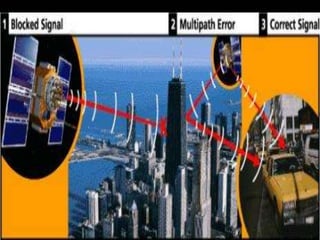
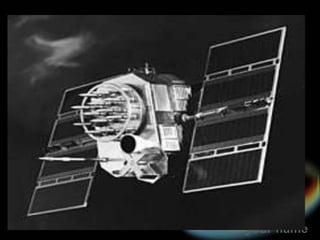
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system consisting of 24 satellites orbiting the Earth. GPS satellites transmit signal information that GPS receivers on the ground use to calculate the user's exact location through triangulation. For a 2D position, a receiver needs signals from at least 3 satellites, and 4 satellites are needed for a 3D position. Civilian GPS accuracy is around 3-5 meters and can be improved to less than 3 meters with WAAS or DGPS corrections.