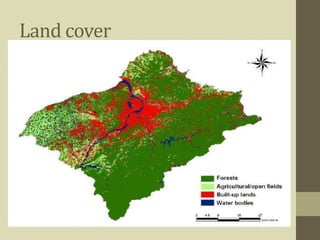
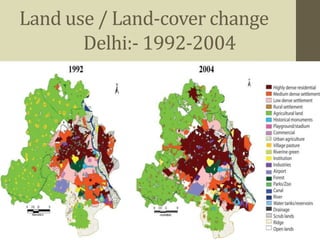
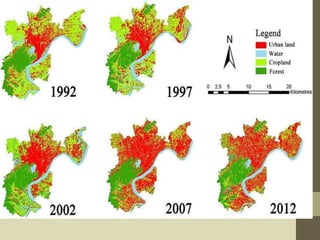
The document discusses land use and land cover mapping using remote sensing. It defines land cover as the physical state of the land surface, such as vegetation or water, which can be directly observed from remote sensors. Land use refers to how humans use the land, such as for agriculture, residential areas, or industry. Remote sensing allows analysis of land use and land cover for various applications like natural resource management, urban planning, and tracking land use changes over time. High resolution imagery can be used to estimate housing density, identify transportation patterns, and ensure agriculture is properly managed. Land cover change is detected by comparing multi-date images and can include both seasonal and long term annual changes.