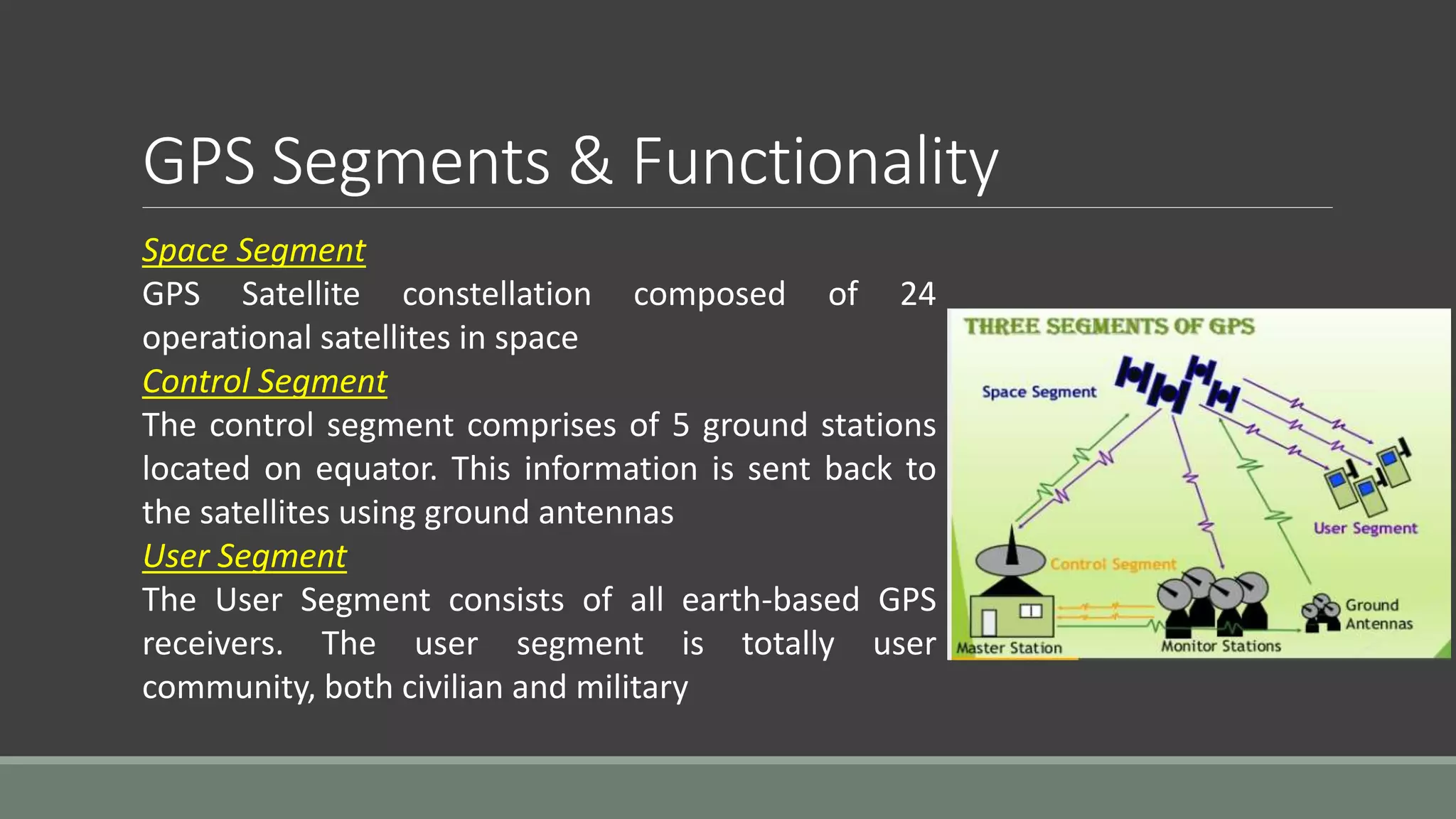
The Global Positioning System (GPS) uses a constellation of 24 satellites to determine accurate positions globally. It was originally developed by the US Department of Defense for military navigation but is now widely used by civilians. GPS works by precisely timing the signals from at least 3 satellites to triangulate the user's position on Earth. Its applications include navigation, mapping, tracking of vehicles, vessels and aircraft.