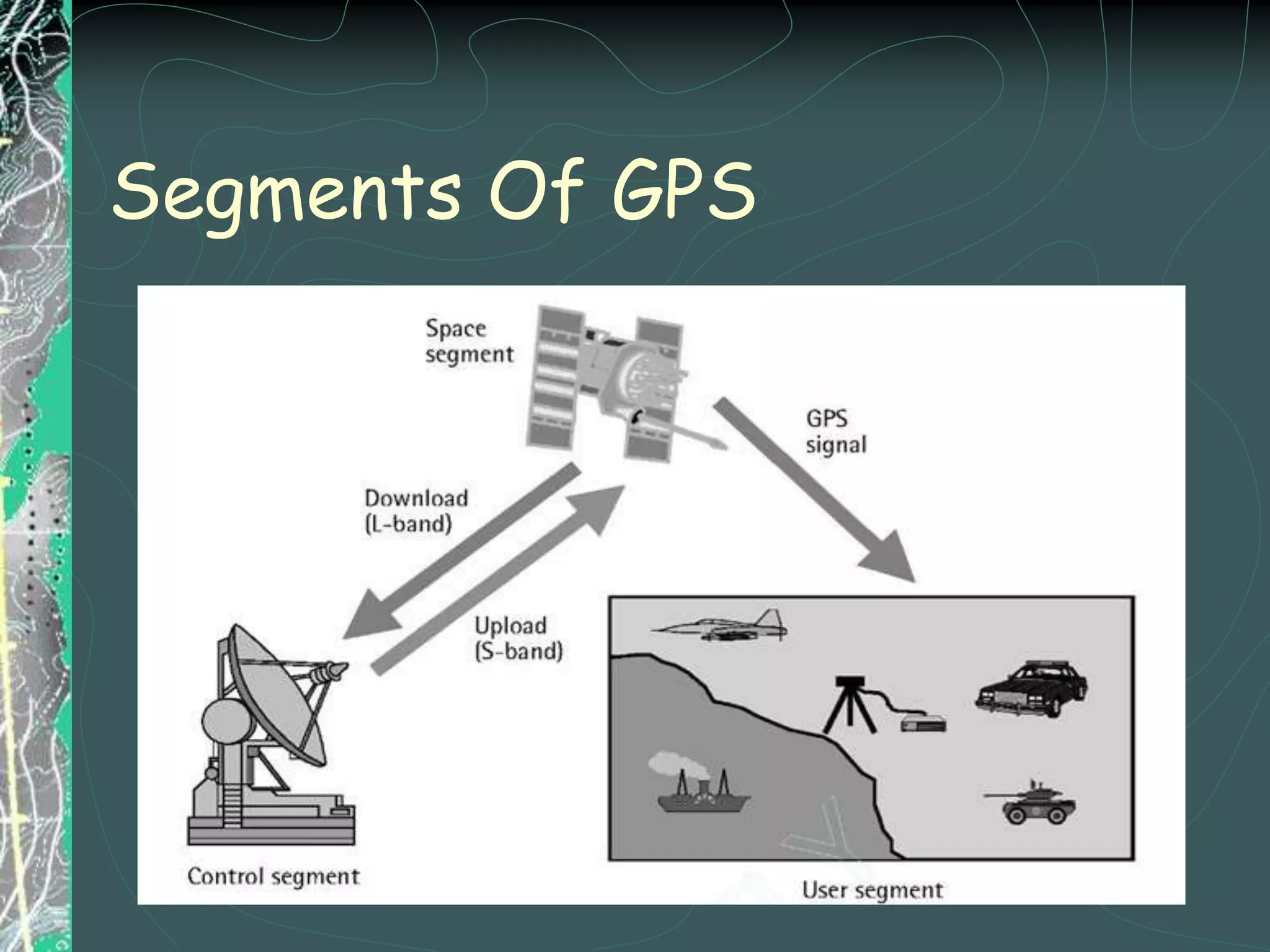
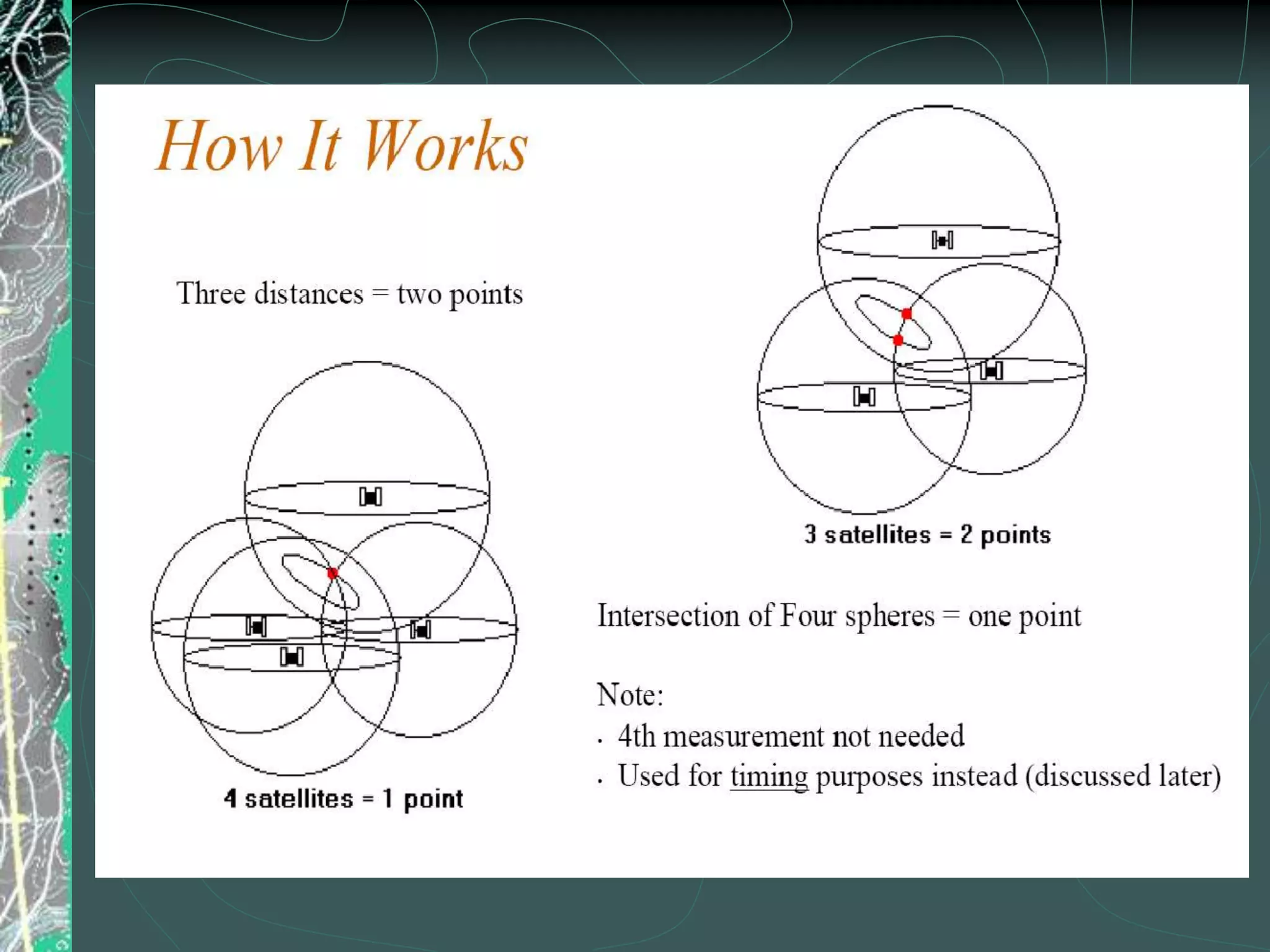
GPS uses 24 satellites orbiting Earth to allow GPS receivers to determine their precise location by calculating the time delay of signals received from multiple satellites. It provides location, velocity, direction of travel, and accurate time anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day in all weather conditions. GPS involves calculating the distance from the receiver to at least 3 satellites through trilateration to determine a 2D position, or 4 satellites for a 3D position. Its applications include vehicle navigation systems, tracking ship locations, precision agriculture, and scientific data collection.