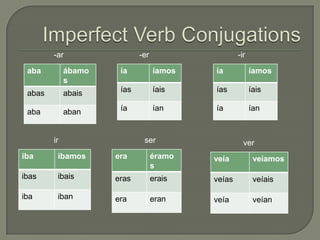
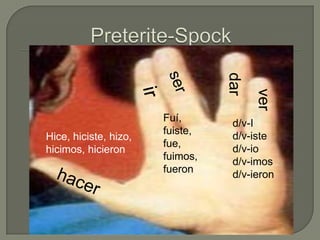
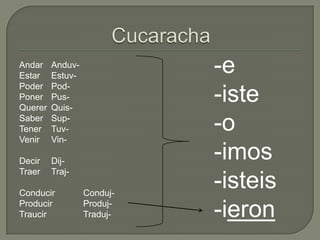
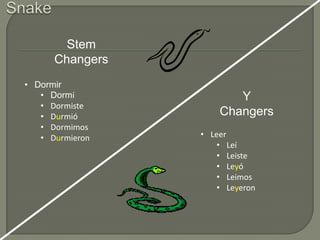
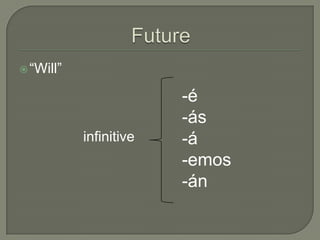
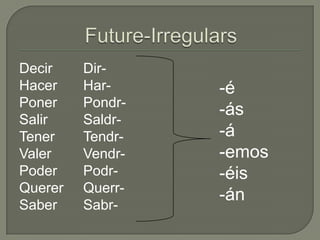
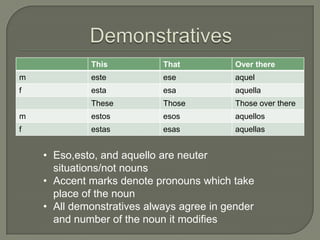
This document provides information on Spanish verb tenses and forms including the imperfect, preterite, future, conditional, and commands. It discusses imperfect verb conjugations, triggers that indicate the imperfect tense, and uses of the imperfect such as ongoing or repeated actions. Various Spanish verb charts are included showing conjugations for regular and stem-changing verbs in different tenses. Adverbs, modal verbs, progressive tenses, and superlatives are also covered.