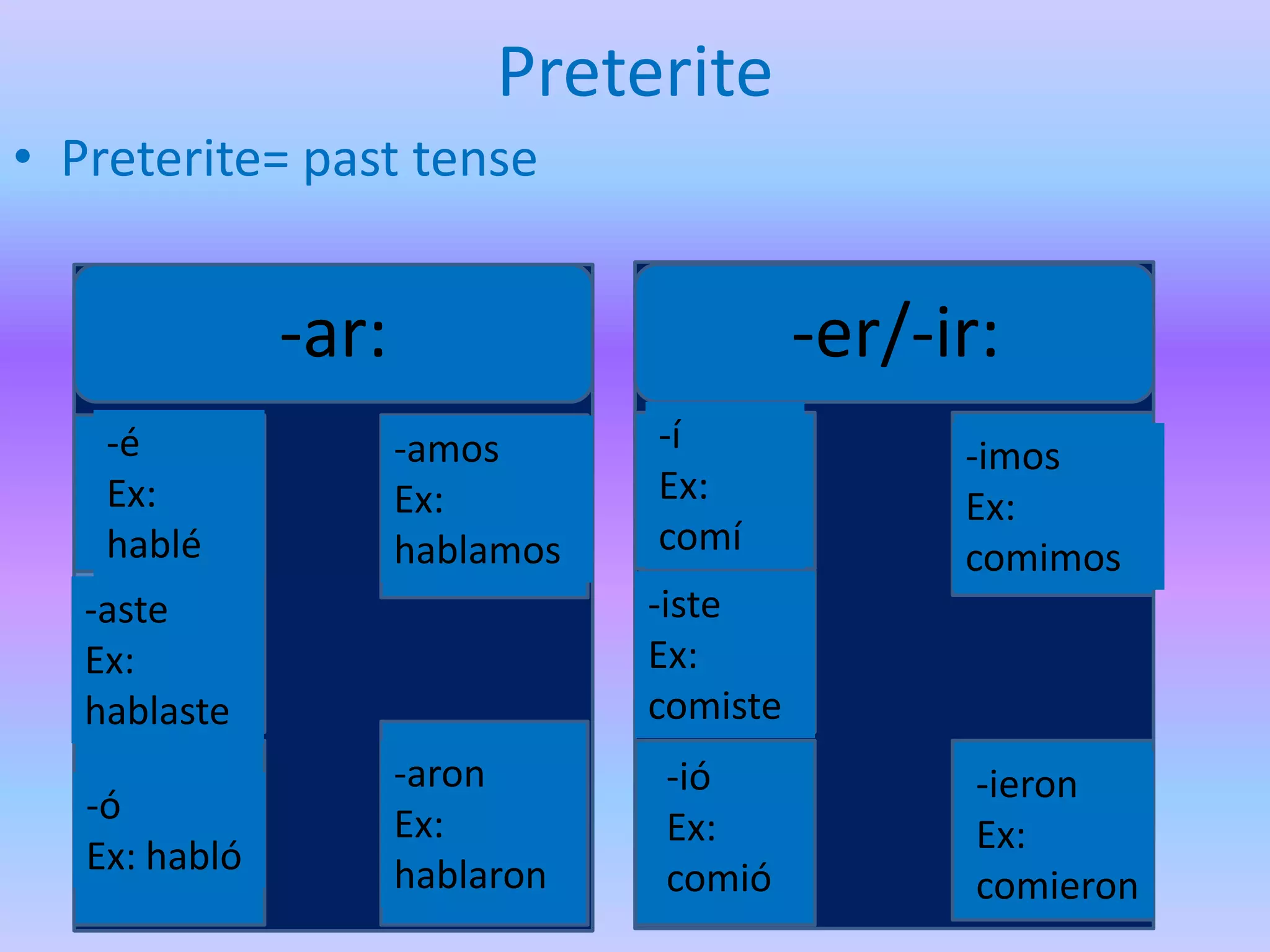
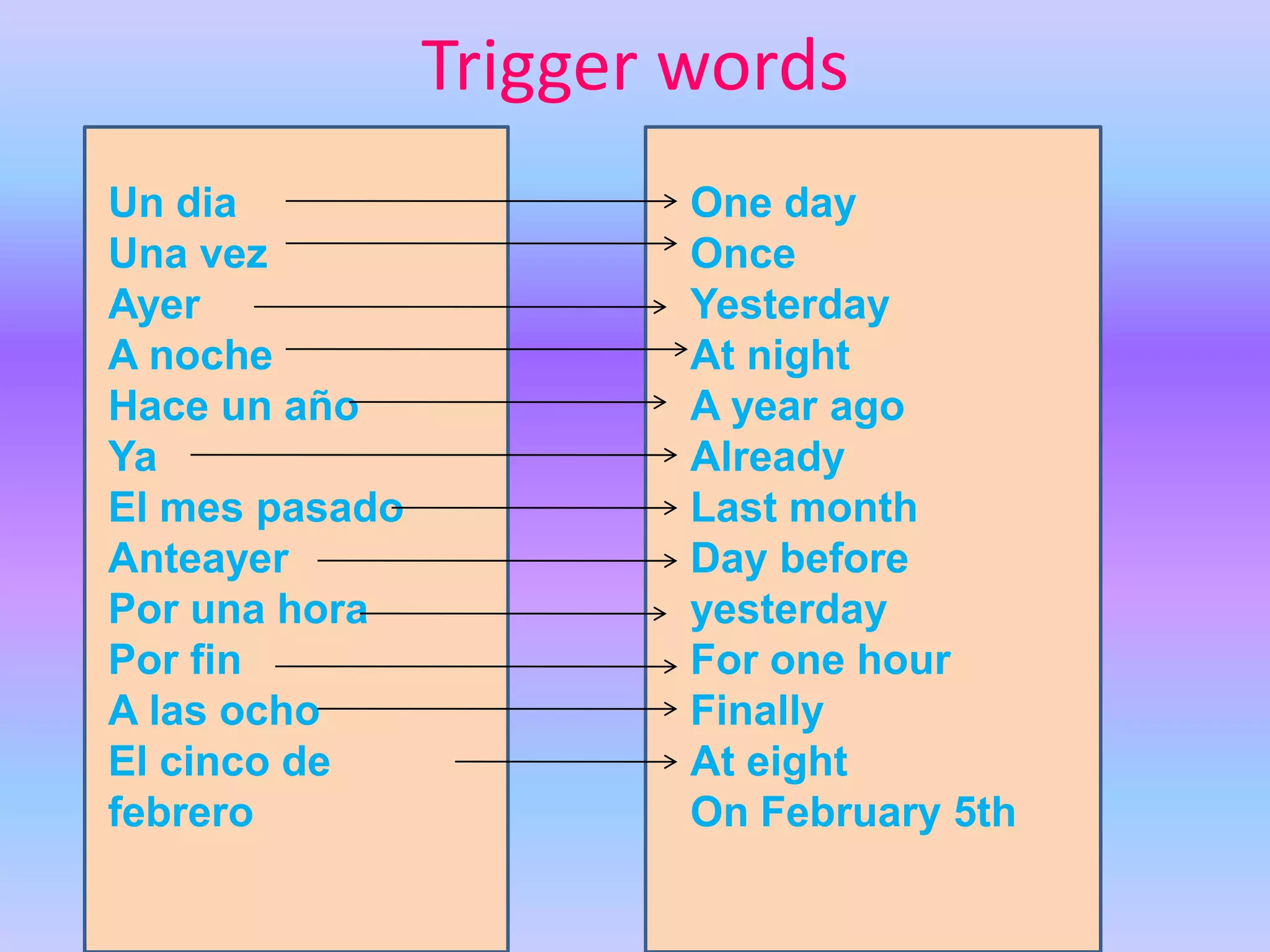
This grammar book covers many Spanish grammar topics in 3 sentences or less including: stem changers, pronoun placement, indirect object pronouns, gustar, affirmative and negative words, superlatives, reflexives, commands, sequencing events, the preterite, trigger words, -car -gar -zar verbs, deber + infinitive, modal verbs, the present progressive, and adverbs.